Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
XML Ingestion
XML file ingestion supports crawling XML files with append and CDC mode. XML Ingestion supports the following features:
- Schema crawl
- Data Crawl
- Append Mode
- CDC and Merge
Creating XML Source
For creating a XML source, see Creating Source. Ensure that the Source Type selected is XML.
Configuring XML Source
For configuring a XML source, see Configuring Source.
NOTE: If the source is ECB enabled, the From Filesystem option will be selected by default and the other options will be disabled.
- Enter the source base path.
- In Record Scope field, select Line if the files have one XML record per line or select File if all the files are valid XMLs themselves.
- Select split on records if the XML files are larger than 128 MB and you want to split them while processing so they can be parallel-processed.
NOTE: The splitting will be done on the end of the record tag you specify.
- To skip processing of some files in the folder, provide a regex in Exclude files containing pattern. File paths having this regex will be skipped.
- Check Ingest sub-directories to crawl each file present in the File System tree where the source base path is the root.
- Character Encoding takes the charset encoding of your XML files.
- Select the ECB Agent, if the source is ECB enabled.
- Click Save Settings.
Creating Table and Crawling Schema
- Click the Source Configuration icon.
- Click Configure Mapping. The Specify XSD page is displayed.
- Enter the XSD path the Absolute path to XSD file field.
NOTE: If the XSD includes other XSDs, those XSDs must also be present in the path relative to the specified XSD.
- In the Root element field, enter the tag to be the root of your schema. The root must also include the prefix that is used in the xml file.
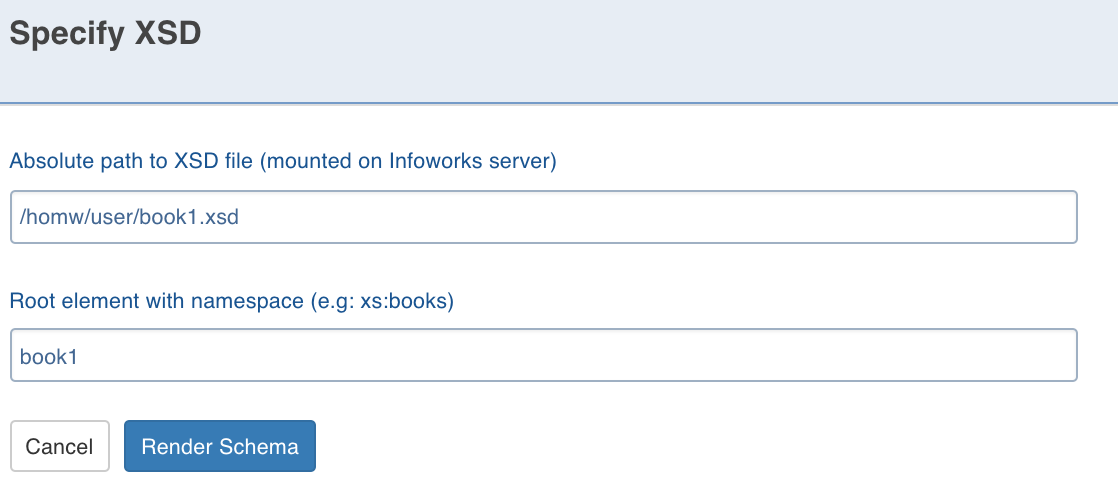
- Click Render Schema. A tree representing the XML schema created is displayed.
NOTE: If the splitting is enabled, you can provide a child root of the given XML, provided the element is globally declared. The splitting of the record is done on the selected root provided. If splitting is not enabled, specify the parent root of the XSD/XML.
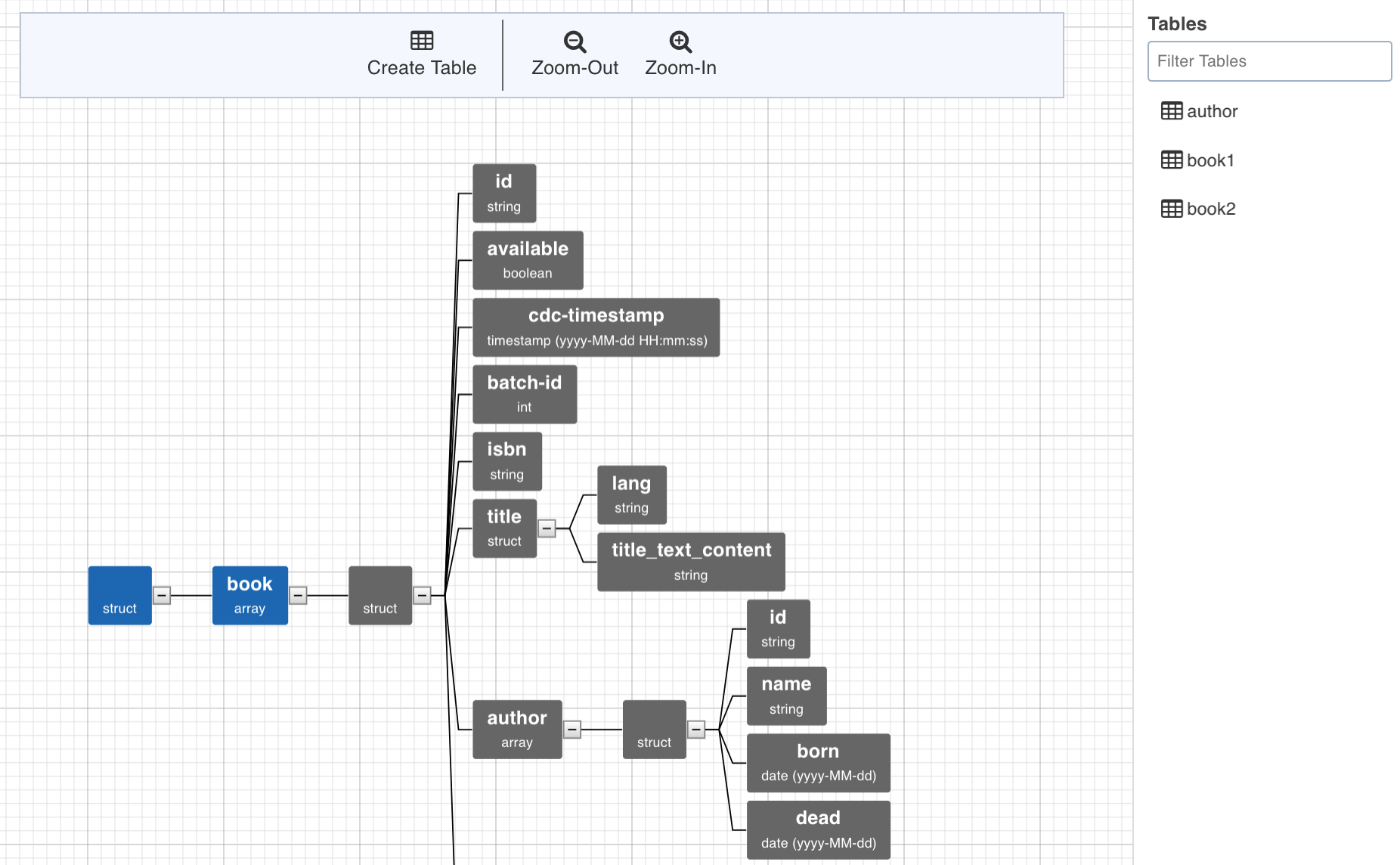
- To create a table, select a path from the tree and click Create table. The path nodes can only be of type array or struct. A table schema will be created out of all the non-path child nodes of the nodes which are present in the path.
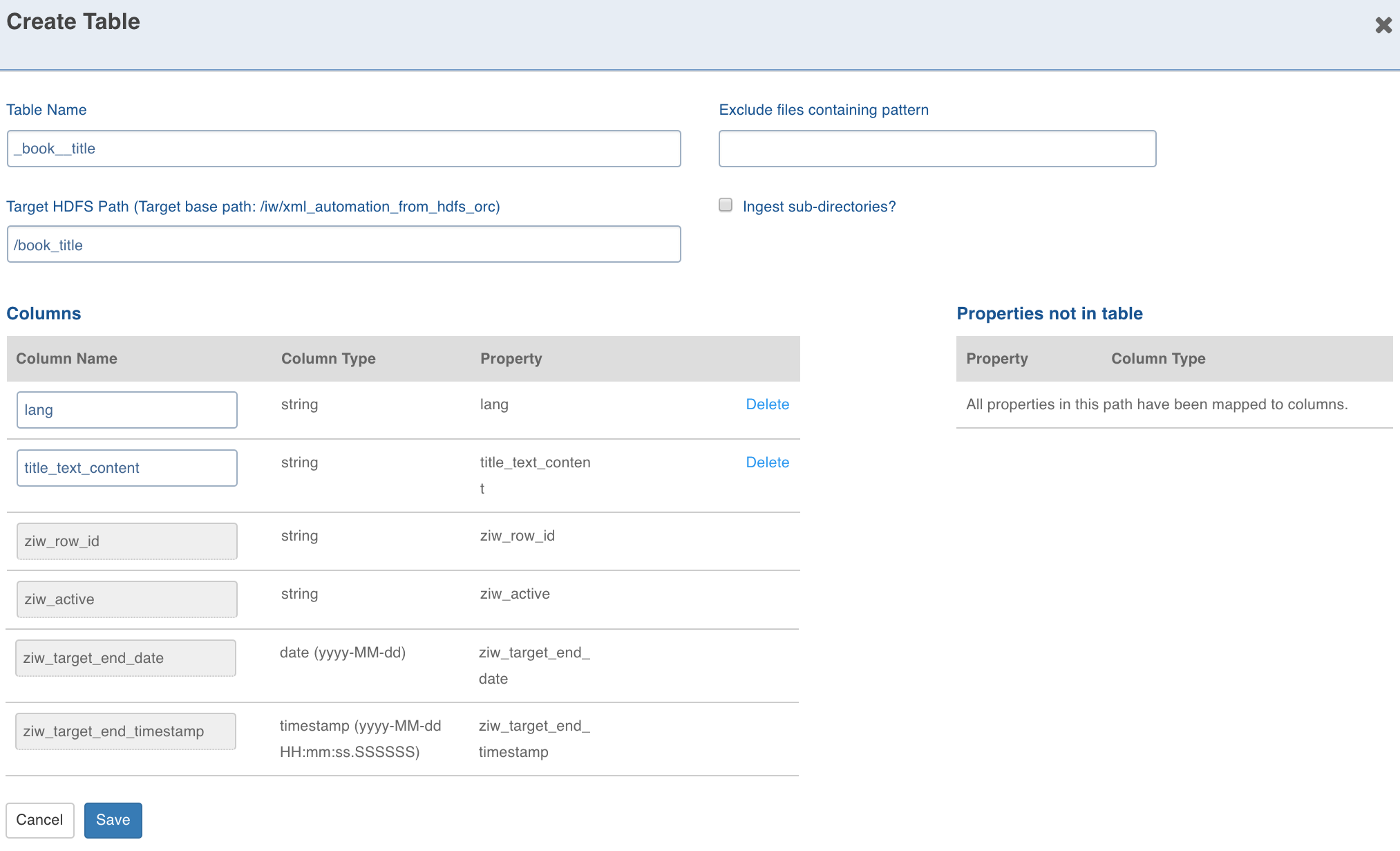
- Enter the target Hive Table Name, Target HDFS Path (this is relative to the source target base path we entered during source creation).
Exclude files containing pattern and Ingest sub directories options override the source level settings of the same names. The columns can be deleted and added back again.
- Configure the columns and click Save.
Configuring XML Source for Ingestion
- Click the Configure button for the table that requires a full load data crawl.
- Select the Ingest Type as Full Load, enter the required values and click Save Configuration.
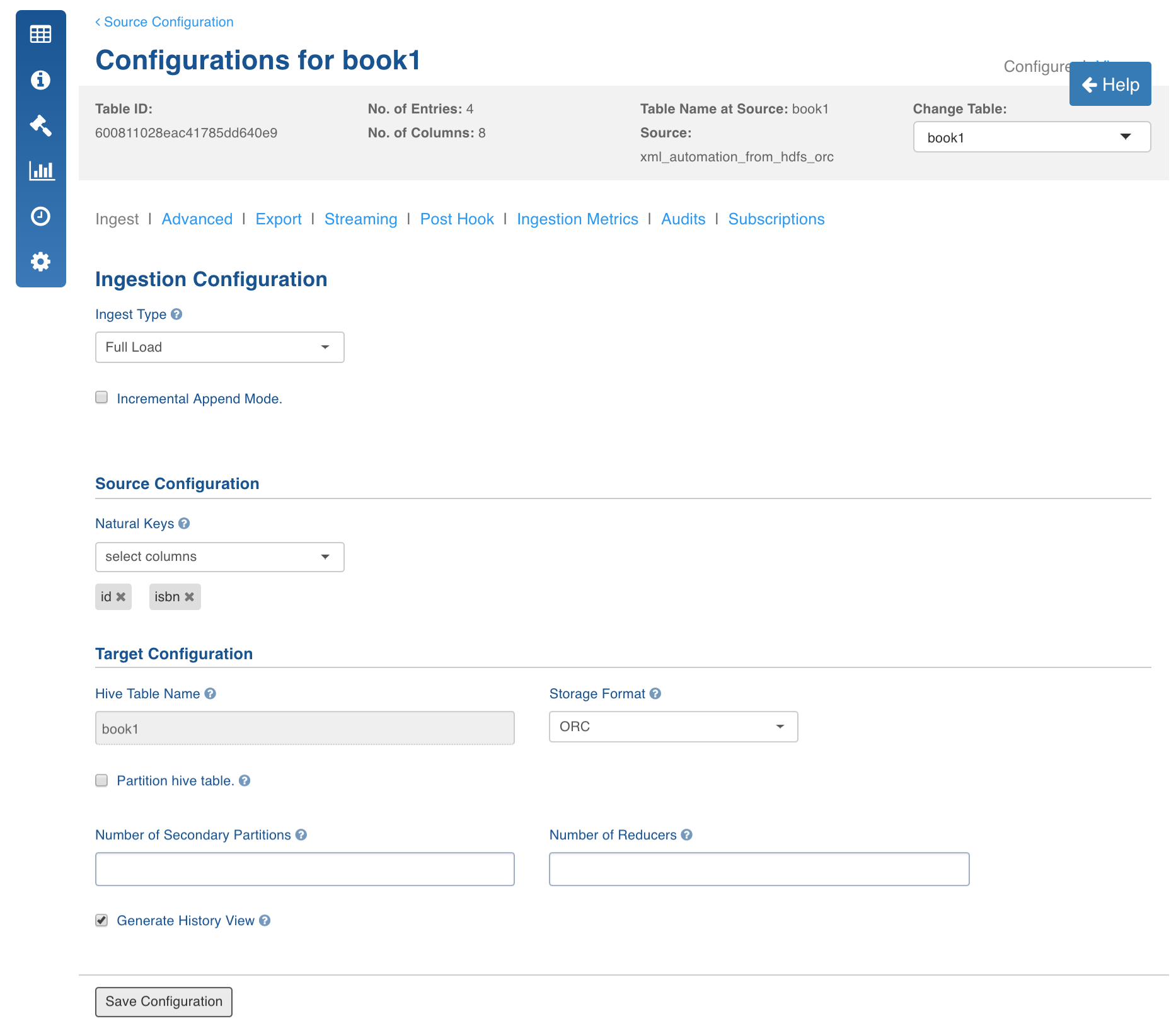
- In the Table page, click the Table Group tab.
- Click the View Table Group icon for the required table group.
- For first time ingestion, and if you need a clean crawl, click Initialize and Ingest Now.
NOTE: This mode should be used for cases where new inserts come in new files and there are no updates.
- To append new data to the crawled source click Ingest Now from the second crawl onwards. The new data can be put in the same location. Only new and changed files would be picked.
NOTE: This mode should be used for cases where new inserts and new updates are present for every crawl.
XML Schema Elements
Following are the formats in which XML schema elements are stored:
NOTE: XS:Any : XS:Any is stored as a Map <string, string> in Hive.
For Example,
<xs:element name="person"> <xs:sequence> <xs:complexType> <xs:element name="firstname" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="lastname" type="xs:string"/> <xs:any minOccurs="0"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element>The XML document can be as follows:
<person> <firstname>Hege</firstname> <lastname>Refsnes</lastname> <children> <childname>Cecilie</childname> </children></person>This will be stored in Hive as follows:
| firstname | ' | lastname | ' | wildcard_elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hege | ' | Refsnes | ' | |
| {"Children": "Cecilie"} | ||||
| Mixed element is an element which can have attributes, child element and text. |
For Example,
<letter> Dear Mr.<name>John Smith</name>. Your order <orderid>1032</orderid> will be shipped on <shipdate>2001-07-13</shipdate>. </letter>This is stored as follows:
| Letter_text_content | ' | name | ' | orderid | ' | shipdate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dear Mr.John Smith. | ' | John Smith | ' | 1032 | ' | 2001-07-13 |
| Your order 1032 | ' | ' | ' | |||
| will be shipped on 2001-07-13. | ' | ' | ' |
XML Configurations
- XML_ERROR_THRESHHOLD: If the number of error records increases this threshold, the MR job will fail. The default value is 100.
- XML_KEEP_FILES: If the host type is local before the MR job runs, the XML files are copied to the tableId/XML directory. If this configuration is true, the files are not deleted after the crawl. The default value is true.
- xml_job_map_mem: Mapper memory for the crawl map reduce. The default value is the value of iw_jobs_default_mr_map_mem_mb in properties.
- xml_job_red_mem: Reducer memory for the crawl map reduce. The default value is the value of iw_jobs_default_mr_red_mem_mb in properties.
Known Issues
- The path cannot have branches. This means that there is only a single one to many relationship in the path. Workaround: Create different tables for each branch, if needed.
- While extracting table from the XML, there is no way to eliminate the records with duplicate natural keys.
- Workaround: Make sure that the natural key provided is unique.
- If there are recursive tag declarations, the XML structure of the second tag is stored as a Hive string.
- AnyAttributes declaration in the XML schema is not supported yet.
- Workaround: Specify all the attributes in XSD.
- Multiple namespaces are not supported.
- Complex type extensions are not supported.
- Workaround: Define the extension type as new complex type.
- Splitting cannot be performed on an empty element.
- Workaround: Split on a parent element and select the empty element for the data.
- An attribute and a child element cannot have the same name.
- The keys in the hierarchy of struct and array cannot have Hive reserved keywords.
- Workaround: If there is a Hive keyword, it must be a column in Hive and not part of the struct.
- The supported character encodings are UTF-8, ASCII, ISO-8859-1.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential