Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Oracle Log-Based Incremental Ingestion
In Oracle log-based incremental ingestion, data is ingested into the Hive and continuously synchronized with the database using Oracle archival logging provided by Oracle. In this method, archival logging must be enabled for the incremental tables.
NOTE: If data contains blob and clob columns and sync type chosen is log-based, these columns will be ignored during ingestion (both full load and CDC). If sync type is changed to query-based or timestamp-based, any data ingested after that change will still have the blob and clob values.
Following are the methods to perform Oracle log-based incremental ingestion:
- Reading archive logs directly from LogMiner
- Using temporary table to store and read archive logs
- Using staging database server with temporary table to read archive logs
1. Reading Archive Logs Directly from LogMiner
In this method, Infoworks starts the LogMiner and starts reading data directly from the view created by LogMiner. Every session from Infoworks requires its own instance of LogMiner. Infoworks Oracle CDC with LogMiner uses Oracle LogMiner to read Change Data from Oracle-archived redo logs. Infoworks then makes the data available to CDC sessions for propagation to targets.
To implement Oracle CDC with LogMiner, you must perform configuration tasks in Oracle and Infoworks. In Oracle, ensure that ARCHIVELOG mode and global minimal supplemental logging are enabled so that Change Data can be retrieved from archived redo logs. Also, ensure that a copy of the Oracle online catalog exists in the archived log destination. Infoworks requires a copy of the catalog to determine restart points for Change Data extraction processing.
WARNING: If you use real-time extraction mode, Infoworks CDC starts a separate Oracle LogMiner session for each extraction session. Running multiple, concurrent sessions can significantly degrade performance of the system where the LogMiner runs.
Source Configurations
- USE_TEMP_TABLE_FOR_LOG_BASED_CDC: Mandatory, when this configuration is set to true, log-based CDC uses temp table to store the archive logs. The default value is true.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Optional, default value is false, setting it to true tries to build a dictionary before every CDC.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Optional, default value is false, it uses offline dictionary. Setting the value to true uses redo log dictionary to read archive logs with DDL tracking. The value must be set to true in case of schema synchronization.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_NAME: Optional, default value is dictionary.ora, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_PATH: Mandatory, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_PATH: Mandatory, absolute path to directory where archive logs are stored.
- LOG_FILE_SEQUENCE_COLUMN_NAME: In case of Oracle RAC setup, this configuration must be set at source level as RECID.
- LOG_BASED_CDC_SCHEMAS: source level configuration, comma-separated schema names of tables in the dummy source.
- TABLE_SCHEMA: schema of the particular table at the table level For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
Limitations
- This ingestion requires more resources since every session requires its own instance of LogMiner.
- Derived split by and derived partition are not supported.
- BFILE, BLOB, CLOB, and XML are not supported.
2. Using Temporary Table to Store and Read Archive Logs
In this method, Infoworks starts the LogMiner instance and copies log data to a temporary table either in the same schema or any other schema to which the Infoworks user has access. This removes dependency of each session having its own LogMiner instance to read logs.
Source Configurations
- USE_TEMP_TABLE_FOR_LOG_BASED_CDC: Optional, default value is true. Setting this value to false falls back to previous approach.
- TEMP_DATABASE_NAME: Optional, default value is empty, where temporary table will be created in the same schema from which logs are being read.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Optional, default value is false. Setting this value to true tries to build dictionary before every CDC.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Optional, default value is false, it uses offline dictionary. If you set it to true, it uses redo log dictionary to read archive logs with DDL tracking. The value must be set to true in case of schema synchronization. NOTE: Schema synchronization is applicable only to addition of columns.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_NAME: Optional, default is dictionary.ora, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_PATH: Mandatory, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_PATH: Mandatory, Absolute path to directory where archive logs are stored).
- USE_UDF_FOR_WIDE_TABLE_CONCAT: Default value is False, uses Infoworks provided custom UDA for concatenation of wide tables instead of xmlagg method. You must create UDA in the Infoworks temp schema manually.
- NUMBER_OF_LOG_FILES_TO_LOAD: Default value is _-1_which represents all log files. This configuration allows you to restrict the number of log files to load in each run of CDC.
- PERSIST_LOG_BASED_TEMP_TABLE: Default value is False, setting the value to _true_does not clean up the temp table created by Infoworks at the end of the job for debug purposes.
- LOG_BASED_CDC_SCHEMAS: source level configuration, comma-separated schema names of tables in the dummy source.
- TABLE_SCHEMA: schema of the particular table at the table level For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
- LOG_FILE_SEQUENCE_COLUMN_NAME: In case of Oracle RAC setup, this configuration must be set at source level as RECID.
USE_ONLINE_CATALOG_AS_DICTIONARY: Setting this value to _true_uses the dictionary from Oracle online catalogue. This does not support Schema synchronization.
To improve the performance of temp table creation, you can specify temp table creation parallelism, the default value is 1. If more than one archive log file is available, the files will be split across multiple threads to start LogMiner in parallel. This method works only with Online Catalog as a dictionary or with an offline dictionary. Both the dictionary options do not support schema synchronization. In case of schema changes you must switch back to redo log dictionary option with parallelism as 1. To use this optimization, set the following configurations at the source level:
- PARALLEL_LOGMINER_SESSIONS: The number of open sessions to Oracle to start LogMiner in parallel.
- USE_ONLINE_CATALOG_AS_DICTIONARY: Set this value to true.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Set this value to false.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Set this value to false.
Limitations
- Derived Split by and derived partition are not supported.
- BFILE, BLOB, CLOB, and XML are not supported.
3. Using Staging Database Server with Temporary Table to Read Archive Logs
This method is similar to the previous method. However, instead of using production database to read archive logs, Infoworks uses staging database server to read archive logs, thus ensuring minimal load on the production database.
Archive Logs Using Staging Database Server
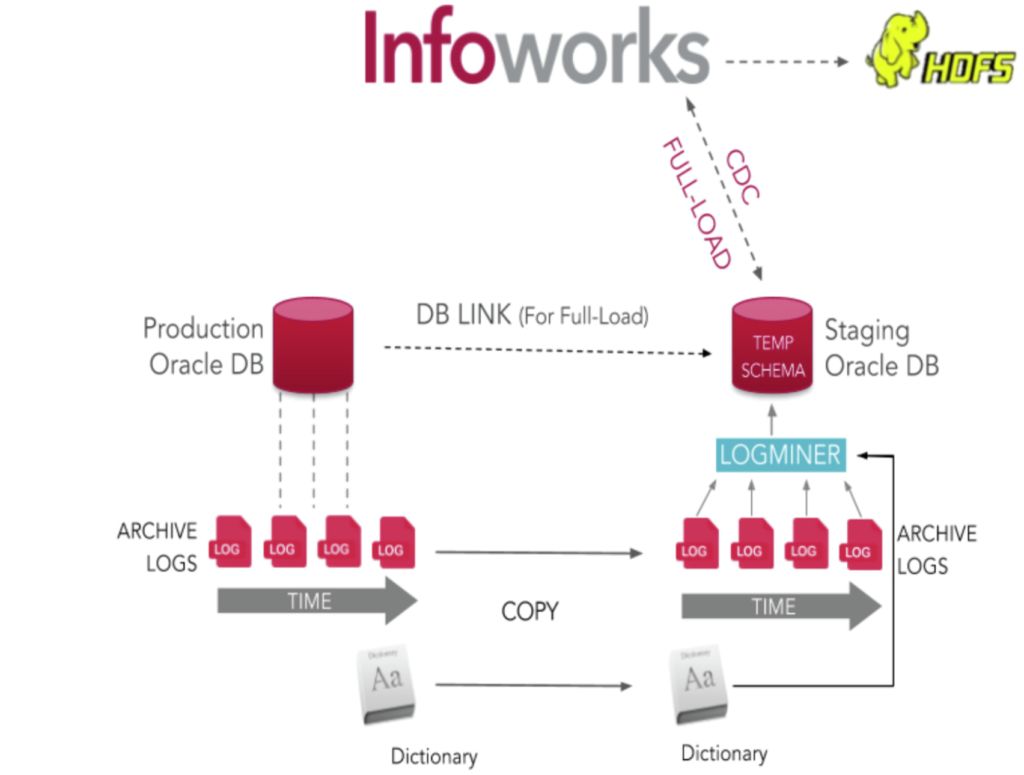
Source Configurations
- USE_TEMP_TABLE_FOR_LOG_BASED_CDC: Mandatory, must be set to true.
- TEMP_DATABASE_NAME: Optional, default value is empty, where temporary table will be created in the same schema from which logs are being read.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Mandatory, should be set to false. Since Infoworks reads logs from staging database, it cannot build dictionary on the source system.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Mandatory, should be set to false. This approach only works with offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_NAME: Optional, default will be dictionary.ora.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_PATH: Mandatory, absolute path to directory where dictionary file is stored.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_INFO_OBJECT_NAME: Mandatory, object name on staging database which is a DBlink to view v_$archived_log on production server.
- IS_STAGING_ORACLE_SERVER: Mandatory, must be set to true. Default is false.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_PATH: Mandatory, absolute path to directory where archive logs are stored.
- SFTP_HOST: Mandatory, IP of the staging database server.
- SFTP_PORT: Optional, Default is 22.
- SFTP_USER_NAME: Mandatory, SFTP username to login to staging database.
- SFTP_ENCRYPTED_USER_PASSWORD: Optional, required only if password is needed to login to staging database server.
- USE_UDF_FOR_WIDE_TABLE_CONCAT: Uses Infoworks provided custom UDA for concatenation of wide tables instead of xmlagg method. You must create UDA in the Infoworks temp schema manually.
- NUMBER_OF_LOG_FILES_TO_LOAD: Default value is -1 which represents all log files. This configuration allows you to restrict the number of log files to load in each run of CDC.
- PERSIST_LOG_BASED_TEMP_TABLE: Default value is False, setting the value to true does not clean up the temp table created by Infoworks at the end of the job for debug purpose.
- LOG_BASED_CDC_SCHEMAS: source level configuration, comma-separated schema names of tables in the dummy source.
- TABLE_SCHEMA: schema of the particular table at the table level For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
- LOG_FILE_SEQUENCE_COLUMN_NAME: In case of Oracle RAC setup, this configuration must be set at source level as RECID.
To improve the performance of temp table creation, you can specify temp table creation parallelism default value is 1, if there are more than one archive log files, they will be split across multiple threads to start LogMiner in parallel.
This method works only with offline dictionary since the LogMiner is run in a different database. This dictionary option does not support schema synchronization. In case of schema changes, you must switch back to redo log dictionary option with parallelism as 1.
To use this optimization, set the following configurations at the source level:
- PARALLEL_LOGMINER_SESSIONS: The number of open sessions to Oracle to start LogMiner in parallel.
- USE_ONLINE_CATALOG_AS_DICTIONARY: Set this value to false.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Set this value to false.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Set this value to false.
Limitations
- Derived split by and derived partition are not supported.
- BFILE, BLOB, CLOB, and XML are not supported.
- Schema synchronization is not supported.
Planning Oracle CDC with LogMiner
Before you configure Oracle CDC with LogMiner change data capture, review the following requirements and performance considerations:
- Verify that a valid Oracle environment exists for the Infoworks user.
- The Oracle source instance must be running in ARCHIVELOG mode, and Oracle global minimal supplemental logging must be enabled.
- A copy of the Oracle catalog must exist in the Oracle archived logs.
- Oracle LogMiner continuous mining reads archived redo logs only from the directory to which they were originally written.
- If Infoworks is not installed on the same machine as the Oracle instance, configure a TNS entry on the client machine with SERVER=DEDICATED in the CONNECT_DATA section of the connect descriptor. This specification is also required if the network is configured for Multi-Threaded Server (MTS) mode.
- Infoworks requires the Oracle Client binaries. When you install Oracle, the Client binaries are installed by default. To use SQL*Net connectivity on a machine that does not have an installed Oracle instance, you must install the Oracle Client.
- If you use Oracle materialized views, Infoworks can capture change data from the master tables that underlie those views. Infoworks supports change capture for any type of materialized view. The view and its underlying table have a one-to-one correspondence and share the same name.
- Infoworks uses Oracle LogMiner to read change data from archived logs. If you use an archived log destination other than the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 path and LogMiner processing lags behind, problems might occur. In this situation, LogMiner starts reading change data from the archived logs in the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 directory. If these archived logs are inaccessible from the machine with the Oracle instance to which you are connected, the LogMiner session might fail.
Oracle Datatypes Supported for CDC
Infoworks uses Oracle LogMiner to retrieve changes from the Oracle redo logs. Since Oracle does not log data or does not completely log data with some datatypes in the redo logs, Infoworks Oracle CDC with LogMiner cannot retrieve change data for all Oracle datatypes.
Following table indicates the Oracle datatypes supported by Infoworks Oracle CDC with LogMiner:
| Oracle Datatypes | Supported | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| BFILE | N | Data for columns that have this datatype are not completely logged in the Oracle redo logs and cannot be captured. |
| BINARY_DOUBLE | Y | |
| BINARY_FLOAT | Y | |
| CHAR | Y | |
| DATE | Y | |
| FLOAT | Y | |
| LOBs | N | |
| LONG | N | Columns of this datatype cannot be included in capture registrations. |
| LONG RAW | N | Columns of this datatype cannot be included in capture registrations. |
| NCHAR | Y | |
| NUMBER | Y | PowerExchange handles NUMBER columns as follows: Numbers with a scale of 0 and a precision value less than 10 are treated as INTEGER. Numbers with a defined precision and scale are treated as NUMCHAR. Numbers with an undefined precision and scale are treated as DOUBLE. |
| NVARCHAR2 | Y | |
| RAW | Y | |
| ROWID | Y | |
| TIMESTAMP | Y | |
| TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE | N | |
| TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE | N | |
| UROWID | N | |
| VARCHAR2 | Y | |
| XML types | N |
Configuring Oracle for CDC
For details on configuring Oracle for LogMiner based CDC, see How to Configure Oracle for CDC.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential