Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Mongo DB Ingestion
MongoDB is an open source database management system (DBMS) that uses a document-oriented database model which supports various forms of data.
Creating MongoDB Source
For creating a MongoDB source, see Creating Source. Ensure that the Source Type selected is MongoDB. The target Hive schema is where the Hive tables will be created corresponding to each Mongo DB table.
Configuring MongoDB Source
For configuring an MongoDB source, see Configuring Source.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection URL | The URL for Infoworks DataFoundry to connect to the database. The URL must include the port in the following format: HostName:Port |
| Auth Mechanism | The authentication mechanism to connect to the Mongo DB server. The options include MONGODB-CR, SCRAM-SHA-1, SCRAM-SHA-256. |
| Username | The username of the target database. |
| Password | The password of the target database. |
| Database Name | The name of the target database. |
- Click Save Settings and perform a test connection. Ensure the test connection is successful and perform the collection crawl.
Collection Crawl
In MongoDB, databases hold collections of documents. MongoDB stores documents in collections. Collections are analogous to tables in relational databases and each document is analogous to record in table. By default, a collection does not require its documents to have the same schema which implies it is not necessary for the documents in a single collection to have the same set of fields and, data type for a field can differ across documents within a collection.
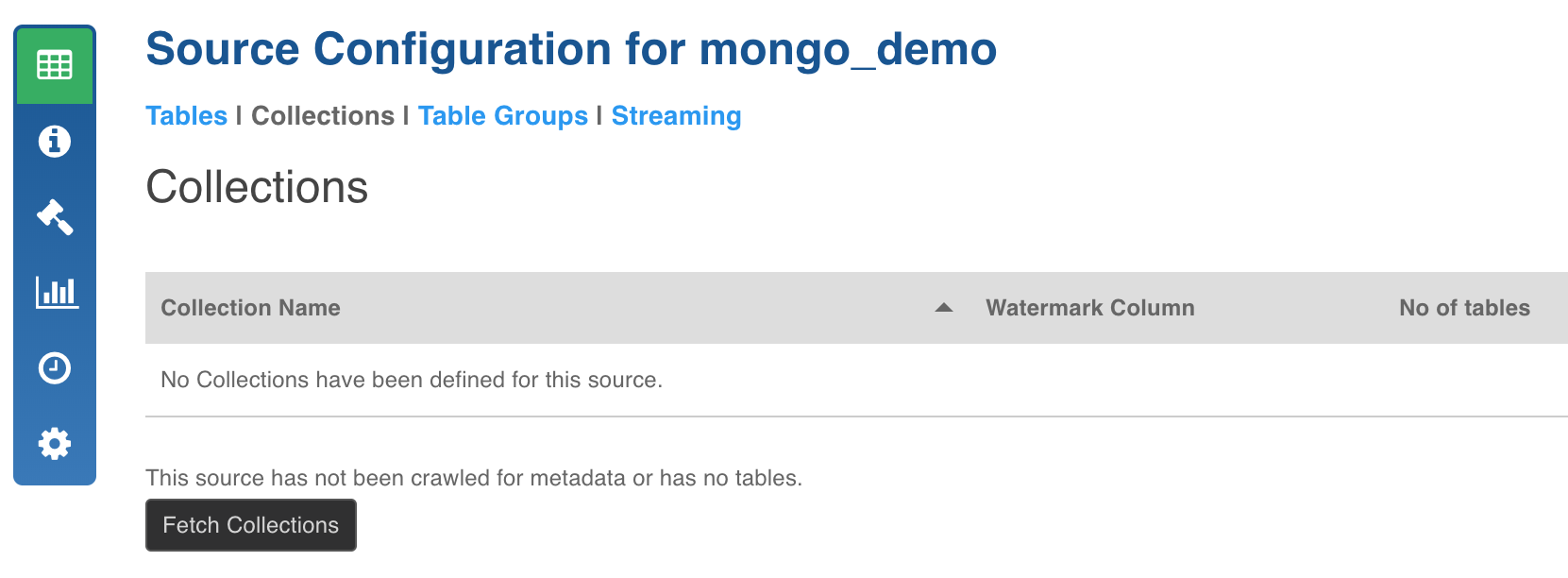
- Click the Source Configuration menu (grid icon) and navigate to the Collections tab.
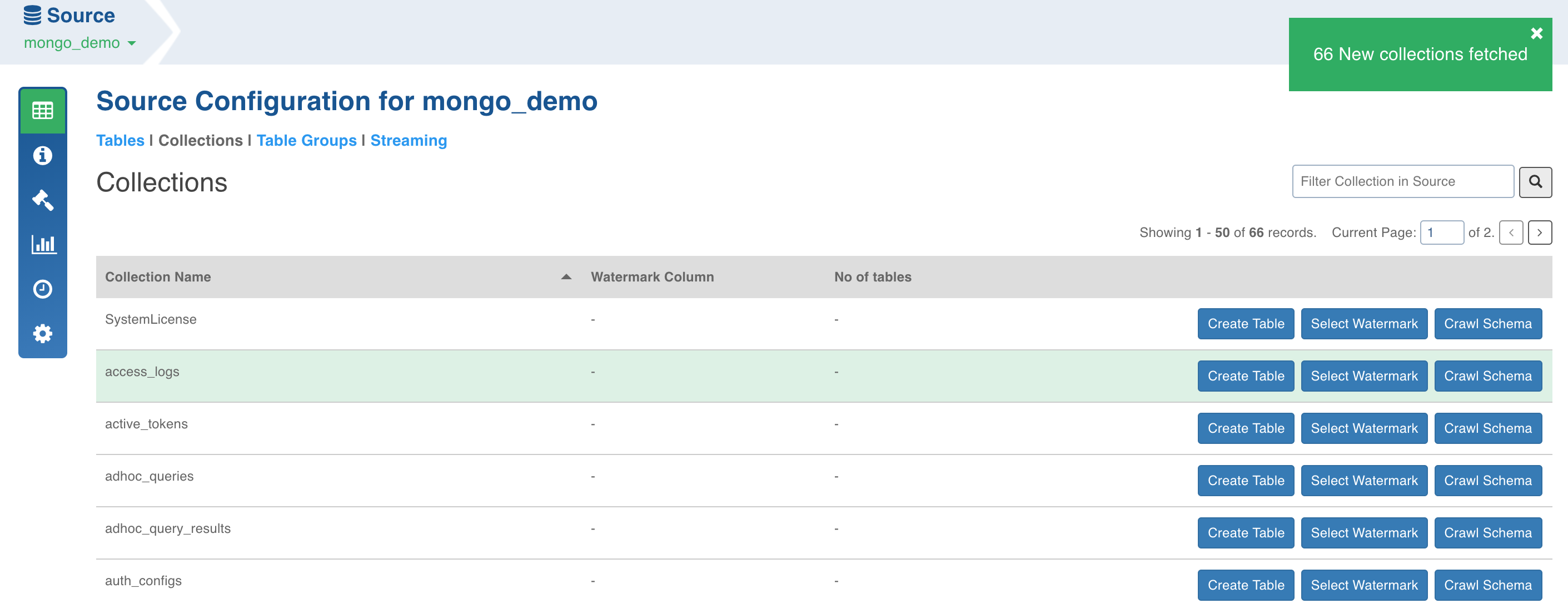
- Click the Fetch Collections button. The collections from the database will be fetched.
Schema Crawl for Collection
- Click the Crawl Schema button for the collection from which the tables must be created. The tree structure will be displayed, which is a unified schema of all the documents present in the specified collection.
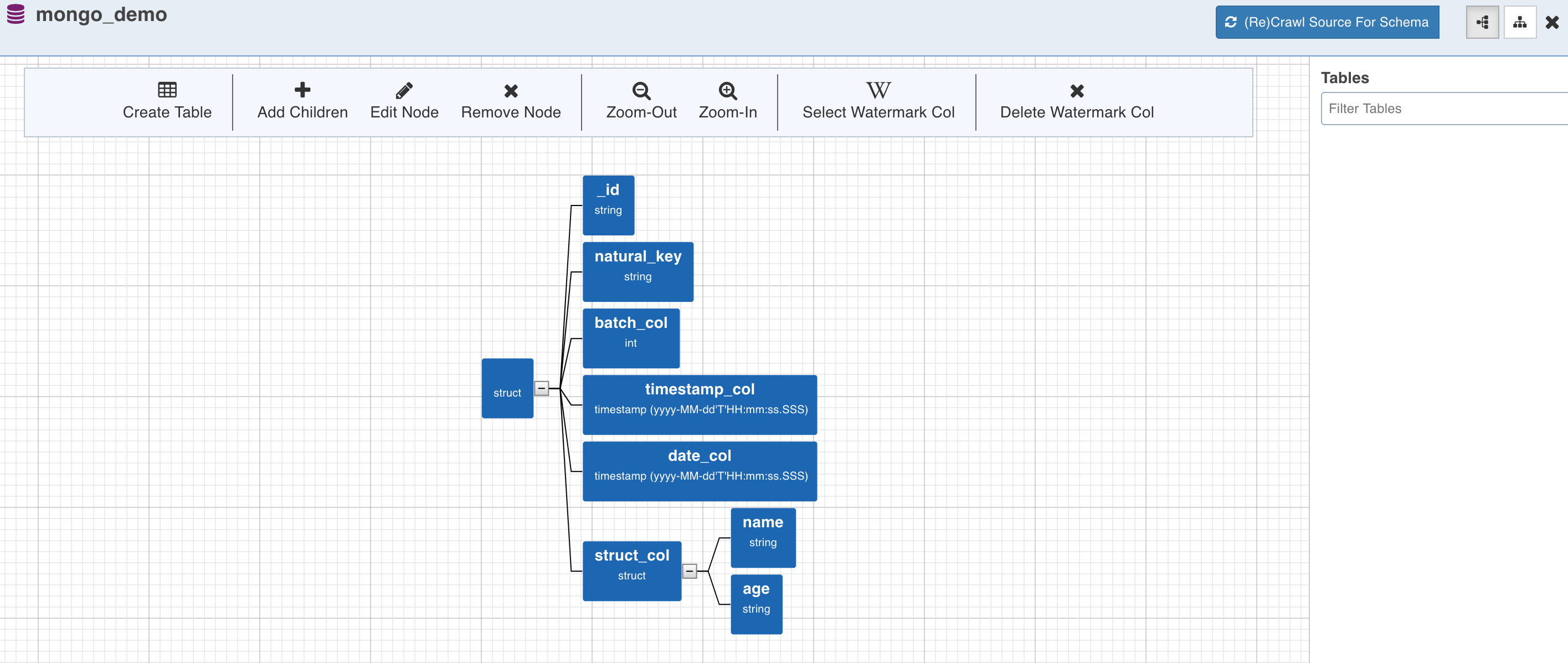
Watermark Column Selection
- To perform incremental ingestion for the tables created from the collection, select the watermark column by clicking on the required node and click the Select Watermark Col (W) option. Skip this step to perform only full ingestion.
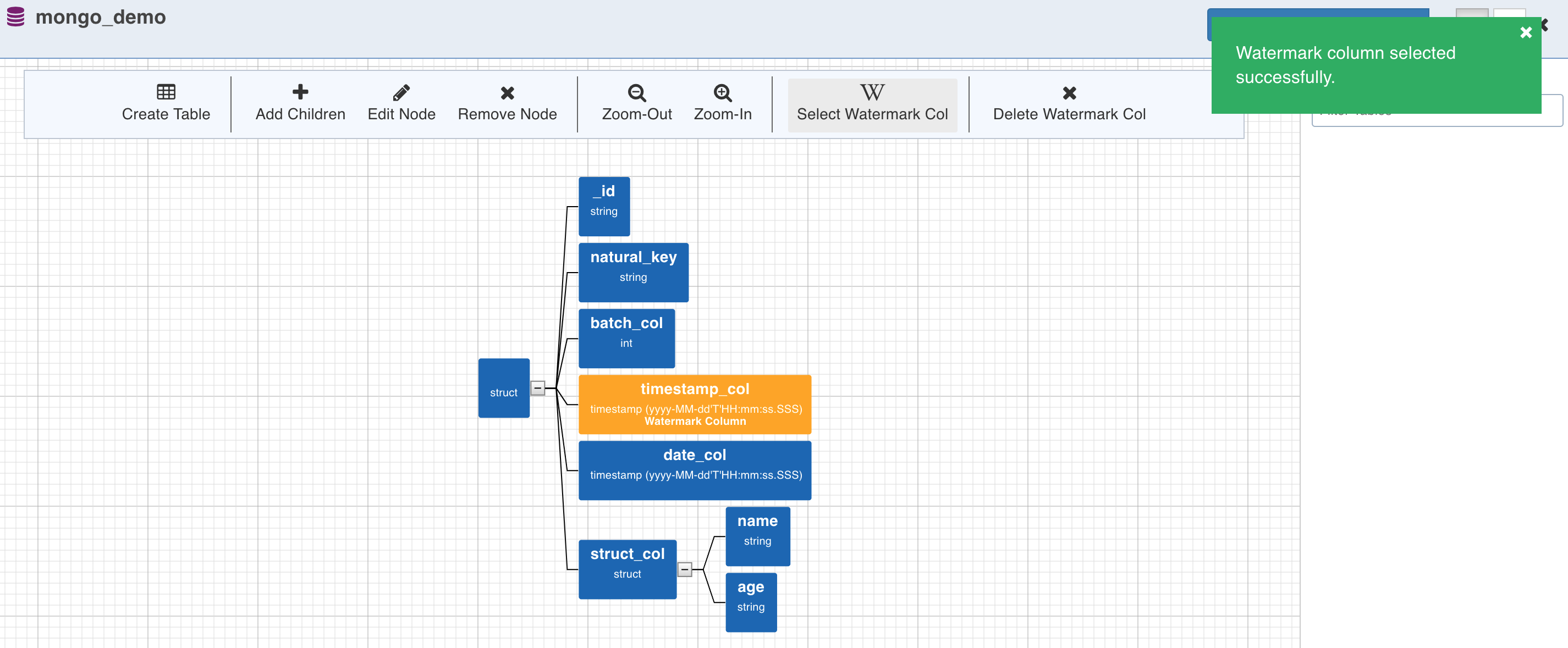
Table Creation
- Table can now be created by selecting a path from the tree. The path in this case is a group of single or multiple contiguous nodes without any branches. The path nodes can only be of type array or struct.
- Select the path and click Create Table. This creates a table schema out of all the non-path child nodes of the nodes present in the path along with the watermark column selected for the collection.
NOTE: If you create a table without selecting a watermark column for the collection, the following message will be displayed:

To create only full load table (complete refresh every time), click Yes, Create Table Without Watermark Column. Else, click Cancel and select the watermark column for the collection.
- Enter the target Hive Table Name, Target HDFS Path (this is relative to the source target base path entered during source creation).
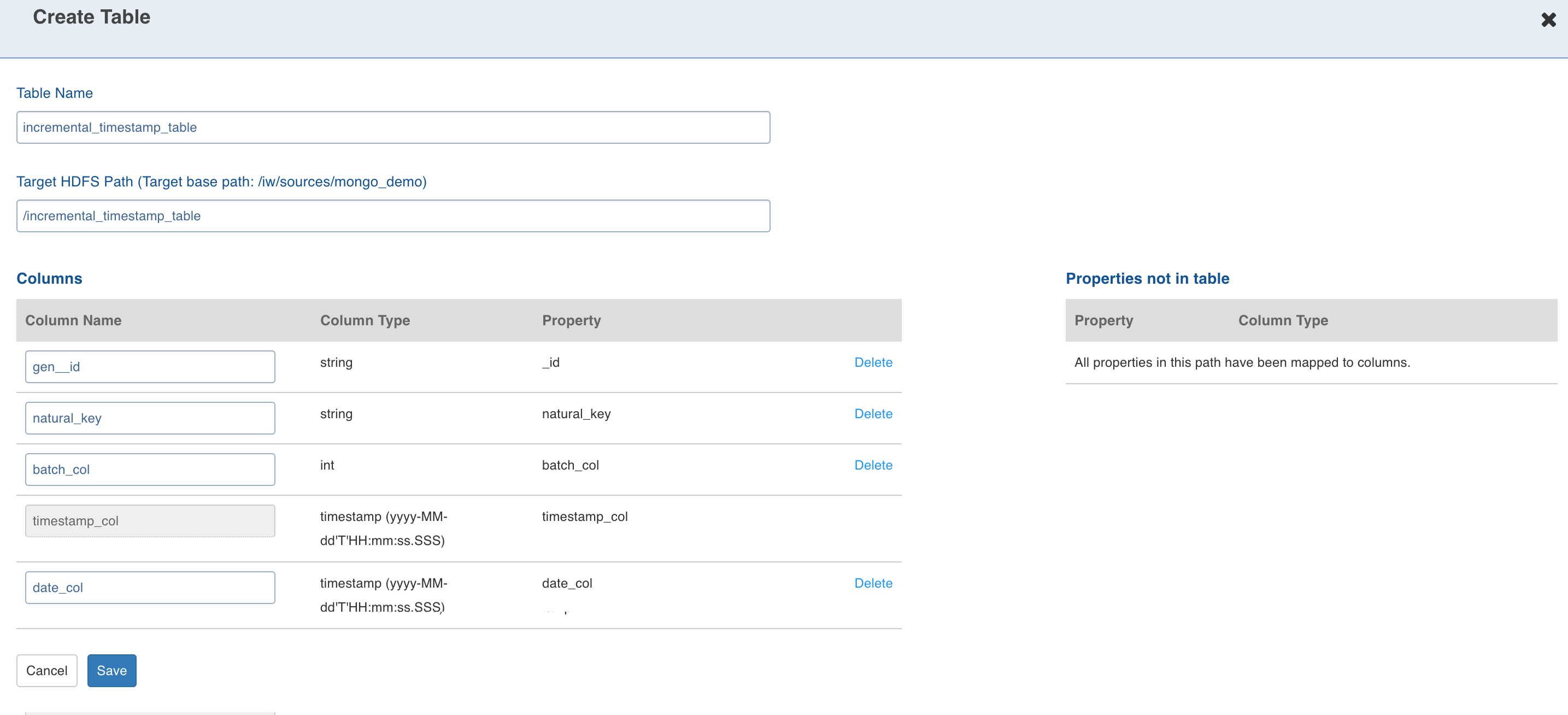
- Configuring the columns and click Save.
Configuring MongoDB Source for Ingestion
For crawling a MongoDB source, see Configuring Source for Ingestion.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Ingest Type | The types of synchronization that can be performed on the table. The options include Full Load, Timestamp-Based Incremental Ingestion, Query Based Incremental Ingestion, Batch ID Based Incremental Ingestion. |
| Segmented Load Status | The option to crawl large tables by breaking into smaller chunks. The smaller chunks can be crawled in parallel. Select the column to Perform Segmented Load On. To derive a column, check the Use substring from field option and select the Extract function. After completing the Segmented Load, ensure to set this value to Completed to submit Incremental Load or Full Load jobs. NOTE: In case of date, datetime, timestamp column types you can extract new columns. The possible extraction options are year, month, year-month, month-day and day-num-in-month. |
| Source Configuration | |
| Natural Keys | The key to identify the row uniquely. This key is used to identify and merge incremental data with the existing data on target. Distribution of data into secondary partitions for a table on target will be computed based on the hashcode value of the natural key. This field is mandatory for incremental ingestion tables. NOTE*: The value of natural key column cannot be updated when updating a row on source; all the components of the natural key are immutable. |
| Split by | The option to crawl the table in parallel with multiple connections to database. Split-by column can be an existing column in the data or derived from an existing column. The numbers, date, datetime and timestamp columns are allowed to be selected as split-by key. In general, any column for which min and max can be computed can be a split-by key. NOTE: Keys which increase or decrease gradually can be used as split-by. To derive a column, check the Use substring from field option and select the Extract function. |
| Synchronization Configuration | |
| CDC Start Date | The option to fetch a specific portion of the delta, based on the time window. The start date of the time window. |
| CDC End Date | The option to fetch a specific portion of the delta, based on the time window. The end date of the time window. |
| Enable Schema Synchronization | The option to synchronize the Hive table schema, if the source table is modified after the table ingestion is complete. |
| Timestamp-Based Incremental Load | |
| Timestamp Column for Insert | The source column to be used as insert watermark. |
| Timestamp Column for Update | The source column to be used as update watermark. NOTE: It can also be the source column to be used as insert watermark. |
| Query-Based Incremental Load | |
| Slowly Changing Dimension Type | The type of the query based ingestion. The options include SCD Type 1 and SCD Type 2. SCD Type 1 always overwrites the existing record in case of updates. |
| Configure Insert Query | The option to input the query which identifies and fetches the incremental insert records from the source table, using the record insertion row from the audit table. |
| Join Column for Insert | The column used to identify the inserts. This column will be joined with audit table column. This field uses source datatype. |
| Configure Update Query | The option to input the query which identifies and fetches the incremental update records from the source table, using the record update row from the audit table. |
| Join Column for Update | The column used to identify the updates. This column will be joined with audit table column. |
| External Audit Schema Name | The schema name of the audit table where the timestamps are being stored. |
| External Audit Table Name | The name of the audit table where the timestamps are being stored. |
| External Audit Join Column | The column by which the data table and the audit table will be joined. |
| External Audit Timestamp Column | The timestamp column in the audit table, which maintains record audit. |
| BatchID-Based Incremental Load | |
| Batch-ID Column | This column used for fetching of delta. This column must be a numeric column. Source datatype and target datatype must be equal. |
| Start Batch Id | The numeric value of Batch ID column (configured by the user during table configurations) starting which the delta is fetched. |
| End Batch Id | Numeric value of Batch ID column (configured by the user during table configurations) till which the delta is fetched. |
| Target Configuration | |
| Hive Table Name | The name of the table in Hive which will be used to access the ingested data. |
| Storage Format | The format of the data file to be stored in HDFS. The options include ORC and Parquet. |
| Partition Hive Table on | The option to partition the data in target. The partition column also can be derived for date, datetime and timestamp column. This will further partition the data. A hierarchy of partitions are supported with both normal partitions and derived partitions. NOTES: Ensure that the partition columns data is immutable. You can also provide a combination of normal and derived partitions in the hierarchy. |
| Extract a New Column | Check this option for supported datatypes to derive a partition from an existing column. NOTE: Fill the corresponding field values based on the derived type. |
| Is Epoch | When extracting a new column, checking this field indicates whether the selected column is epoch. This allows you to select the partitions from epoch value based on the date’s function. For example, year month, year, month, date. Epoch is supported for all numeric datatypes except int and float. |
| Derived Column Name | This is a mandatory field to be filled when deriving a partition column. NOTE: Ensure no other columns in this table have the same name. |
| Extract Function | The extract function. If the parent column is a timestamp or date column, you can select extract function as one of the following: day num in month, month, year, year month, month day. If the parent column is other than timestamp or date, use the regular expression as the extract function. NOTE: This is a mandatory field to be selected when deriving a new column. |
| Data file pattern (regex) | If you select regular expression as the extract function, you must enter corresponding regular expression. NOTE: This field is a mandatory field if regex is used as an extract function. |
| Extract format | When using regex derived partition, this field specifies the values to extract from a data pattern to partition the data. NOTE: This field is mandatory if regex is used as an extract function. |
| Number of Secondary Partitions | The number of secondary partitions to run the MR jobs in parallel. The target data can be distributed among various partitions and each partitions in turn can have various secondary partitions. A table with no primary partition can also have secondary partitions. Secondary partition helps in parallelising the ingestion process. |
| Number of Reducers | The number of reducers for the ingestion map reduce job. Increasing the number of reducers helps reduce the ingestion duration. This will help in processing the MR jobs faster. This will be effective with the combination of partition key and number of secondary partitions. In any data processing using MR job, this will help in bringing the parallelism based on the data distribution across number of primary partitions and secondary partitions on Hadoop. |
| Generate History View | The option to create history view table (along with the current view table) in Hive, which contains the versions of incremental updates and deletes. |
| Number of Secondary Partitions to Merge in Parallel | The number of secondary partitions that can be merged in parallel for a table. |
To append new data to the crawled source click Ingest Now from the second crawl onwards. The new data can be placed in the same location. Only new and changed files will be picked. This mode should be used for cases where new inserts come in new files and there are no updates.
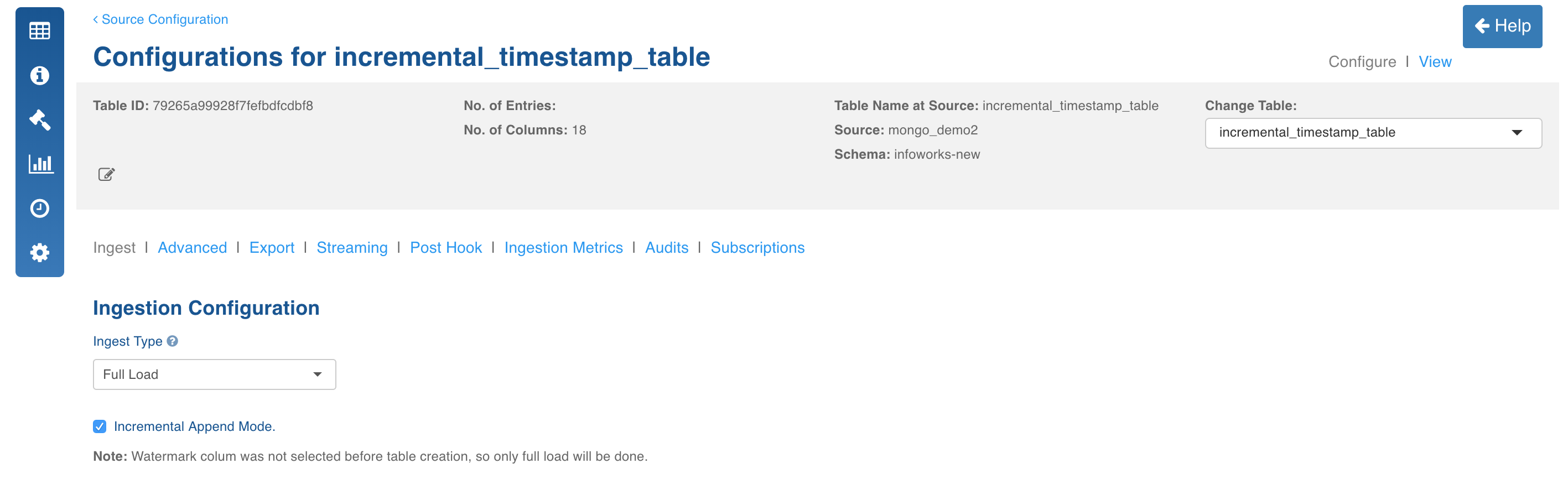
Append Mode
This mode must be used only when new inserts are present for every incremental crawl.
- Select the watermark column for the collection (mandatory). For details, see Watermark Column Selection.
- Select the Ingest Type as Full Load.
- Select the Incremental Append Mode check box.
- Enter the required fields and click Save Settings.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential