Delimited File Ingestion (DFI) supports crawling delimited text files with append and CDC modes.
DFI ingestion can be performed in the following ways:
- Record-level processing - supports Schema crawl, Data Crawl, Append Mode, CDC and Merge
- File-level processing - supports Schema crawl, Data Crawl, CDC append mode
Creating DFI Source
For creating a DFI source, see Creating Source. Ensure that the Source Type selected is Structured Files (CSV, Fixed-width, Mainframe Data Files).
Configuring DFI Source
For configuring a DFI source, see Configuring Source.
Source Configurations
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| From Filesystem | |
| Source Base Path (mounted on Infoworks server) | The base path where all the files to be ingested are stored. |
| ECB Agent | The ECB agent for the source. This field is displayed if ECB is enabled when the source is created. |
| From Hadoop Cluster | |
| Source Base Path (on Hadoop cluster) | The path where the structured files are stored in the Hadoop cluster. |
| From Remote Server (using SFTP) | |
| Source Base Path | The base path of all the directories that will be read from the file system. |
| SFTP Host | The host from which data will be read. |
| SFTP Port | The port where the SFTP service is run. |
| Username | The username to login to the host. |
| Using Password | If this option is enabled, enter the password to login in to the host. |
| From Cloud Storage | |
| Cloud Type | The options include Google Cloud Service and S3. For Google cloud service, enter the project name, select the Service Account Type, and the Source Base Path on Google Cloud Storage. If the Service Account Type selected is Custom Service Account, copy the Service Account JSON Credentials File to the edge node and provide the path. For S3, select the Access Type. If you choose Use IAM, ensure that the Edge noderuns with the same IAM role and has access to the S3 bucket. If you choose Use Access Credentials, provide the access credentials of S3 bucket. Enter the Source Base Path on S3 bucket. |
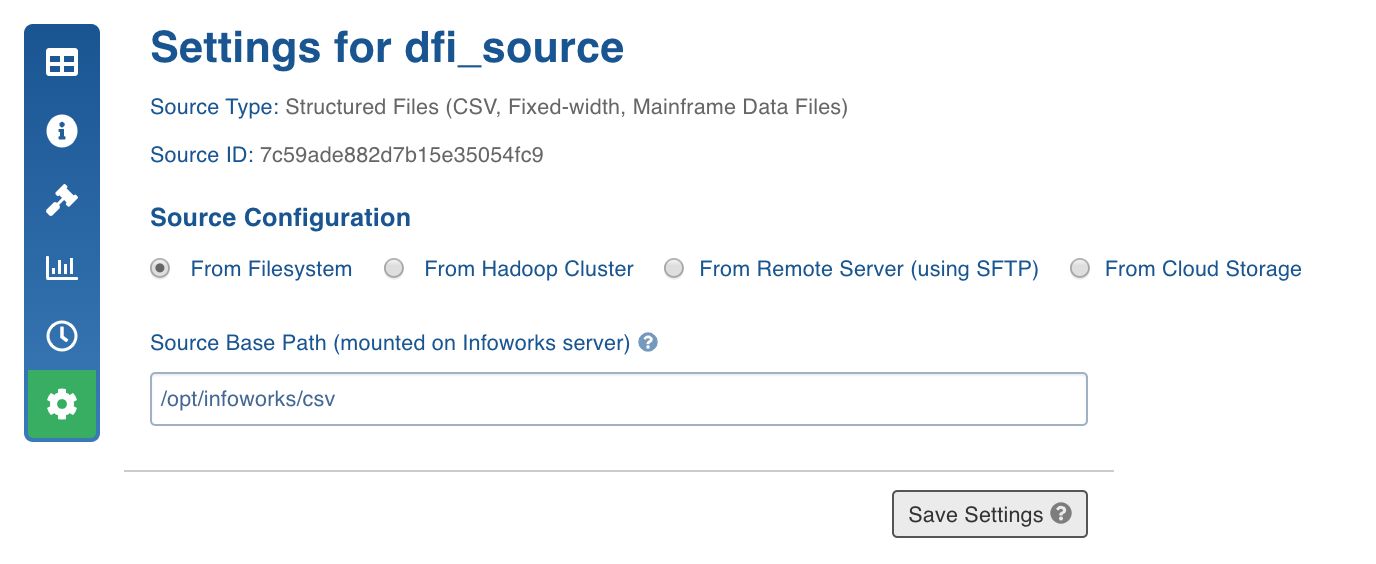
Once the setting is saved, you can test the connection or scroll down to create tables.
Creating Table and Crawling DFI Metadata
- Scroll down the Source Settings page and in the File Mapping section, click Add Entry to add a table.
- Provide the table details.
NOTE: For a folder that contains files with similar structure, the system can detect the types of all columns.
Mapping Configurations
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Table | The name by which the table will be represented in Infoworks User Interface. |
| Hive Table Name | The name of the Hive table which will hold the crawled data. |
| Source Path | The directory path (relative to source base path) where all the delimited files are stored. |
| Relative Target HDFS Path | The HDFS directory path (relative to the target base path) where the crawled output must be stored. The Hive external tables will be created on this directory. |
| Include Files Pattern | The regex pattern to include files. Only the files matching this Java regex will be crawled. |
| Exclude Files Pattern | The regex pattern to include files. Only the files which do not match this Java regex will be crawled. |
| Ingest sub-directories | The option to crawl the files in the recursive structure of the specified source path. |
| File Type | Select the file type as CSV. |
| Number of Header Rows | If the files contain header rows enter 1 as the value. If n lines are to be skipped after the header in all the files, enter n+1. This value can be zero or greater than zero. If greater than zero, for example, n, the first line of the file will be used to get the column names. The next n-1 lines will be skipped. |
| Number of Footer Rows | The number of footer rows in the file. |
| Column Separator | The delimiter in the delimited files. All the files in the mentioned Source Path must have the same value. This value must be a character. |
| Column Enclosed By | The character to enclose the data in the delimited columns. Quote is generally used in CSV files for this purpose. All the files in the mentioned Source Path must have the same value. This value must be a character. |
| Escape Character | The character used in the delimited files to escape occurrences of Column Separator and Column Enclosed By and Escape Character in data. All the files in the mentioned Source Path must have the same value. This value must be a character. The default value is . |
| Character Encoding | The character encoding of the delimited files. The default value is UTF-8. |
| Archive source files | Archives the files for which the data has been crawled and inserted into Hive. The files will be archived on the edge node. |
| Enable File Archiving on Infoworks Server | The option to archive the crawled files on the Infoworks server. |
| Path to store archived files | The path to store archived files. After the crawl is done, a file will be copied to the this location on the Infoworks server. |
| Move files from source after archiving | The option to move files from source after archiving. |
| Processing Level | The processing level, the options include record and file. Record processes each row of data and stores in orc/parquet format. File copies the file to existing Hive table in CSV format. |
| Source contains control files | This option can be used when every delimited file has a corresponding control file, which will be used for validation after the crawl is performed. If this field is enabled, enter the Data files pattern and Extract format. Data files pattern: The regular expression that represents all the delimited files. For example for CSV files, the value can be (.).csv. Extract format*: The option to extract the control file names that are present in the same directory. |
NOTE: Truncate and Truncate reload of table will not affect archived files. For every data file the control file will also be archived.
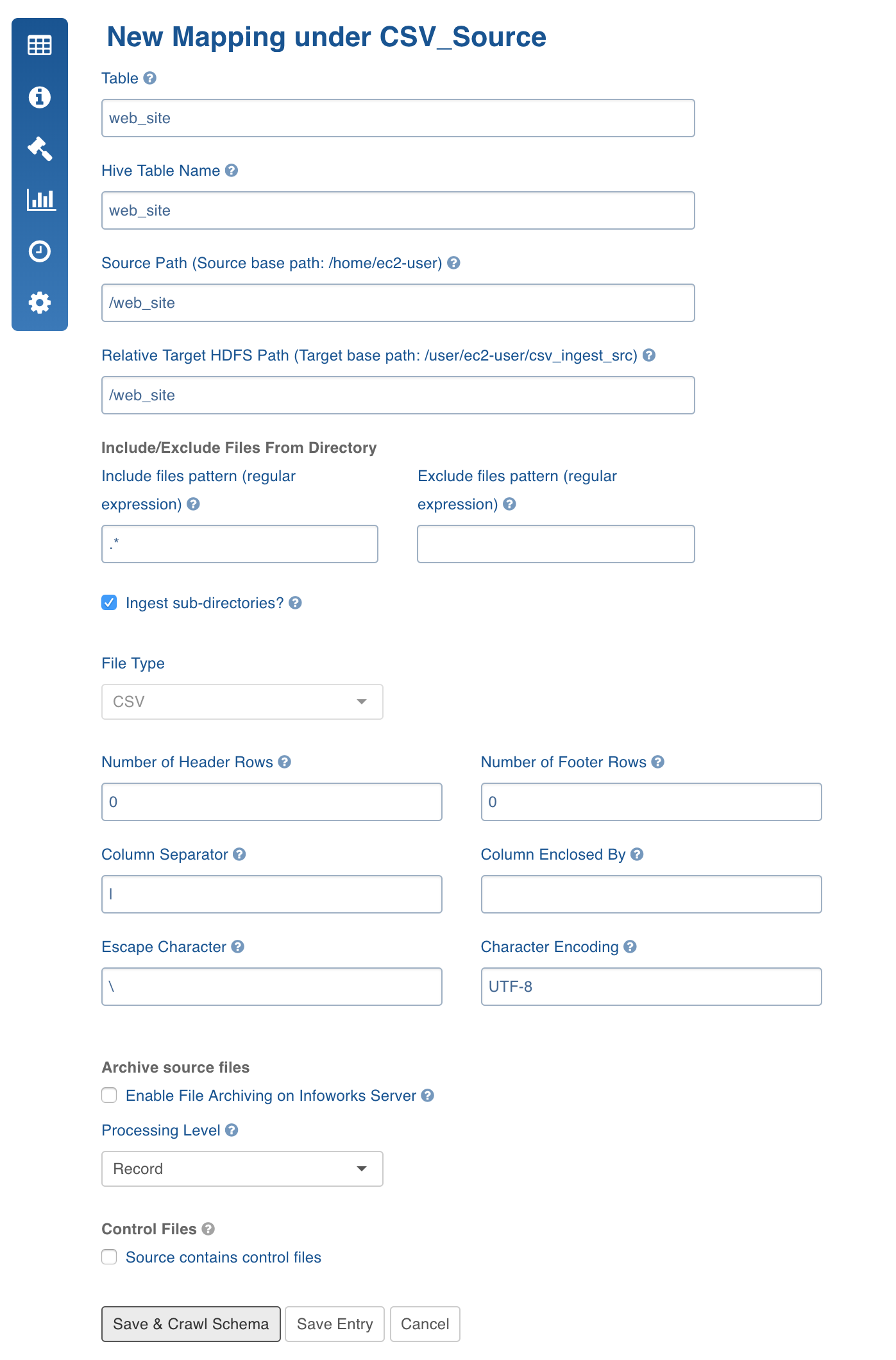
- Control Files: A control file (a file with data file metadata) against which you can validate the data file. The regular expression fields, Data Files pattern and Extract format, allows you to specify the corresponding control file for every data file as a function of the data file path. Every file with CSV extension will be considered as a data file and the same file path ending with CTL extension will be treated as control file.
Ensure that the data directory after applying the include and exclude filters only returns data files and control files. When processing, the system first applies include and exclude filters for every file. Assuming that the file path which passes the Data Files pattern regex is a data file, the corresponding control file is found using the mentioned regex patterns. Also ensure that control files should not pass Data Files pattern regex.
Currently, the control files support java properties file format which validates checksum , count, and file size.
NOTE: Control file features with compressed files in are not supported in DFI ingestion.
Following is an example:
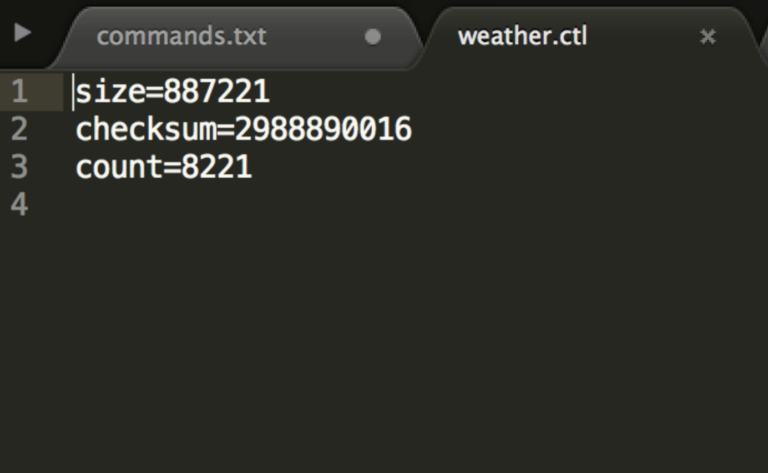
The validation logic and control file reading logic is pluggable. Hence multiple validation variables and different control file parsing logics can be plugged to extend this feature.
NOTE: For the validations to function, the calc_file_level_ing_metrics configuration must be set as true.
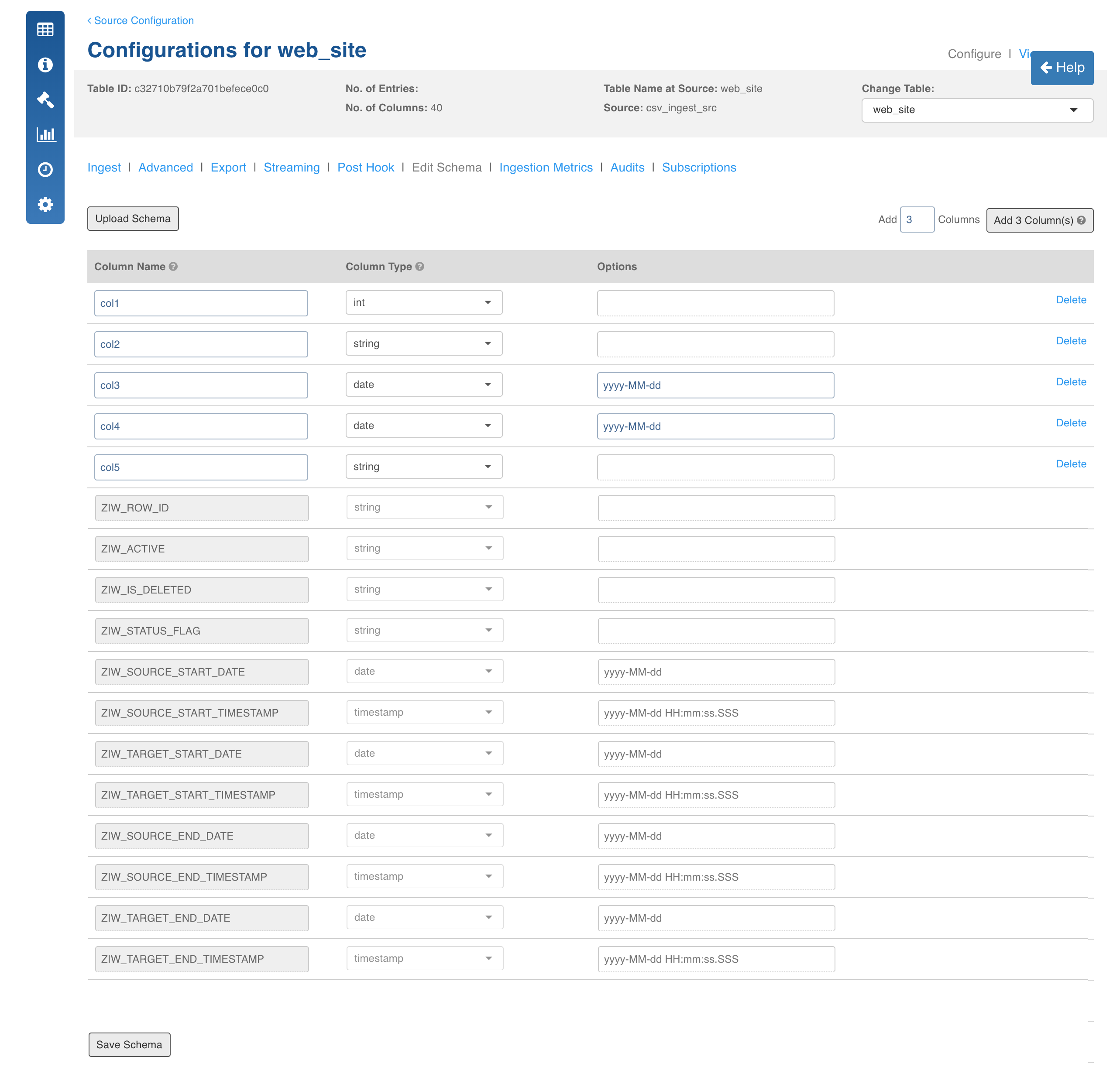
- Click Save and Crawl Schema. You will be redirected to the Edit Schema page where you can add or edit columns.
- Click Save Schema.
- To recrawl metadata, navigate to the Source Configuration page and click Recrawl Metadata.
NOTE: If the table is not mapped the Crawl Metadata button will be displayed in the Source Configuration page.
Crawling DFI Data
For crawling a DFI source, see Crawling Data.
Limitations
- If multiple versions of the same record (same natural key) are present in the same file, one of the records will be picked randomly and the others will be moved to the history table.
- Editing previously ingested files is not supported since the current version of the record might be affected.
Schema Specification
For a given folder which contains files with similar structure, you can specify the table schema.
To specify the table schema, follow these steps:
- Create tables as described in the Prerequisites section.
- Navigate to source configuration section and click Recrawl Metadata.
- Click the View button for the table after the metadata crawl is complete. You will find the types are assigned to column names if header is specified. Otherwise, columns will have names such as Col1 and Col2.
Configurations
- CSV_ERROR_THRESHHOLD: if the number of error records increases this threshold, the mr job will fail. Default is 100.
- CSV_KEEP_FILES: if the host type is local before the mr job runs, the csv files are copied to the tableId/csv directory. If this config is true, the files are not deleted after the crawl. Default is true.
- CSV_TYPE_DETECTION_ROW_COUNT: Number of rows to be read for type detection/metacrawl. Default is 100.
- CSV_PARSER_LIB: The underlying CSV parser library used by Infoworks. The default value is UNIVOCITY. It is recommended to use the default parser. In case of any issue, user can try setting COMMONS, JACKSON or OPENCSV parser. This configuration can be set at the source or table level.
- CSV_SPLIT_SIZE_MB: Split size to be used for mr for every file. Default 128.
- dfi_job_map_mem: mapper memory for the crawl map reduce. Default is the value of iw_jobs_default_mr_map_mem_mb in properties.
- dfi_job_red_mem: reducer memory for the crawl map reduce. Default is the value of iw_jobs_default_mr_red_mem_mb in properties.
- calc_file_level_ing_metrics: If this is set to true, the file level ingestion metrics are calculated at the end of the job. Default is true.
- modified_time_as_cksum: If this is true, the modified time is used to determine if the file has been changed or not. If it is set to false, the actual checksum is calculated. Default is false.
- delete_table_query_enabled: By default, Delete Query feature is available at table level. Set IW Constant delete_table_query_enabled to false from UI to hide Delete Query.
- multiline.mode: Set this to true if the file has multiline records and all the columns are quoted/unquoted.
- CSV_NULL_STRING: The configuration to set the NULL string. This configuration is available on table, source and global level. The default value is NULL.
- USE_GTE_FOR_CDC: This configuration allows you to fetch the CDC records based on the use case.
true: the CDC records will be fetched using the >= comparator. This is the default behaviour and this should be used for merge use cases to make sure that the data from the last batch is brought again. This is done for the scenarios where some data for the last batch and timestamp was still being populated in the source system when the ingestion job finished.
false: the CDC records will be fetched using the > comparator. This behaviour should be used for append mode scenarios, where the data for the last batch or timestamp in the source system is fully populated and the user does not want the old data again. This configuration is applicable for Timestamp and BatchID sync type tables.
NOTE: Data might be lost when the > comparator is used. If records with same batch ID are being inserted in the source system when the ingestion job is running, all the records that are inserted just after the job is run and with same batch ID will be missed in next CDC job.
- IGNORE_EXTRA_COLUMNS_IF_ANY: Set this value to true to ignore the newly added columns (if any). The value must be set to true at the table or source level before running the job. The default value is false.
Limitations
- Column order must be maintained; a new column always gets added at the end.
- If data is not enclosed and data contains delimiter it has to be escaped with escape char.
- If data is enclosed and data contains enclose character it has to be escaped.
Known Issues
- Infoworks managed tables are not supported as of now, that is, we can only add data to an existing Hive table.
- Since file-level processing adds data to existing table, Initialize and ingest button should not be used.
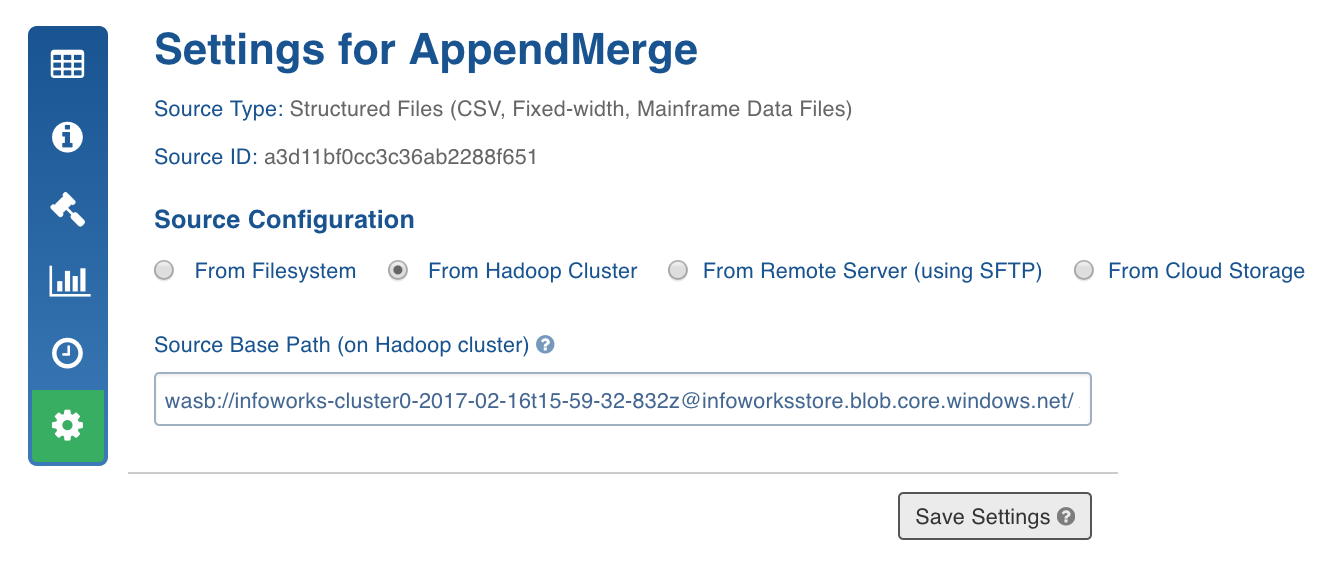
Azure Blob Storage Ingestion
Following are the Azure Blob Storage configurations:
- In the Source Settings page Source Configuration section, select the host type as From Hadoop Cluster.
- Prefix the Source Base Path with the wasb protocol and container address as follows:
wasb://<CONTAINER_NAME>@<STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME>.blob.core.windows.net/
The table path can then be specified as the path of the table folder in that container.
For example, consider the following:
- a Resource Group, R1, with a storage account, ASC, is used, which in turn has a container, C
- and, inside the container two files are available in the following folder structure: /a/b/x/file1.csv, /a/b/y/file2.csv
- where file1.csv and file2.csv have different schemas, two tables must be created.
You can provide the following as the source base path: wasb://C@asc.blob.core.windows.net/a/b
- The target path for table 1 will be x or x/file1.csv
- The target path for table 2 will be y or y/file2.csv
For containers which are private, if the source container has the access type as private in azure, then the following configuration must be added in the custom core-site.xml file:
- Key:
fs.azure.account.key.<STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME>.blob.core.windows.net - Value: Container Access Key (available in the accessKeys section of the azure storage account).