Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Advanced Ingestion Functionalities
Handling NULL Values
This section describes the process and impact of ingesting records having NULL values in watermark columns for timestamp based incremental tables during historical data ingestion (full ingestion).
This feature impacts Data Ingestion and Data Transformation as follows:
- Full Ingestion: During full ingestion, the records having NULL values in watermark columns for timestamp based incremental tables will be fetched from the database. For these records, the values of the audit columns, ZIW_SOURCE_START_DATE and ZIW_SOURCE_START_TIMESTAMP , values will be NULL in the target tables. If either of the timestamp columns or date columns is used in SPLIT BY configuration, the records with the NULL values will not be fetched during ingestion.
- Incremental Ingestion: During incremental ingestion, records having NULL values for both the columns will not be fetched from the database. If only one value is NULL, the record will be fetched from the database. For these records, ZIW_SOURCE_START_DATE and ZIW_SOURCE_START_TIMESTAMP values will be NULL in the target tables.
- Data Transformation: No impact due to NULL values in the downstream. Data Transformation uses only ZIW_TARGET_START_TIMESTAMP. Export functionality will be impacted only if all the values of ZIW_SOURCE_START_TIMESTAMP are NULL, which is unlikely.
To enable or disable this feature, the following admin configurations must be configured:
- fetch_null_timestamped_records=true: Records having NULL values will be fetched.
- fetch_null_timestamped_records=false: Records having NULL values will be ignored during ingestion.
Boundary Query
NOTE: Boundary Query is used to determine splits for ingestion jobs pulling data from RDBMS sources. If the split-by column split values are known in advance, for example, monthInYear (1-12), dayInMonth(1-31), users can save processing time by specifying the query upfront, for example, select 1,12 from dual.
The Boundary Query checkbox is available when you select split by from Infoworks DataFoundry.
Once you check Enable Boundary Query, a text box to enter the custom query will be displayed.
Secure Data Transmission
In this form of Transport Layer Security, a one-way authentication is performed. This means that the database server has to authenticate itself to the client (Infoworks) during the handshake. This is achieved by placing the server certificate in the client truststore on the edge nodes and the data nodes.
Currently we support secure data transmission (network encryption with server validation) for the databases mentioned below. By default, this is the java truststore, cacerts. The JDBC URL for each of these databases must be modified with some additional parameters.
NOTE: By default, the server certificates must be placed in the default JVM truststore, cacerts, of the edge nodes and data nodes. If you are not using the default configuration for Oracle and Sybase, and to customize the truststore paths and store the certificates there, see the following Custom TrustStores for Oracle and Sybase section.
| Database | JDBC URL | Extra Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/SAMPLE?verifyServerCertificate=true& useSSL=true&requireSSL=true | verifyServerCertificate Parameter to true for production and CA certificate. |
| MariaDB | jdbc:mariadb://localhost/SAMPLE?useSSL=true& trustServerCertificate=true | -trustServerCertificate is false for CA certificate |
| SQL Server | jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;databaseName=SAMPLE; encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=true | -trustServerCertificate is false for CA certificate |
| Teradata | jdbc:teradata://localhost/TMODE=ANSI,database=SAMPLE, ENCRYPTDATA=ON | |
| Netezza | jdbc:netezza://hostname:5480/sampleDB;securityLevel=onlySecured | security levels: onlySecured, preferredSecured |
| Oracle | jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST= (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=hostname)(PORT=2484))) (CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=servicename))) | Port number 2484 and TCPS Protocol preferred for Encryption - Uses JVM Default truststore |
| SAP Hana | jdbc:sap://hostname:39013/?encrypt=true&validateCertificate=true | Port number should be added as per the instance trustStore, trustStoreType and trustStorePassword parameters to be set in URL if JVM default truststore is not used. |
| DB2 | jdbc:db2://hostname:50001/SAMPLE:user=user-id;password=password;sslConnection=true; | NA |
Custom TrustStores for Oracle and Sybase
The following customizations are available for the TLS settings for Oracle and Sybase:
Source Level Configurations
- ENABLE_RDBMS_IMPORT_TLS (boolean): The default value is false. This value is set to proceed with custom truststore configurations, viewing logs, etc.
NOTE: Do not set this configuration if the default truststore and password is to be used.
- Enable_encryption_logs (boolean): The default value is false. Setting this value to true prints ssl debug logs.
- ingestion_truststore_path: The path of the truststore on the edgenode.
- ingestion_truststore_password: The password of the custom truststore on the edgenode.
- sqoop_truststore_path: The path of the truststore on the datanode.
- sqoop_truststore_password: The password of the truststore on the datanode.
NOTE: Ensure that the path and password to the truststore is same on all data nodes.
Data Masking
The data masking feature for RDBMS sources allows you to opt for masking certain columns of the table during ingestion. This masking is server-side, which means the data brought into the Infoworks node will already be masked. This feature helps in storing sensitive data that must not be stored in the data lake in its true form.
Following are the steps to enable data masking for a table:
- Navigate to the Metadata section of the specified table on the Tables page and click Edit Masking.
- Select the Mask-Column checkbox to mask the particular column.
Masking Types
Currently, Infoworks supports only the following types of data masking for RDBMS sources:
- Fixed Data Masking: The data in the column will be entirely replaced by the value in the Replace Pattern box and stored in the data lake. The target type in data lake will be String. Following are the data bases supported: Oracle, Teradata, SQL Server, DB2, MariaDB, Mysql, Sybase, SAP Hana, Redshift and Vertica.
- Regex-Based Data Masking: The data in the column will be replaced based on the match made by the regular expression in the Find Pattern text box. The regular expression format is database specific (POSIX for most sources). The target type in data lake will be String. Following are the data bases supported: Oracle, Teradata, Db2, Mysql and MariaDB.
NOTE: Currently, this type is only supported for Oracle, Teradata and MariaDB (v 10.5 upwards).
Find Pattern: For Regex-Based Masking, the Find Pattern field specifies the regular expression in the POSIX format, which will be matched in the column. Replace Pattern: The value in the Replace Pattern field will replace the matching regular expression (in case of Regex-Based) or the entire column (in case of Fixed Data Masking).
NOTE: The columns selected as masked columns cannot be used for any other purpose like, natural key, split-by keys, CDC keys, etc, and vice-versa. This is disabled by Infoworks.
Workload Management
The primary goal of workload management is to control the load (number of connections to the database) on source database while ingestion occurs. We can ingest data to Infoworks either by creating a table group or loading a table in segments (the latter one is useful for bigger tables).
This section covers workload management for both table group ingestion and segmented load ingestion while describing how we control number of connections to source.
##
Ingestion Metrics
The Ingestion Report feature generates ingestion-related metrics at the table, table group, and job levels.
Following are the steps to generate the ingestion reports:
In the Source Configuration page, click the Ingestion Reports icon. The Select Report Type drop-down displays the options.
- Table Group Metrics
This report displays aggregated ingestion metrics at table group and table level. The grey rows indicate table groups and white rows indicate the tables in the table groups. You can filter records using the Submitted After, Submitted Before and Table Groups options. You can export this report using the Export to CSV/Excel option.
- Table Metrics
This report shows ingestion metrics of jobs for a table. You can filter records using the Submitted After, Submitted Before options and select a table for records. You can also export this report using the Export to CSV/Excel option.
- Job Metrics
This report shows ingestion metrics of jobs for current source. You can filter records using the Submitted After, Submitted Before, Status, Job IDs and Job type options. You can also export this report using the Export to CSV/Excel option.
- Table Reconciliation Metrics
For details, see the Table Reconciliation Metrics section.
- Table Group Reconciliation Metrics
For details, see the Table Group Reconciliation Metrics section.
Table Groups Options
After ingesting a table group, you can click the Table Groups tab in the Source Configuration page and view the ingested table groups.
This section describes the icons in the Table Groups page.
- Configuration Audits When you click the Configuration Audits icon, the audit logs for the table group is displayed.
When you click show modifications links, the details of the modifications performed on the table group is displayed.
View Table Group
When you click the View Table Group icon, the table group details are displayed. It includes the following options:
- Generate Sample Data Now: Generates the sample data.
- Export Tables: Exports all the tables in a table group.
- Ingest Now: Ingests incremental delta from data source.
- Initialize And Ingest Now: Truncates and reloads the existing table, if any.
- Configure Table Group: Option to modify the table group configuration.
- Delete Table Group Data: Option to drop the tables in the target (hive) for the corresponding tables in the table group (the table group will still exist).
- Delete Table Group: Deletes only the table group and its corresponding configurations from the metadata store.
- Maintenance Options: This option is described in detail in the section below.
Data Ingestion Maintenance Options
Maintenance options in Ingestion provides access to ad-hoc requests from the user. These are available at table group level. Currently, maintenance options are available for any RDBMS JDBC based extractions and Teradata TPT based extractions.
Following are the steps to access the maintenance options at the table group level:
- Navigate to the required source.
- In the Source Configuration page, click Table Groups.
- For the required table group, click the View Table Group icon.
- On the Table Group Configurations page, click Maintenance Options.
Following are the maintenance options:
- Run CDC: Fetches the incremental delta from data source without merging records onto Hadoop.
- Run Delta Merge: Merges available incremental delta files to the already existing data on Hadoop.
- Run CDC and Run Delta Merge work like Ingest Now.
- Run Full Load: Truncates and reloads the table. It works just like Initialize and Ingest Now.
- Run Post-Ingestion Hook: Normally, Post-Ingestion Hook scripts will be executed as part of the ingestion job (full/incremental). To run the scripts externally, this will provide a UI hook at the table group level.
- Re-Organize Data: This feature allows you to change some of the table-level configurations without having to truncate-reload the table. For more details, see the Data Restructuring and Table Configuration Management section.
- Run Data Reconciliation: This feature gives the user a provision to reconcile table data on source and target. For more details, see the Data Reconciliation section.
Post Ingestion Hook
Post hook ingestion is a feature where you can provide bash scripts to be run after ingestion completes. The post hook runs in the same job as the ingestion job. The scripts run after each table ingestion (full load, incremental load, and merge).
The script is invoked when the job is successful and also, when the job fails.
The script should be idempotent, that is, the action performed should not be affected by the number of times the script is called, as the script is called after each ingestion job.
Adding a Script
To add a post ingestion script, follow these steps:
NOTE: To add a script, you must have admin privileges and access to the edge node (the server where Infoworks service is running).
- Click Admin on the main menu.
- Click the Post Hook Script icon.
- Click Add Script. The following page opens.
- Enter the script name, description, and the path where the script is.
NOTE: Infoworks DF supports Python 3 engine to run the script files. Hence, ensure the script supports Python 3 syntax.
- Click Add Script.
Configuring Source to Run Post Hook
If you want a script to run for all the tables in a source:
- Navigate to the configuration panel of that source.
- Scroll down to the Post-Ingestion Hook section.
- Click Enable Post-Ingestion Script Execution, select the required script and click Save. The post hook is now enabled for all the tables for that source.
Configuring Table to Run Post Hook
To configure a table to run a post hook script, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the specific table and click the configure icon.
- Click Post Hook Ingestion.
- Click Overwrite Post-Ingestion Script Execution checkbox and select the required script.
- Click Save Configuration. The post hook is now configured for the table.
Environment Variables
The environment variables from the ingestion job are passed to the post hook script. In addition to these variables, the following variables, through which the table context for the post hook is available, can also be used.
- IW_TABLE_ID: The tableId of the table for which the script is running.
- IW_HIVE_TABLE_NAME: The name of the table in hive, for the table for which script is running.
- IW_HIVE_SCHEMA: The schema in hive, where the hive table was created
- SOURCE_TABLE_NAME: The name of the table in the source database, from where table was ingested.
- SOURCE_SCHEMA: The schema in the source database, from where the table was ingested.
- IW_TABLE_HDFS_PATH: The HDFS path of the table, where the data is stored.
- IW_SOURCE_ID: The ID of the Infoworks source in which the job is running.
- IW_TABLE_GROUP_ID: The ID for the group for which the job is running.
- IW_TABLE_GROUP_NAME: The name for the group for which the job is running.
- IW_SOURCE_NAME: The name for the source, which has the table.
- IW_JOB_ID: The ID of the running job.
- IW_JOB_TYPE: The job type of the job run. Refer to Ingestion Job Types and Their Descriptions for the possible values.
- IW_JOB_STATUS: The status of the job. The possible values are "successful" and "failed".
Post-Hook Ingestion Known Issue
The script might not run when the job fails due to java heap issue or when the user cancels the job.
Data Reorganization and Table Configuration Management
To avoid some of the situations where user has to change a particular table level configuration and is forced to truncate reload the table.
Configurations which required a truncate reload before this feature.
- natural_key
- split_by_key
- external_audit_schema
- external_audit_table
- external_audit_join_column
- external_audit_timestamp_column
- captured_schema_name
- captured_instance_name
- storage_format
- partition_key
- number_of_secondary_partitions
- generate_history_view
- hive_table_name
- split_by_key_extract_from_col
- split_by_key_derive_function
- split_by_key_derive_column
- partition_key_extract_from_col
- partition_key_derive_column
- partition_key_derive_function
- is_infoworks_managed_table
Changes in the above configurations will be supported with some caveats in the following configuration:
hive table name: Hive table name change is supported in file based sources only, its not supported in RDBMS sources.
Changing the Configurations
The user interface for changing configurations remains the same. The difference is in what the configurations represent.
If the configurations are changed and the changed configurations require a restructuring job to run then on save UI will inform the user about the changed configurations which need a reorganizing job.
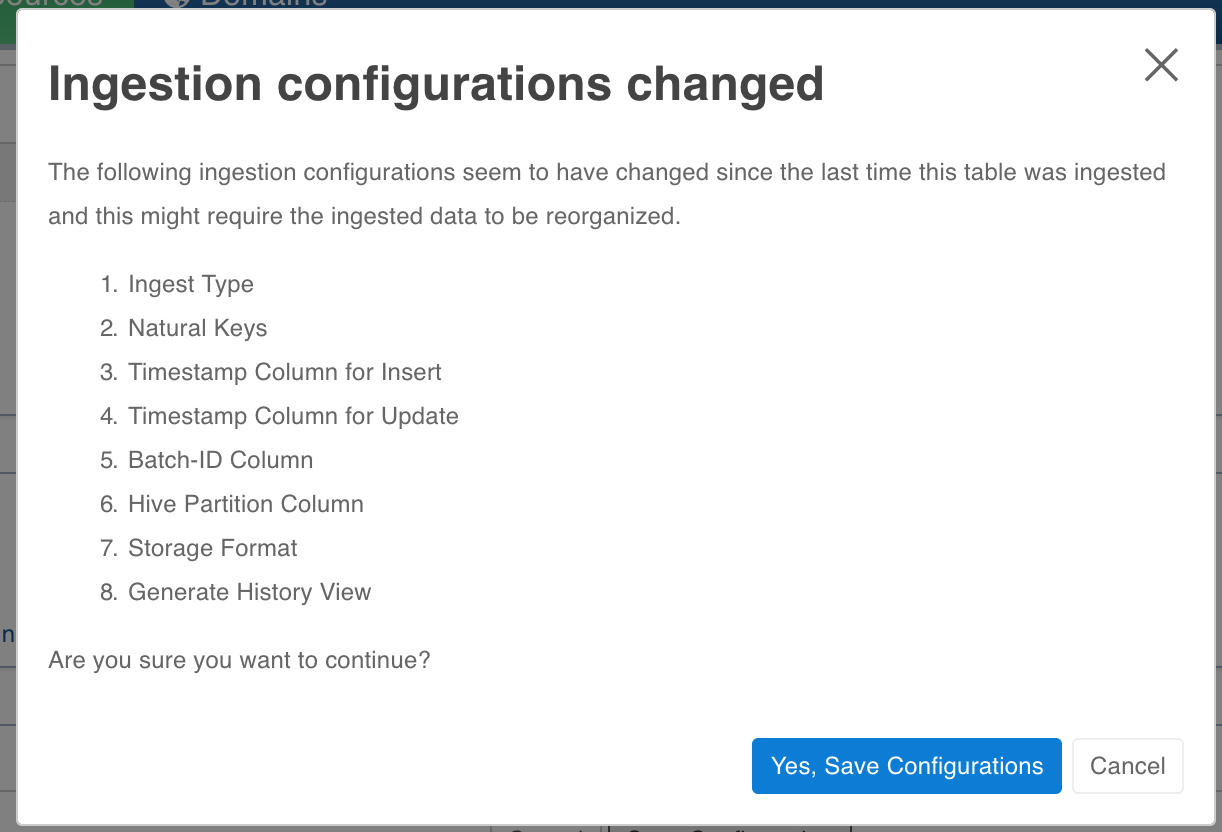
If user chooses to save the configs, he will be warned that a restructuring is required. User can run restructuring by clicking on Reorganize Now. The changes wont be saved if user clicks on cancel.
Segmented Load
For segmented load, the configuration changes are not supported. Currently it is not blocked from the user interface though. Hence all the configurations which are mentioned at the start of the document (the one that required truncate reload to change) should not be changed until all segments are crawled and you click Enable Complete Loading.

Configurations
- restructure_job_map_mem_mb- mapper memory for the crawl map reduce. Default is the value of iw_jobs_default_mr_map_mem_mb in conf.properties.
- restructure_job_red_mem_mb- reducer memory for the crawl map reduce. Default is the value of iw_jobs_default_mr_red_mem_mb in conf.properties.
Once a table is ingested, restructuring to the following ingest types are not supported:
- Timestamp-based Incremental Load: Query-based Incremental Load, Log-based Incremental Load
- Query-based Incremental Load: Log-based Incremental Load
- Batch-ID-based Incremental Load: Query-based Incremental Load, Log-based Incremental Load
- Log-based Incremental Load: Query-based Incremental Load
- Full Load: Query-based Incremental Load, Log-based Incremental Load
- Ogg-based Incremental Load: Query-based Incremental Load, Log-based Incremental Load
Limitations
For tables that have been crawled already, changing the sync type to log based or query based is not supported. You must truncate the table and recrawl with the new configuration.
Cloudera Impala Support
The Impala support in Ingestion can be enabled on Cloudera distribution by setting Admin System Configuration cdh_impala_support to true. This allows the Ingestion Job to create tables over data in HDFS which can be queried through Impala or other applications.
Impala-Related Admin System Configuration
- cdh_impala_support: As explained above, you must set this configuration to true.
- fail_ingestion_on_impala_cache_refresh_failure: After successful completion of Ingestion job, the metadata cache is invalidated so that new files and tables are visible to Impala.
- When this flag is set to true, the job status is set to failed.
- For performance reasons, this flag should be set to false. The tables which were not invalidated are provided in Job summary and can be invalidated manually by running invalidate metadata {tableName} if the table is newly created or refresh {tableName} if the table already existed.
- impala_ingestion_validation: When true, the ingestion job will use Impala query engine to do validation after job. Otherwise, hive will be used.
Impala Support Known Issues
Ingestion known issues in case of Cloudera are dictated by Impala limitations in datatypes supported and compatibility with other tools like Hive.
- Impala does not support some of the datatypes: One of the datatypes not supported is Date. However, our Ingestion jobs convert Date datatype to Timestamp while ingesting values, so that you can ingest sources with schema containing Date. For more details, see Impala Datatypes.
- Impala Hive Timezone mismatch: For data files written by Hive, there can be inconsistency in timestamps when queried in Impala. This is because, Hive stores the timestamp values in local timezone. For compatibility without any workarounds, add -convert_legacy_hive_parquet_utc_timestamps=true as startup flag for impalad. Otherwise, while querying in Impala use from_utc_timestamp function to retreive the values. An example to get values in EDT: select from_utc_timestamp('recordTimestampColName',EDT') from table_name; For more details, see Timestamp Datatypes.
- Impala Datatypes for Partitioning: For more details, see Partition Key Columns.
NOTES:
- Impala support in Ingestion has been tested on Cloudera distribution 5.10.x.
- Impala support requires Parquet as storage_format.
- 3 boolean constants:
| Admin Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| cdh_impala_support | Set to true if Impala support is required. |
| fail_ingestion_on_impala_cache_refresh_failure | Set to true if the ingestion job is to be failed in case Impala cache metadata is not refreshed. |
| impala_ingestion_validation | When true, the ingestion job will use Impala query engine to do validation after the job. Otherwise, hive will be used. |
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential