Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
PostgreSQL Ingestion
Infoworks DataFoundry now supports ingesting data from PostgreSQL database in a scalable and parallelized way. PostgreSQL is an open source object-relational database system that uses and extends the SQL language.
Creating PostgreSQL Source
For creating a PostgreSQL source, see Creating Source. Ensure that the Source Type selected is PostgreSQL.
Configuring PostgreSQL Source
For configuring a PostgreSQL source, see Configuring Source.
PostgreSQL Configurations
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Fetch Data Using | The mechanism for Infoworks DataFoundry to fetch data from the database. |
| Connection URL | The JDBC URL for Infoworks to connect to the database.
The URL must be in the following format: jdbc:postgresql://<hostname>:<port>/<databasename> |
| Username | The username for database connection. |
| Password | The password for the username provided. |
| Source Schema | The database schema to be crawled. |
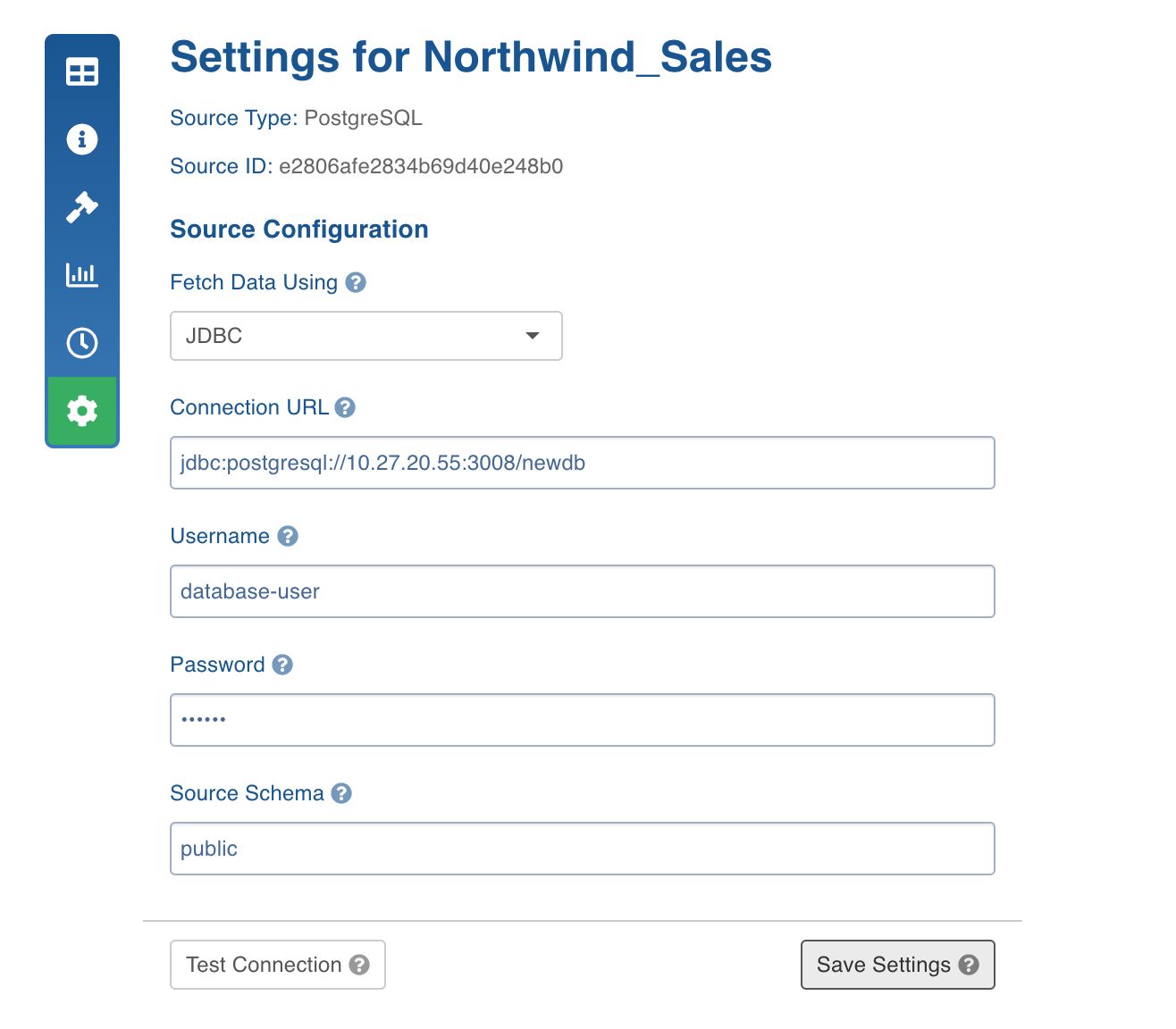
Once the setting is saved, you can test the connection or navigate to the Source Configuration page to crawl the metadata.
Crawling PostgreSQL Metadata
For crawling a PostgreSQL source, see Crawling Metadata.
Configuring PostgreSQL for Ingestion
For configuring a PostgreSQL source for ingestion, see Configuring Source for Ingestion.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
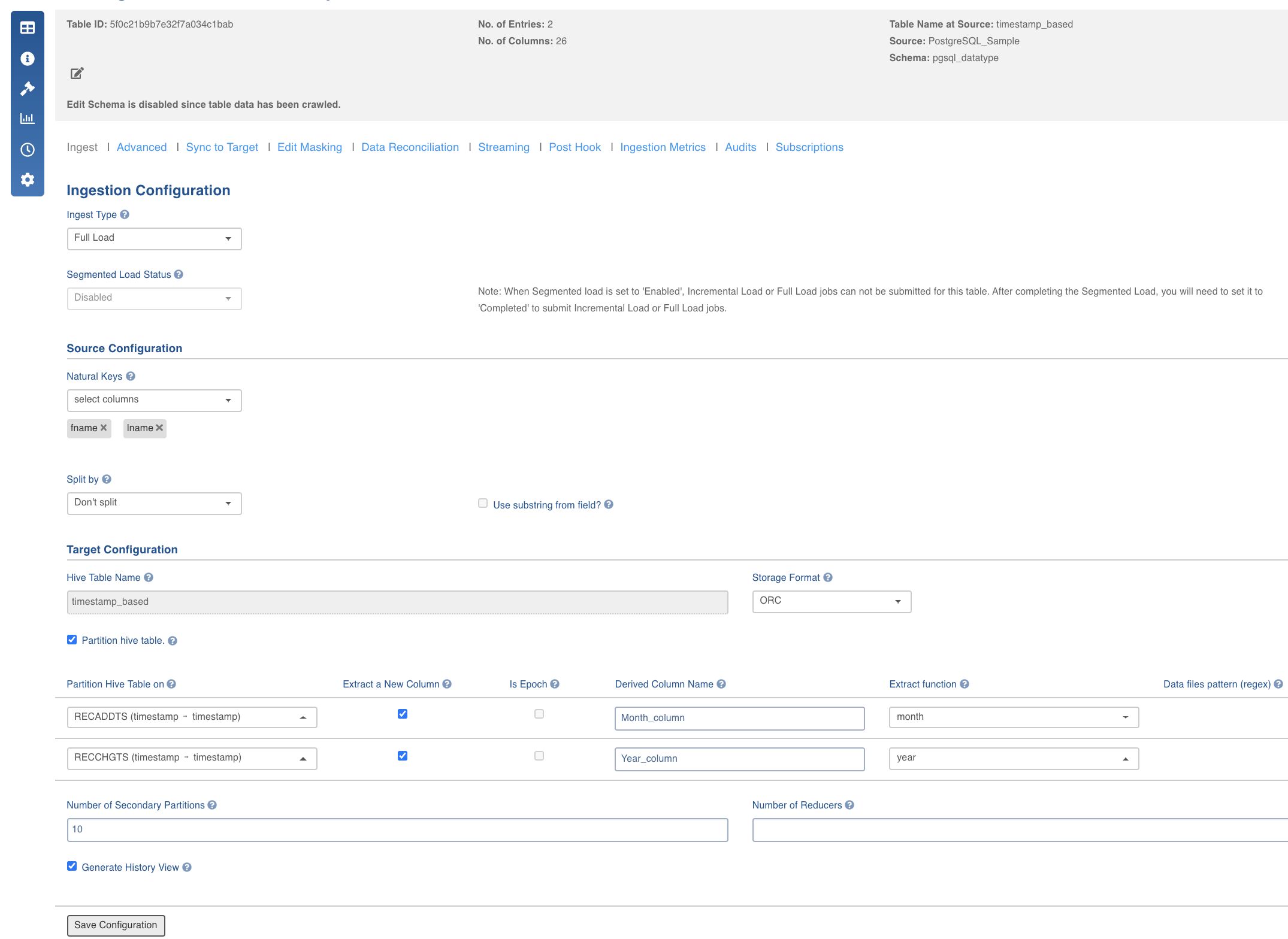
| Ingest Type | The types of synchronization that can be performed on the table. The options include Full Load, Timestamp-Based Incremental Ingestion, Query Based Incremental Ingestion, Batch ID Based Incremental Ingestion. |
| Segmented Load Status | The option to crawl large tables by breaking into smaller chunks. The smaller chunks can be crawled in parallel. Select the column to Perform Segmented Load On. To derive a column, check the Use substring from field option and select the Extract function. After completing the Segmented Load, ensure to set this value to Completed to submit Incremental Load or Full Load jobs. NOTE: In case of date, datetime, timestamp column types you can extract new columns. The possible extraction options are year, month, year-month, month-day and day-num-in-month. |
| Source Configuration | |
| Natural Keys | The key to identify the row uniquely. This key is used to identify and merge incremental data with the existing data on target. Distribution of data into secondary partitions for a table on target will be computed based on the hashcode value of the natural key. This field is mandatory for incremental ingestion tables. NOTE: The value of the natural key column cannot be updated when updating a row on source; all the components of the natural key are immutable. |
| Split by | The option to crawl the table in parallel with multiple connections to the database. Split-by column can be an existing column in the data or derived from an existing column. The numbers, date, datetime and timestamp columns are allowed to be selected as split-by key. In general, any column for which min and max can be computed can be a split-by key. NOTE: Keys which increase or decrease gradually can be used as split-by. To derive a column, check the Use substring from field option and select the Extract function. |
Synchronization Configuration | |
| CDC Start Date | The option to fetch a specific portion of the delta, based on the time window. The start date of the time window. |
| CDC End Date | The option to fetch a specific portion of the delta, based on the time window. The end date of the time window. |
| Enable Schema Synchronization | The option to synchronize the Hive table schema, if the source table is modified after the table ingestion is complete. |
| Timestamp-Based Incremental Load | |
| Timestamp Column for Insert | The source column to be used as insert watermark. |
| Timestamp Column for Update | The source column to be used as update watermark. NOTE: It can also be the source column to be used as insert watermark. |
| Query-Based Incremental Load | |
| Slowly Changing Dimension Type | The type of the query based ingestion. The options include SCD Type 1 and SCD Type 2. SCD Type 1 always overwrites the existing record in case of updates. |
| Configure Insert Query | The option to input the query which identifies and fetches the incremental insert records from the source table, using the record insertion row from the audit table. |
| Join Column for Insert | The column used to identify the inserts. This column will be joined with audit table column. This field uses source datatype. |
| Configure Update Query | The option to input the query which identifies and fetches the incremental update records from the source table, using the record update row from the audit table. |
| Join Column for Update | The column used to identify the updates. This column will be joined with audit table column. |
| External Audit Schema Name | The schema name of the audit table where the timestamps are being stored. |
| External Audit Table Name | The name of the audit table where the timestamps are being stored. |
| External Audit Join Column | The column by which the data table and the audit table will be joined. |
| External Audit Timestamp Column | The timestamp column in the audit table, which maintains record audit. |
| BatchID-Based Incremental Load | |
| Batch-ID Column | This column is used for fetching of delta. This column must be a numeric column. Source datatype and target datatype must be equal. |
| Start Batch Id | The numeric value of Batch ID column (configured by the user during table configurations) starting which the delta is fetched. |
| End Batch Id | Numeric value of Batch ID column (configured by the user during table configurations) till which the delta is fetched. |
| Target Configuration | |
| Hive Table Name | The name of the table in Hive which will be used to access the ingested data. |
| Partition Hive table | The option to partition the data in target. The partition column also can be derived for date, datetime and timestamp column. This will further partition the data. A hierarchy of partitions are supported with both normal partitions and derived partitions. NOTES: Ensure that the partition columns data is immutable.__You can also provide a combination of normal and derived partitions in the hierarchy. |
| Number of Secondary Partitions | The number of secondary partitions to run the MR jobs in parallel. The target data can be distributed among various partitions and each partitions in turn can have various secondary partitions. A table with no primary partition can also have secondary partitions. Secondary partition helps in parallelising the ingestion process. |
| Number of Reducers | The number of reducers for the ingestion map reduce job. Increasing the number of reducers helps reduce the ingestion duration. This will help in processing the MR jobs faster. This will be effective with the combination of partition key and number of secondary partitions. In any data processing using MR jobs, this will help in bringing the parallelism based on the data distribution across a number of primary partitions and secondary partitions on Hadoop. |
| Generate History View | The option to create the history view table (along with the current view table) in Hive, which contains the versions of incremental updates and deletes. |
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential