Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
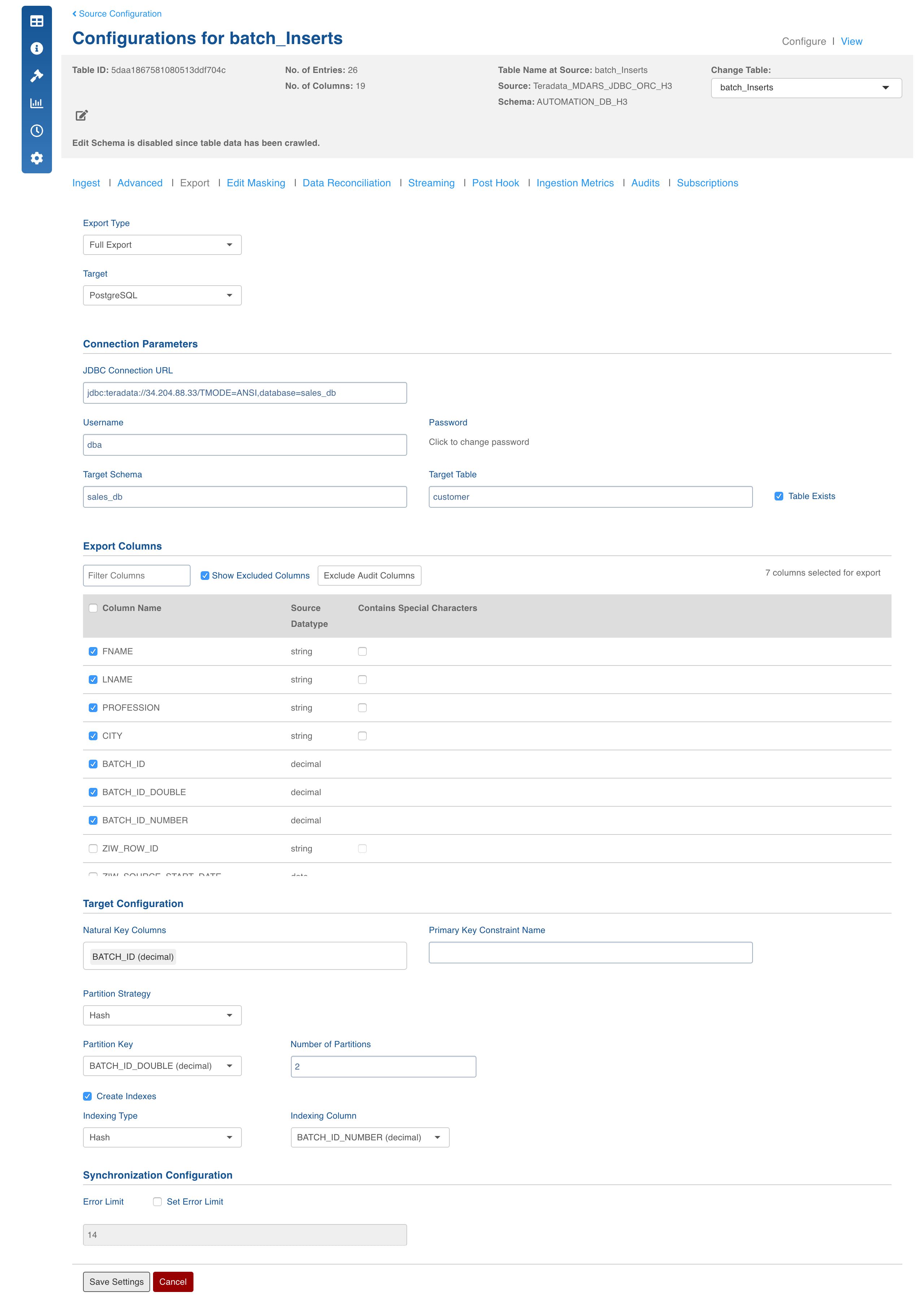
PostgreSQL Export
This feature exports the data from Hive to PostgreSQL database. This feature also allows users to create a new table or use an existing table in PostgreSQL, which can be used as a consumption target for reports and dashboards. PostgreSQL, also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source Relational DataBase Management System (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and technical standards compliance.
Prerequisites
For PostgreSQL export feature to work, a source must be created and data should have been ingested.
Field Description
- Export Type: Select Full Export/Incremental Export into PostgreSQL database.
- Target Database: The database type you want to export to (PostgreSQL).
- JDBC Connection URL: The connection URL needed to connect to the target database.
- Username: Username of the target database.
- Password: Password of the target database.
- Target Schema: The schema in which you want the target table to be created.
- Target Table: Name of the target table.
- Table Exist: Check this option if the table already exists in the PostgreSQL database. If the table does not exist, an error is displayed.
- Natural Key Columns: Natural Key Columns are the columns that help determine a row uniquely. Primary Index and Partition Column must be a part of the Natural Key Columns for export to PostgreSQL.
- Partition Strategy: The options include list and hash.
List partition: For each partition, provide the name and value of partition key. Use the +Add button to add multiple partitions.
Hash partition: Provide the number of partitions required.
- Partition Key: The column used to partition the table. It must be a part of the primary key.
- Create Indexes: Option to create indexes. Provide the Indexing Type and Indexing Column. The indexing types include B Tree and Hash.
- Set Error Limit: If this checkbox is checked, you can specify an error limit.
- Error Limit: The limit on the numbers of rows that go to error table, before the job fails.
NOTE: If the exported table has more columns than the existing table, an error is thrown. If the exported table has lesser columns than the existing table, data will be inserted only in the existing columns and the other column values will be null.
Existing Table Behaviour
If the table already exists in the PostgreSQL database, the system checks if the same table is usable (compatible) for export based on configurations like column names and types, primary indexes, partitions etc:
- If the table is usable for export, the system creates a temp table, exports the data, and transfers the data to the existing table. This also ensures that the actual table can be used by users while export is happening.
- If the table in the PostgreSQL database is not compatible, the system deletes the existing data based on admin configuration variable (that is, if full_export_overwrite_table=true).
- Export Columns: The selections of columns that must be exported to the target database. You must select at least one column. You can use the "Select all" and "Deselect All" buttons to make the selection faster.
NOTE: To perform an incremental export, follow all the steps above, but select Incremental Export in the Export Type drop down.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential