Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
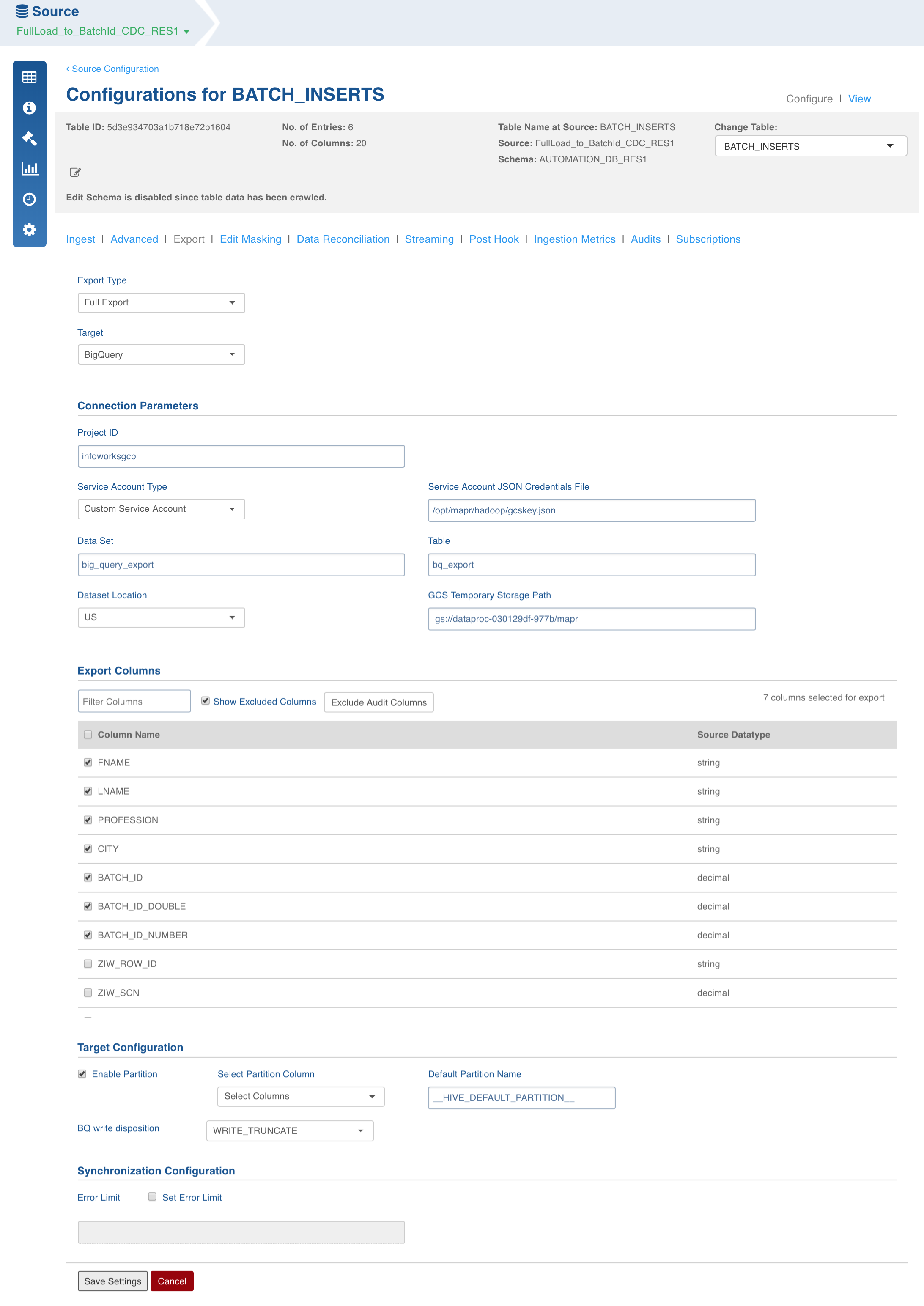
BigQuery Export
Field Description
- Export Type: Select Full Export/Incremental Export.
- Target Database: Select the database type to be exported as BigQuery.
- Project ID: Enter the Google Cloud project in which the BigQuery tables will be exported.
- Service Account Type:
Select Default to use the service account of the Dataproc cluster.
Select Custom to specify a credential JSON file. This displays a text box for entering the file path to Service Account JSON file. Note that this must be available from edge node and cluster nodes.
- Dataset: Enter the BigQuery dataset name.
- Table: Enter the BigQuery table name.
- Dataset Location: Select US or EU. Default is US.
- GCS Temporary Storage Path: Enter the path to Google Cloud Storage folder which is accessible to Infoworks application. This is used as temporary storage during load to BigQuery. Ensure that the service account has read/write access to this storage path.
- Export Columns: Select the columns that must be exported to the target table. At least one column must be selected. The Select All and Deselect All buttons can be used to make the selection faster.
- Target Configuration: Select a Partition column to be used in the BigQuery table. It can have only date or timestamp type. Leave it unchecked in case you do not want partitions in BigQuery.
- Enable Partition: Select this checkbox to specify a partition column.
- BQ Write Disposition: The following two modes are supported for writing in BigQuery:
WRITE_TRUNCATE (Default): Completely truncates the previous BigQuery table entries and writes the Hive table to BigQuery. This mode merges the data by truncating the entire data for the partition and then writing the updated data (old data + updates + inserts) to BigQuery.
WRITE_APPEND: Appends the Hive table entries to BigQuery. This mode appends the new data to the existing data in BigQuery. This approach is faster as the amount of data written is much lesser. This mode works only for append data; the previous data remains the same in the BigQuery tables.
NOTE: WRITE APPEND mode might lead to duplicate entries when appending the same table. This mode works at both partition and table levels.
NOTE: To enable partition for BigQuery target table, the Hive table must be partitioned.
- Select Partition Column: Select the partition column.
- Synchronization Configuration:
- Set Error Limit: Select this checkbox to specify an error limit.
- Error Limit: Enter the limit on the numbers of rows which will be allowed before failing the BigQuery load job.
BigQuery Export Datatypes
The export feature supports the following datatypes in Hive:
- TINYINT
- SMALLINT
- INTEGER
- BIGINT
- TIMESTAMP
- DATE
- STRING
- BOOLEAN
- BINARY
- CHAR
- VARCHAR
- STRUCT
- ARRAY
BigQuery does not support the following datatypes:
- UNION
- MAP
Best Practices
If you use partitioning for incremental load, use a partition column which is a good indicator of incremental changes. For instance, a Sale_Date column for Sales table is a good choice for incremental partition as daily jobs will have only one incremental partition to load to BigQuery.
Permissions for BigQuery Data Load
The permissions required to write to BigQuery as per the documents of google cloud (https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/tables) are as follows:
- To create a table, you must have WRITER access at the dataset level, or you must be assigned a project-level IAM role that includes bigquery.tables.create permissions.
- The following predefined, project-level IAM roles include bigquery.tables.create permissions:
- bigquery.dataEditor
- bigquery.dataOwner
- bigquery.admin
- Also, for temporary storage the storage.objectAdmin role should have access to the location provided in GCS Temporary Storage Path.
NOTE: Binary datatype is currently not supported.
IW Constants and Configurations
- iw_bq_parallelism: The number of partitions to load in parallel. Default value is 10.
- bq_staging_cleanup: Indicates whether the temporary storage must be cleaned after the job is successful. Default value is true.
- bq_view_create: Indicates whether a view should be created in BigQuery for the partitioned tables loaded using partition column provided as alias to _PARTITIONTIME. Default value is false.
- bq_hive_aux_jars: The path to hcatalog and GCS connector jars. This can be set at global or table (preferable) level. Default value is /usr/lib/hive-hcatalog/share/hcatalog/hive-hcatalog-core.jar,/usr/lib/hadoop/lib/gcs-connector-latest-hadoop2.jar.
- bq_hive_conf_vars: The configuration to set the Hive properties during BigQuery export. This can be set at global or table (preferable) level. For example, hive.tez.container.size = 4196,hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict.
BigQuery Datatype Mapping
BigQuery export supports limited datatype mapping. For example, mapping within numeric family - decimal, integer, long to numeric; timestamp to datetime.
The column types can be remapped using the following configuration at table-level or pipeline-level:
bq_col_overrides: The configuration to remap the column type.
- Value:
<ColumnName1>:-:FLOAT,<ColumnName2>:-:FLOAT - Example: eid:-:FLOAT,sales:-:FLOAT
- Separator: :-:
The BigQuery NUMERIC datatype is slightly different than Hive DECIMAL in the precision and scale ranges. BigQuery precision can range from 0-38 and scale from 0-9 compared to Hive (38,38). Also, the precision-scale difference should not be more than 29. So, an integer of maximum length 29 is supported. After this limit, you can remap the columns to Float.
Remapping can be done within same numeric family. For example, mapping Decimal to Integer.
BigQuery ColumnName Override
The column names can be overridden during export using the following configuration:
bq_col_name_override: The configuration to rename the column name.
- Value:
<SourceColumnName1>:-:<TargetColumnName1>,<SourceColumnName2>:-:<TargetColumnName2> - Example: eid_source:-:eid_target,sales_source:-:sales_target
- Separator: :-:
For details on BigQuery export from MapR and HDP, see BigQuery Export from MapR and BigQuery Export from HDP respectively.
Big Query Export Scenarios
NOTE: With PARTITIONING, tables start working at partition level instead of the whole table.
| SYNC_TYPE | BQ_WRITE_DISPOSITION | Behaviour Without PARTITIONING | With PARTITIONING |
|---|---|---|---|
| FULL LOAD | WRITE_TRUNCATE | BigQuery table will be overwritten by the current data in Hive table. After export, the BigQuery table will be in synch with the exported table. | Partitions being exported will be overwritten by data in the corresponding Hive partitions. |
| INCREMENTAL | WRITE_TRUNCATE | Same behaviour as full load without partitioning (recommended to be used with partitioning). | Data from changed partitions (inserts/updates) in Hive table will overwrite the corresponding BigQuery partitions. |
| FULL LOAD | WRITE_APPEND | Data in current Hive table will be appended to the BigQuery table. Duplication might occur if the same data is exported again. | Data from Hive partitions will get appended to corresponding BigQuery partitions. |
| INCREMENTAL | WRITE_APPEND | Same behaviour as full load without partitioning (recommended to be used with partitioning). | Only the changed partitions will have their data appended in BigQuery tables. |
NOTE: If the table to be exported is empty, no changes occur to the BigQuery tables.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential