Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Query-Based Incremental Ingestion
Query Based Ingestion is supported for MySQL, Oracle, Teradata, SQL Server, SAP HANA, Netezza, Sybase, Apache Ignite, MariaDB, Vertica, Redshift and DB2 databases.
Prerequisites
Query-Based incremental ingestion expects the record audit information (insert and update timestamps) will be available in a separator audit table. The audit table can be in the same schema as the table or in a new schema.
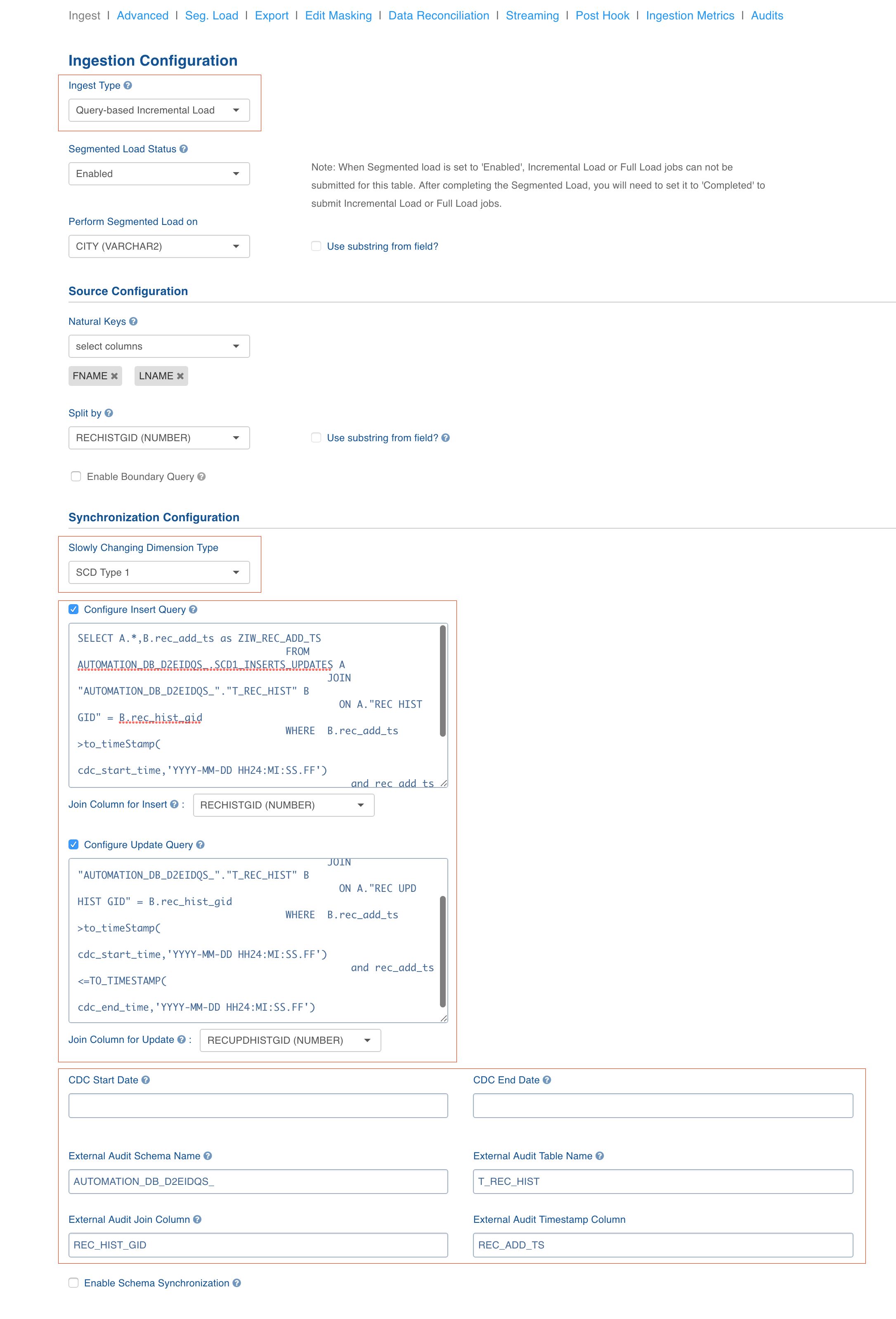
Query-Based SCD1 Incremental Ingestion
Tables ingested using this method will be loaded fully in the first ingestion. Subsequent ingestions will be incremental data ingestion. Delta will be fetched and merged with the data that already exists on the target(hive) target. This type of Ingestion should be used in the cases where there is an external audit table which contains the timestamp determining when the particular record in the main table was inserted / modified.
In case of SCD1, the updates always overwrite the data.
Sample Insert Query
In case of the query below, the table to be crawled is SCD1_INSERTS_UPDATES and the table with the audit data is T_REC_HIST, with both of them being joined on REC_HIST_GID. The insert timestamp is REC_ADD_TS, that is part of the T_REC_HIST table.
SELECT A.*, B.rec_add_ts as ZIW_REC_ADD_TSFROMAUTOMATION_DB.SCD1_INSERTS_UPDATES AJOIN AUTOMATION_DB.T_REC_HIST BON A.REC_HIST_GID = B.REC_HIST_GIDWHEREB.REC_ADD_TS >= TO_TIMESTAMP(CDC_START_TIME, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF')AND B.REC_ADD_TS <= TO_TIMESTAMP(CDC_END_TIME, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF')Sample Update Query
In case of the query below, the table to be crawled is SCD1_INSERTS_UPDATES and the table with the audit data is T_REC_HIST, with both of them being joined on REC_HIST_GID. The insert timestamp is REC_MOD_TS, that is part of the T_REC_HIST table.
SELECT A.* , B.REC_ADD_TS AS ZIW_REC_ADD_TSFROMAUTOMATION_DB.SCD1_INSERTS_UPDATES AJOIN AUTOMATION_DB.R_REC_HIST BON A.REC_UPD_HIST_GID = B.REC_HIST_GIDWHEREB.REC_ADD_TS >= TO_TIMESTAMP(CDC_START_TIME, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF')AND REC_ADD_TS <= TO_TIMESTAMP(CDC_END_TIME, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF')In the queries,
- timestamp is aliased as ZIW_REC_ADD_TS. If this field is not aliased, incremental ingestion will fail.
- CDC_START_TIME and CDC_END_TIME are admin configurations used as placeholders for high watermark values.
If only insert queries are used, use the comparison operator > on timestamp instead of >= and turn incremental append mode ON. This enables the merge run faster.
NOTE: Schema synchronization in query-based CDC is enabled for all databases (Oracle, SQLServer, SAP Hana, Netezza, DB2, Teradata, Sybase, MySQL, MariaDB, Apache Ignite, Vertica, Redshift) for column additions.
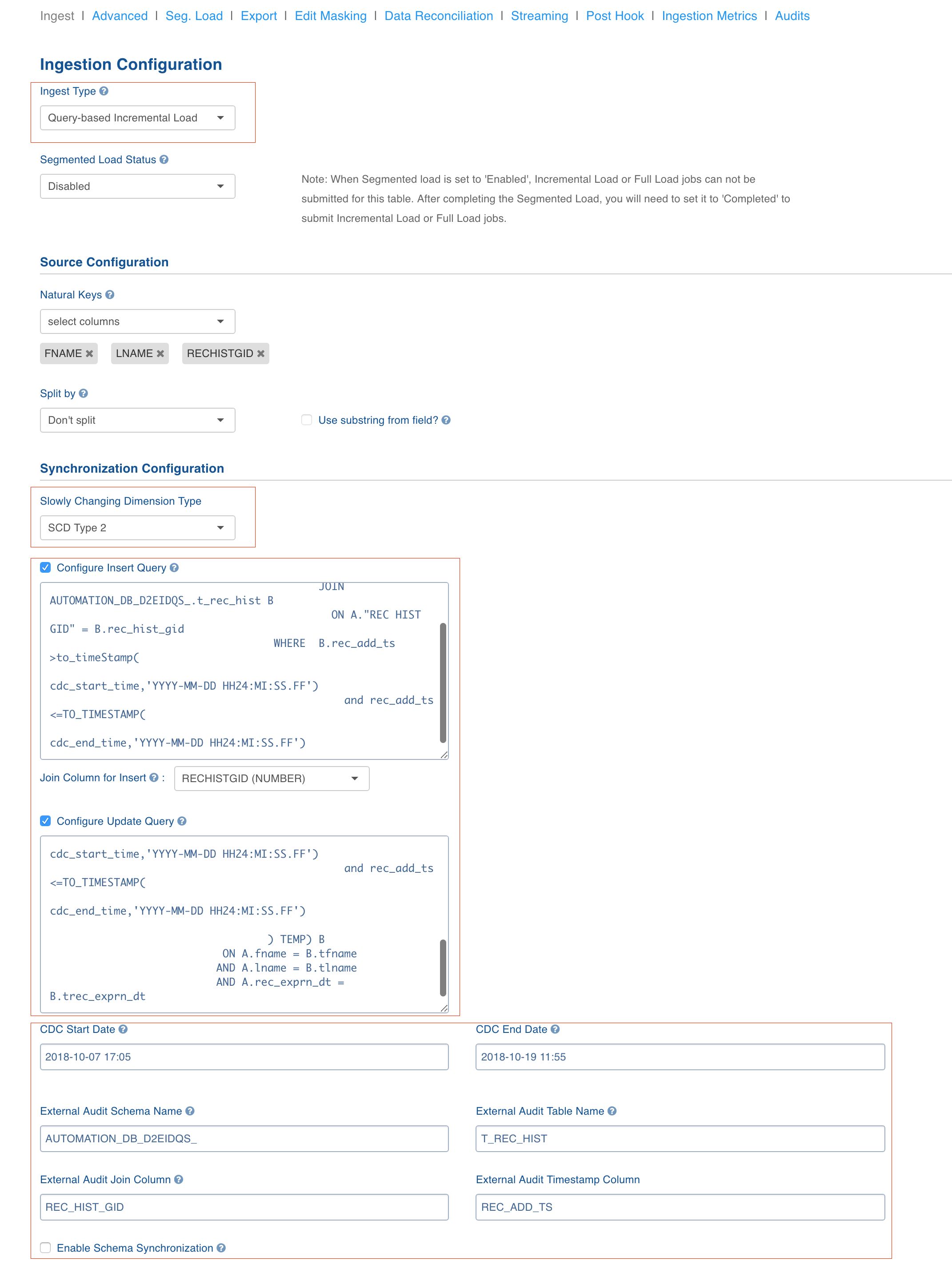
Query-Based SCD2 Incremental Ingestion
Tables loaded using this method will be loaded fully in the first ingestion. Subsequent ingestions will be incremental data ingestion. Delta will be fetched and merged with the data that already exists on target. Fetching of delta uses the insert and update queries.This type of Ingestion should be used in the cases where there is an external audit table which contains the timestamp determining when the particular record in the main table was inserted / modified and the source table maintains the data as SCD2.
In case of SCD2, the new records are added in addition to the new record and the "ziw_is_active" audit column is made false for the previous record.
NOTE: Query-based CDC supports sliding window-based CDC feature where any manual updates on the table are captured by moving the CDC start date and CDC end dates using the UI (CDC start offset and CDC end offset).
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential