Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Incremental Ingestion
Following are the methods to perform incremental ingestion:
- Timestamp-Based Incremental Ingestion*
- Query Based SCD1 Incremental Ingestion*
- Query Based SCD2 Incremental Ingestion*
- Batch ID Based Incremental Ingestion*
- Log-Based Incremental Ingestion**
*****MySQL, Oracle, Teradata, SQL Server, SAP HANA, Netezza, Sybase, Apache Ignite, MariaDB, Vertica, Redshift and DB2 Query Based Ingestion are supported.
** Sybase IQ, Oracle, DB2, and SQL Server Log based Ingestion are supported.
WARNING: Switching the incremental ingestion from Append to Merge mode might result in some missing records that were previously ingested. It is therefore, strongly recommended that users perform Initialize and Ingest and perform a full load immediately after switching the modes.
Timestamp-Based Incremental Ingestion
Tables ingested using this method will be loaded fully in the first ingestion. Subsequent ingestions will be through incremental data ingestion. Delta will be fetched and merged with the data that already exists on the target. Fetching of delta uses the timestamp columns (for inserts and updates, configured by the user during table configurations). These columns are expected to be in the same table.
Following are the steps to perform timestamp-based incremental ingestion:
- Click the Configure button for the required table.
- Select the Ingest Type as Timestamp-Based Incremental Load. For descriptions of fields, see the *Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions *section.
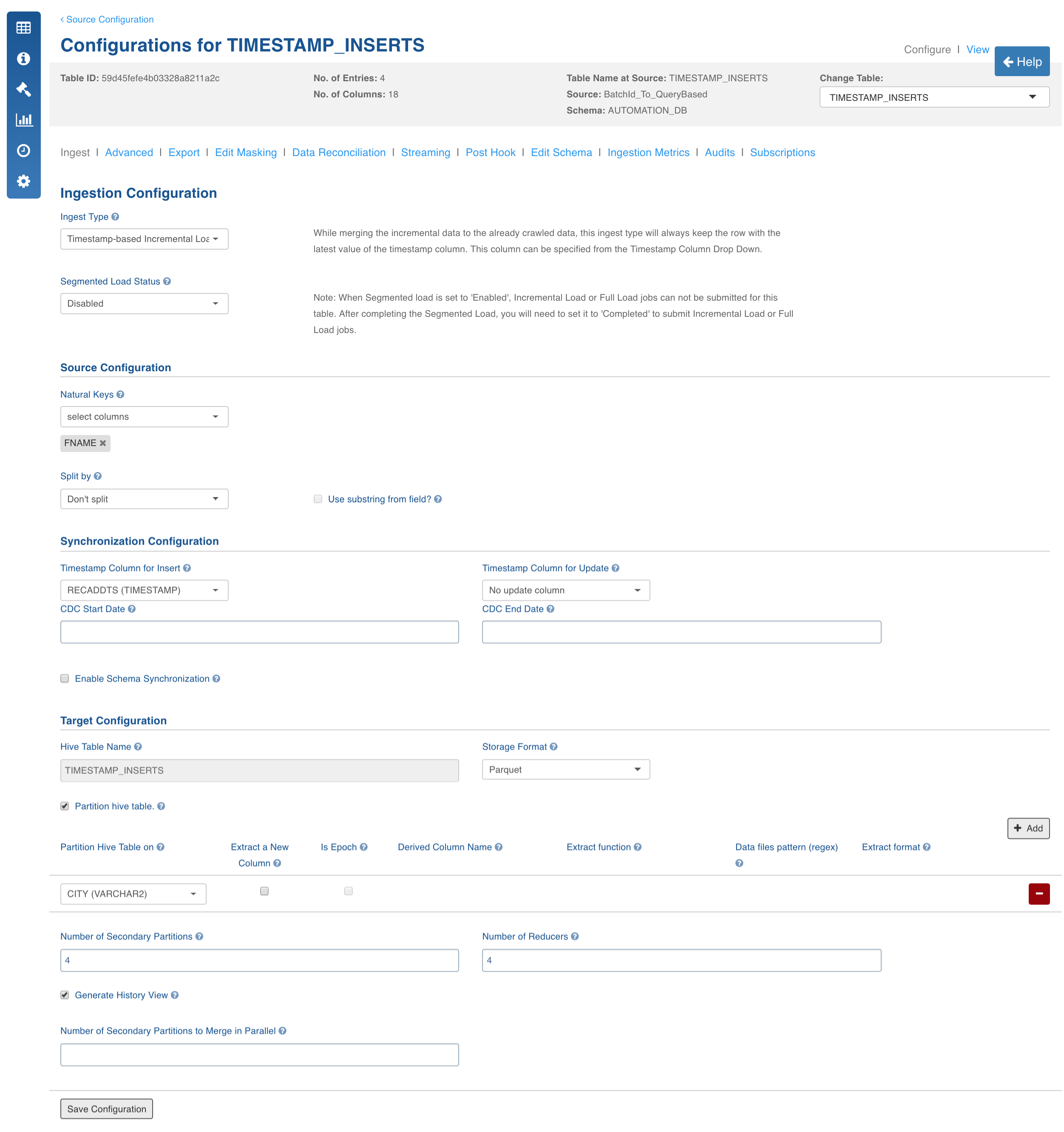
Configuration to Set Comparator to Fetch CDC Records
The USE_GTE_FOR_CDC configuration allows you to fetch the CDC records based on the use case.
- true: the CDC records will be fetched using the >= comparator. This is the default behaviour and this should be used for merge use cases to make sure that the data from the last batch is brought again. This is done for the scenarios where some data for the last batch and timestamp was still being populated in the source system when the ingestion job finished.
- false: the CDC records will be fetched using the > comparator. This behaviour should be used for append mode scenarios, where the data for the last batch or timestamp in the source system is fully populated and the user does not want the old data again.
This configuration is applicable for Timestamp and BatchID sync type tables.
NOTE: Data might be lost when the > comparator is used. If records with same batch ID are being inserted in the source system when the ingestion job is running, all the records that are inserted just after the job is run and with same batch ID will be missed in next CDC job.
Query-Based SCD1 Incremental Ingestion
Tables ingested using this method will be loaded fully in the first ingestion. Subsequent ingestions will be incremental data ingestion. Delta will be fetched and merged with the data that already exists on the target. Fetching of delta uses the insert and update queries.
This is same as timestamp based incremental ingestion, however, the record audit information (insert and update timestamps) will be available in an audit table. The audit table can be in the same schema as the table or in a new schema. In case of SCD1, the updates always overwrite the data.
NOTE: Schema synchronization in query-based CDC is enabled for all databases (Oracle, SQLServer, SAP Hana, Netezza, DB2, Teradata, Sybase, MySQL, MariaDB, Apache Ignite, Vertica, Redshift) for column additions.
Following are the steps to perform Query-Based SCD1 incremental ingestion:
- Click the Configure button for the required table
- Select the Ingest Type to Query-Based Incremental Load.
- In the Synchronization Configuration section, select the Slowly Changing Dimension Type as SCD Type1. *For descriptions of fields, see the *Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions.
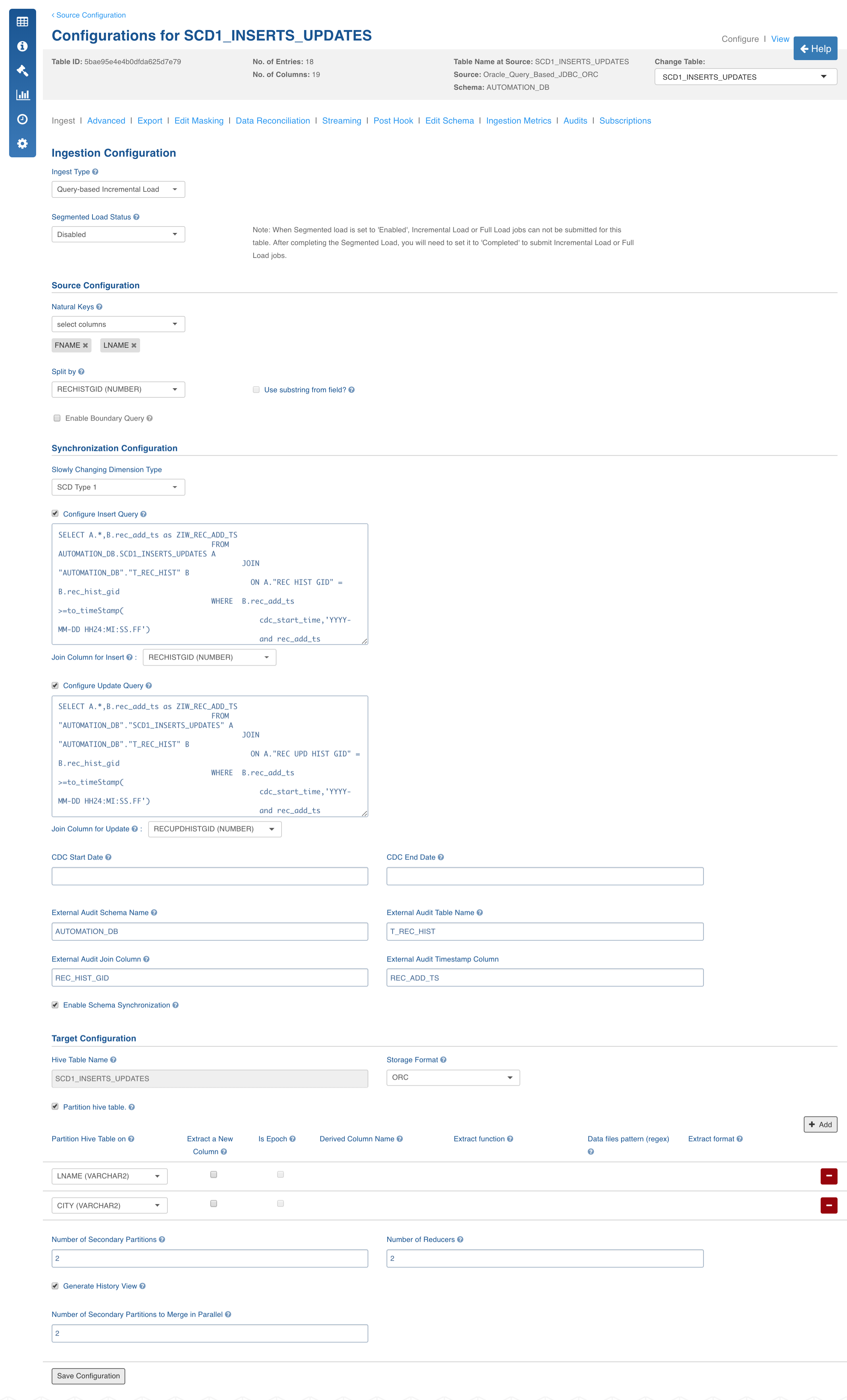
Query-Based SCD2 Incremental Ingestion
Tables loaded using this method will be loaded fully in the first ingestion. Subsequent ingestions will be incremental data ingestion. Delta will be fetched and merged with the data that already exists on target. Fetching of delta uses the insert and update queries. This is same as timestamp-based incremental ingestion, however, the record audit information (insert and update timestamps) will be available in an audit table. The audit table can be in the schema same as the table or in a new schema. In case of SCD2, the update will expire the old record and insert the new record.
NOTE: Query-based CDC supports sliding window-based CDC feature where any manual updates on the table are captured by moving the CDC start date and CDC end dates using the UI (CDC start offset and CDC end offset).
Following are the steps to perform Query-Based SCD2 incremental ingestion:
- Click the Configure button for the required table.
- Select the Ingest Type to Query-Based Incremental Load.
- In the Synchronization Configuration section, select the Slowly Changing Dimension Type as SCD Type2. For descriptions of fields, see the Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions section.
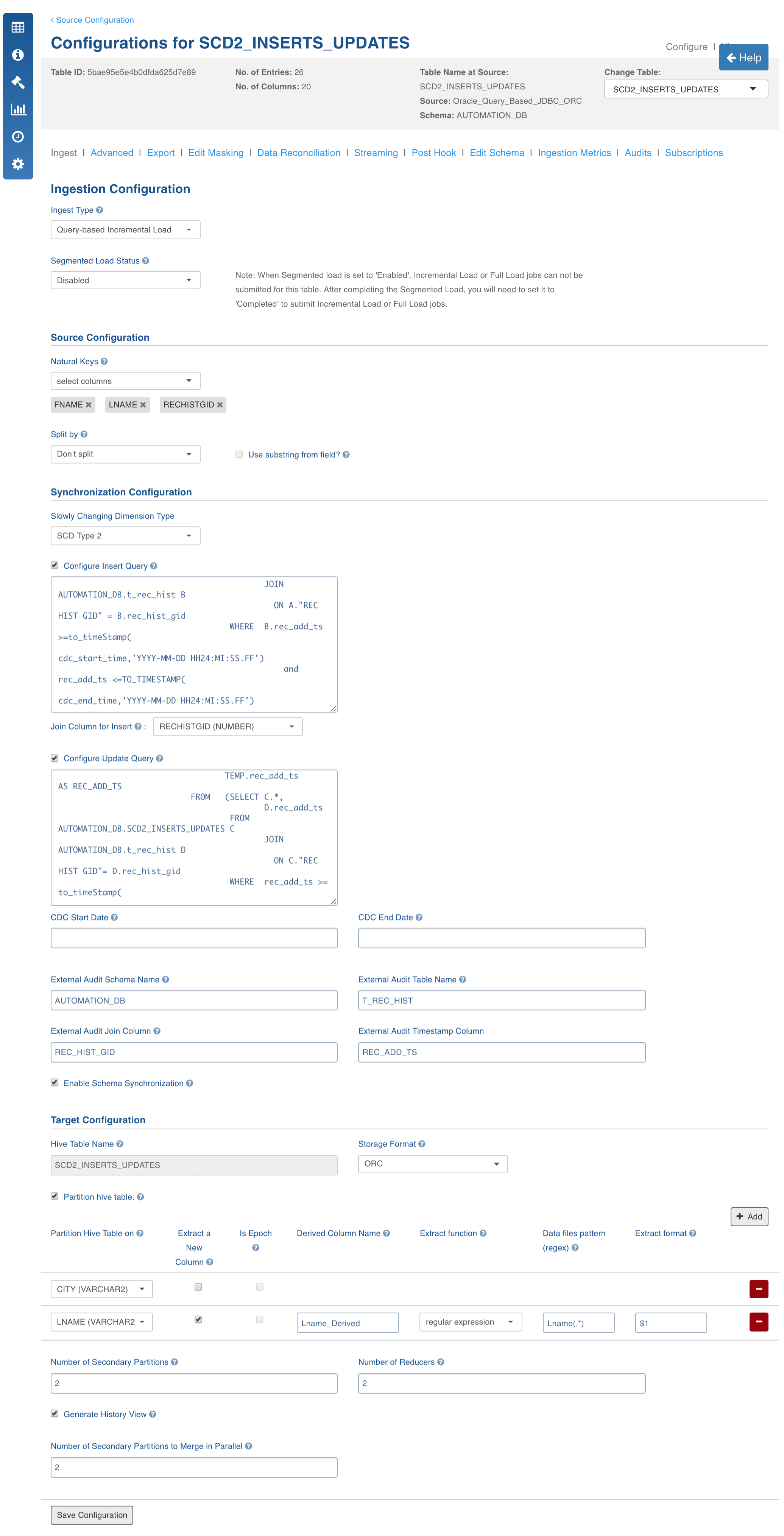
Batch ID Based Incremental Ingestion
Tables ingested using this method will be loaded fully in the first ingestion. Subsequent ingestions will be incremental data ingestion. Delta will be fetched and merged with the data that already exists on target. Fetching of delta uses a numeric value called Batch ID column (for inserts and updates configured by the user during table configuration). These columns are expected to be in the same table.
NOTE: Sliding window-based adhoc incremental loads are not supported in case of Batch ID based CDC.
Following are the steps to perform BatchID-Based incremental ingestion:
- Click the Configure button for the required table.
- Select the Ingest Type to Batch-ID-based Incremental Load. For descriptions of fields, see the Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions section.
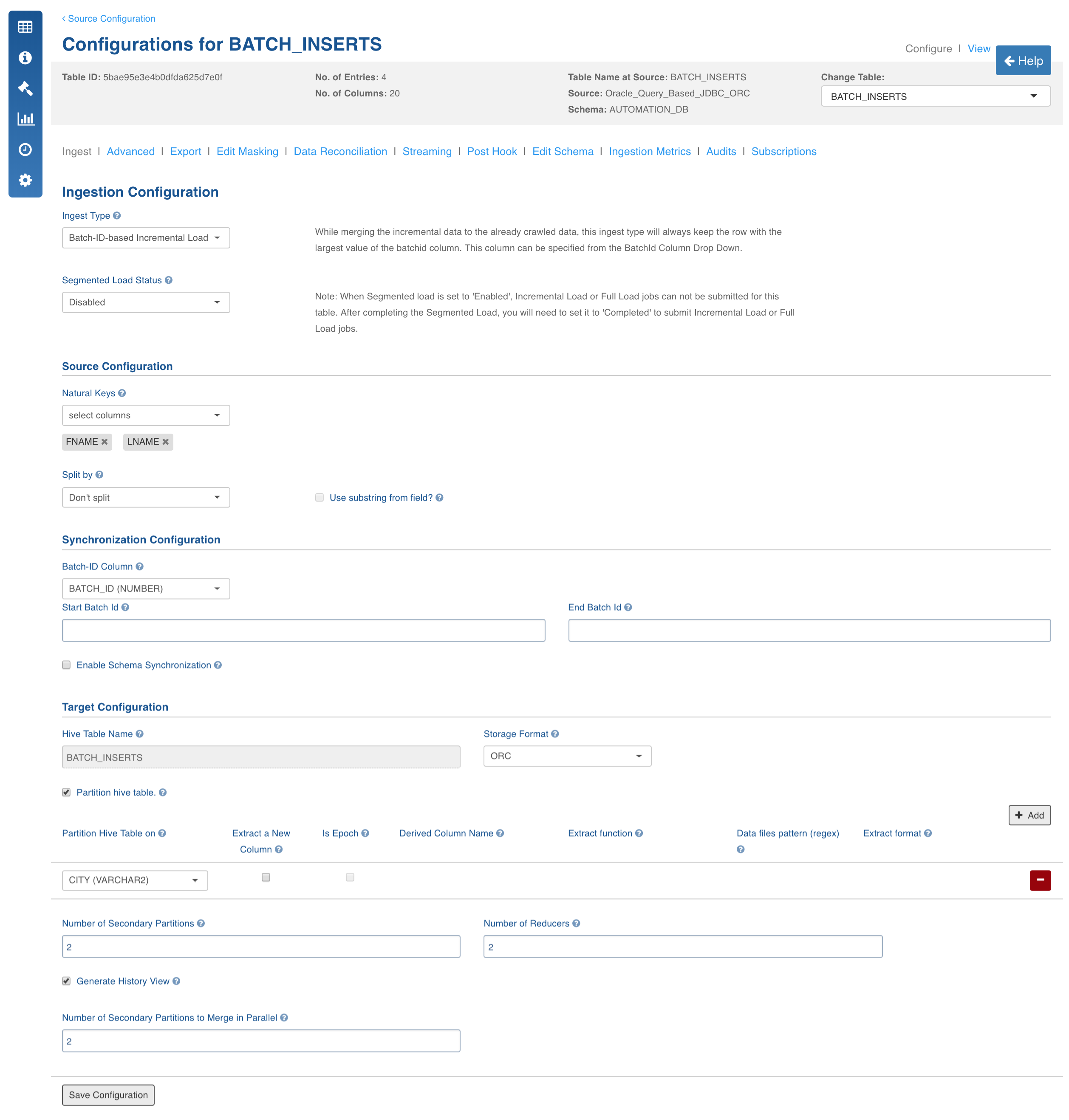
Configuration to Set Comparator to Fetch CDC Records
The USE_GTE_FOR_CDC configuration allows you to fetch the CDC records based on the use case.
- true: the CDC records will be fetched using the >= comparator. This is the default behaviour and this should be used for merge use cases to make sure that the data from the last batch is brought again. This is done for the scenarios where some data for the last batch and timestamp was still being populated in the source system when the ingestion job finished.
- false: the CDC records will be fetched using the > comparator. This behaviour should be used for append mode scenarios, where the data for the last batch or timestamp in the source system is fully populated and the user does not want the old data again.
This configuration is applicable for Timestamp and BatchID sync type tables.
NOTE: Data might be lost when the > comparator is used. If records with same batch ID are being inserted in the source system when the ingestion job is running, all the records that are inserted just after the job is run and with same batch ID will be missed in next CDC job.
Log-Based Incremental Ingestion
Log-based incremental ingestion does not add any load on source databases. The incremental data is read from the log statements (DMLs) stored in database log files (archival log in Oracle). Tables in the log-based incremental ingestion require natural keys to be configured like query-based CDC. As incremental data is read from logs, deletion of records is handled from source tables. Infoworks supports Oracle, MSSQL, Sybase IQ and DB2 log-based CDC.
NOTE: Oracle log-based CDC supports schema synchronization (only addition of columns). There is no sliding window-based CDC in case of log-based incremental ingestion, because any manual updates or inserts will be added to the database logs in the next CDC. Hence, moving CDC start times is not required. However, an adjustable CDC end time can be set using CDC end date so that you can restrict till when the logs must be read.
Following are the steps to perform Log-Based incremental ingestion:
- Click the Configure button for the required table.
- Select the Ingest Type to Log-based Incremental Load.
For descriptions of fields, see the Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions section.
The following sections provide details for setting up logs in Oracle, MSSQL, DB2, and Sybase IQ.
Oracle Log-Based Incremental Ingestion
In Oracle log-based incremental ingestion, the data is ingested into the Hive and continuously synchronized with the database using Oracle archival logging provided by Oracle. In this method, archival logging must be enabled for the incremental tables.
NOTE: If data contains blob and clob columns and sync type chosen is log-based, these columns will be ignored during ingestion (both full load and CDC). If sync type is changed to query-based or timestamp-based, any data ingested after that change will still have the blob and clob values.
Following are the methods to perform Oracle log-based incremental ingestion:
- Reading archive logs directly from LogMiner
- Using temporary table to store and read archive logs
- Using staging database server with temporary table to read archive logs.
1. Reading Archive Logs Directly from LogMiner
In this method, Infoworks starts the LogMiner and starts reading data directly from the view created by LogMiner. Every session from Infoworks requires its own instance of LogMiner. Infoworks Oracle CDC with LogMiner uses Oracle LogMiner to read Change Data from Oracle-archived redo logs. Infoworks then makes the data available to CDC sessions for propagation to targets.
To implement Oracle CDC with LogMiner, you must perform configuration tasks in Oracle and Infoworks. In Oracle, ensure that ARCHIVELOG mode and global minimal supplemental logging are enabled so that Change Data can be retrieved from archived redo logs. Also, ensure that a copy of the Oracle online catalog exists in the archived log destination. Infoworks requires a copy of the catalog to determine restart points for Change Data extraction processing.
WARNING: If you use real-time extraction mode, Infoworks CDC starts a separate Oracle LogMiner session for each extraction session. Running multiple, concurrent sessions can significantly degrade performance of the system where the LogMiner runs.
Source Configurations
- USE_TEMP_TABLE_FOR_LOG_BASED_CDC: Mandatory, default value is true, setting it to false will fallow this approach.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Optional, default value is false, setting it to true tries to build a dictionary before every CDC.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Optional, default value is false, it uses offline dictionary. Setting the value to true uses redo log dictionary to read archive logs with DDL tracking. The value must be set to true in case of schema synchronization.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_NAME: Optional, default value is dictionary.ora, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_PATH: Mandatory, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_PATH: Mandatory, absolute path to directory where archive logs are stored.
- LOG_FILE_SEQUENCE_COLUMN_NAME: In case of Oracle RAC setup, this configuration must be set at source level as RECID.
- LOG_BASED_CDC_SCHEMAS: source level configuration, comma-separated schema names of tables in the dummy source.
- TABLE_SCHEMA: schema of the particular table at the table level For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
Limitations
- This ingestion requires more resources since every session requires its own instance of LogMiner.
- Derived split by and derived partition are not supported.
- BFILE, BLOB, CLOB, and XML are not supported.
2. Using Temporary Table to Store and Read Archive Logs
In this method, Infoworks starts the LogMiner instance and copies log data to a temporary table either in the same schema or any other schema to which the Infoworks user has access. This removes dependency of each session having its own LogMiner instance to read logs.
Source Configurations
- USE_TEMP_TABLE_FOR_LOG_BASED_CDC: Optional, default value is true. Setting this value to false falls back to previous approach.
- TEMP_DATABASE_NAME: Optional, default value is empty, where temporary table will be created in the same schema from which logs are being read.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Optional, default value is false. Setting this value to true tries to build dictionary before every CDC.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Optional, default value is false, it uses offline dictionary. If you set it to true, it uses redo log dictionary to read archive logs with DDL tracking. The value must be set to true in case of schema synchronization.
- NOTE**: *Schema synchronization is applicable only to addition of columns.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_NAME: Optional, default is dictionary.ora, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_PATH: Mandatory, used only in case of offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_PATH: Mandatory, Absolute path to directory where archive logs are stored).
- USE_UDF_FOR_WIDE_TABLE_CONCAT: Default value is False, uses Infoworks provided custom UDA for concatenation of wide tables instead of xmlagg method. You must create UDA in the Infoworks temp schema manually.
- NUMBER_OF_LOG_FILES_TO_LOAD: Default value is -1which represents all log files. This configuration allows you to restrict the number of log files to load in each run of CDC.
- PERSIST_LOG_BASED_TEMP_TABLE: Default value is False, setting the value to truedoes not clean up the temp table created by Infoworks at the end of the job for debug purposes.
- LOG_BASED_CDC_SCHEMAS: source level configuration, comma-separated schema names of tables in the dummy source.
- TABLE_SCHEMA: schema of the particular table at the table level For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
- LOG_FILE_SEQUENCE_COLUMN_NAME: In case of Oracle RAC setup, this configuration must be set at source level as RECID.
USE_ONLINE_CATALOG_AS_DICTIONARY: Setting this value to trueuses the dictionary from Oracle online catalogue. This does not support Schema synchronization.
To improve the performance of temp table creation, you can specify temp table creation parallelism, the default value is 1. If more than one archive log file is available, the files will be split across multiple threads to start LogMiner in parallel. This method works only with Online Catalog as a dictionary or with an offline dictionary. Both the dictionary options do not support schema synchronization. In case of schema changes you must switch back to redo log dictionary option with parallelism as 1. To use this optimization, set the following configurations at the source level:
- PARALLEL_LOGMINER_SESSIONS: The number of open sessions to Oracle to start LogMiner in parallel.
- USE_ONLINE_CATALOG_AS_DICTIONARY: Set this value to true.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Set this value to false.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Set this value to false.
Limitations
- Derived Split by and derived partition are not supported.
- BFILE, BLOB, CLOB, and XML are not supported.
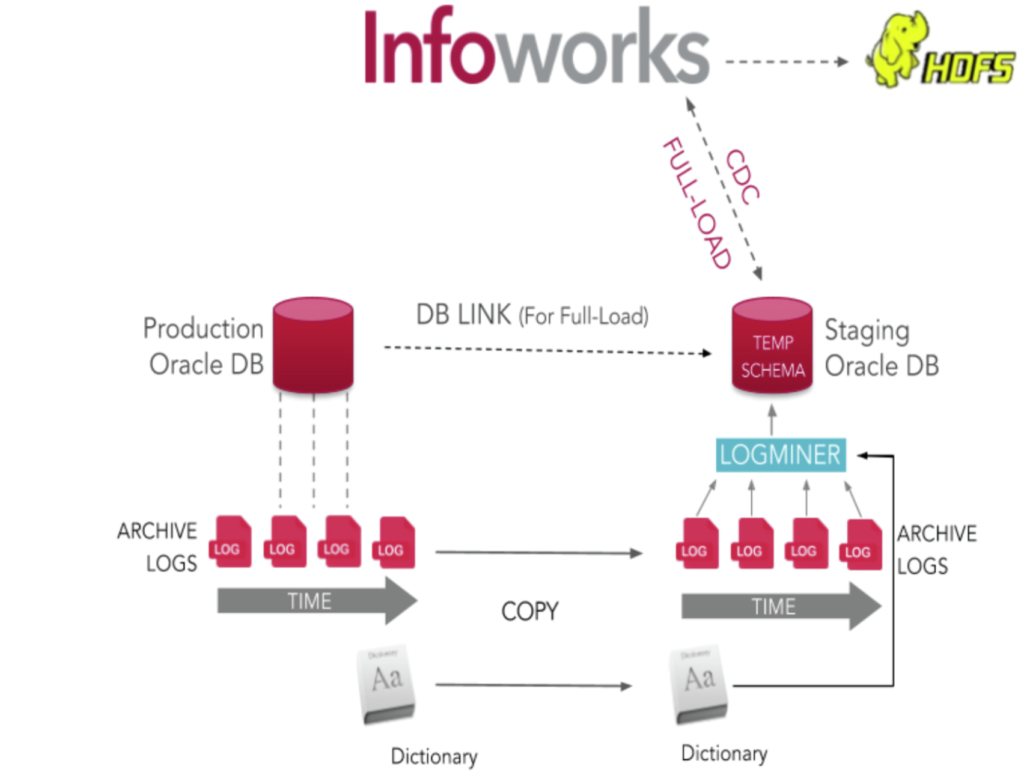
3. Using Staging Database Server with Temporary Table to Read Archive Logs
This method is similar to the previous method. However, instead of using production database to read archive logs, Infoworks uses staging database server to read archive logs, thus ensuring minimal load on the production database.
Archive Logs Using Staging Database Server
Source Configurations
- USE_TEMP_TABLE_FOR_LOG_BASED_CDC: Mandatory, must be set to true.
- TEMP_DATABASE_NAME: Optional, default value is empty, where temporary table will be created in the same schema from which logs are being read.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Mandatory, should be set to false. Since Infoworks reads logs from staging database, it cannot build dictionary on the source system.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Mandatory, should be set to false. This approach only works with offline dictionary.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_NAME: Optional, default will be dictionary.ora.
- ORACLE_LOGMINER_DICTIONARY_FILE_PATH: Mandatory, absolute path to directory where dictionary file is stored.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_INFO_OBJECT_NAME: Mandatory, object name on staging database which is a DBlink to view v_$archived_log on production server.
- IS_STAGING_ORACLE_SERVER: Mandatory, must be set to true. Default is false.
- ORACLE_ARCHIVE_LOG_PATH: Mandatory, absolute path to directory where archive logs are stored.
- SFTP_HOST: Mandatory, IP of the staging database server.
- SFTP_PORT: Optional, Default is 22.
- SFTP_USER_NAME: Mandatory, SFTP username to login to staging database.
- SFTP_ENCRYPTED_USER_PASSWORD: Optional, required only if password is needed to login to staging database server.
- USE_UDF_FOR_WIDE_TABLE_CONCAT: Uses Infoworks provided custom UDA for concatenation of wide tables instead of xmlagg method. You must create UDA in the Infoworks temp schema manually.
- NUMBER_OF_LOG_FILES_TO_LOAD: Default value is -1 which represents all log files. This configuration allows you to restrict the number of log files to load in each run of CDC.
- PERSIST_LOG_BASED_TEMP_TABLE: Default value is False, setting the value to true does not clean up the temp table created by Infoworks at the end of the job for debug purpose.
- LOG_BASED_CDC_SCHEMAS: source level configuration, comma-separated schema names of tables in the dummy source.
- TABLE_SCHEMA: schema of the particular table at the table level For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
- LOG_FILE_SEQUENCE_COLUMN_NAME: In case of Oracle RAC setup, this configuration must be set at source level as RECID.
To improve the performance of temp table creation, you can specify temp table creation parallelism default value is 1, if there are more than one archive log files, they will be split across multiple threads to start LogMiner in parallel.
This method works only with offline dictionary since the LogMiner is run in a different database. This dictionary option does not support schema synchronization. In case of schema changes, you must switch back to redo log dictionary option with parallelism as 1.
To use this optimization, set the following configurations at the source level:
- PARALLEL_LOGMINER_SESSIONS: The number of open sessions to Oracle to start LogMiner in parallel.
- USE_ONLINE_CATALOG_AS_DICTIONARY: Set this value to false.
- BUILD_DICTIONARY_BEFOR_CDC: Set this value to false.
- USE_REDO_LOG_DICTIONARY: Set this value to false.
Limitations
- Derived split by and derived partition are not supported.
- BFILE, BLOB, CLOB, and XML are not supported.
- Schema synchronization is not supported.
Planning Oracle CDC with LogMiner
Before you configure Oracle CDC with LogMiner change data capture, review the following requirements and performance considerations:
- Verify that a valid Oracle environment exists for the Infoworks user.
- The Oracle source instance must be running in ARCHIVELOG mode, and Oracle global minimal supplemental logging must be enabled.
- A copy of the Oracle catalog must exist in the Oracle archived logs.
- Oracle LogMiner continuous mining reads archived redo logs only from the directory to which they were originally written.
- If Infoworks is not installed on the same machine as the Oracle instance, configure a TNS entry on the client machine with SERVER=DEDICATED in the CONNECT_DATA section of the connect descriptor. This specification is also required if the network is configured for Multi-Threaded Server (MTS) mode.
- Infoworks requires the Oracle Client binaries. When you install Oracle, the Client binaries are installed by default. To use SQL*Net connectivity on a machine that does not have an installed Oracle instance, you must install the Oracle Client.
- If you use Oracle materialized views, Infoworks can capture change data from the master tables that underlie those views. Infoworks supports change capture for any type of materialized view. The view and its underlying table have a one-to-one correspondence and share the same name.
- Infoworks uses Oracle LogMiner to read change data from archived logs. If you use an archived log destination other than the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 path and LogMiner processing lags behind, problems might occur. In this situation, LogMiner starts reading change data from the archived logs in the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 directory. If these archived logs are inaccessible from the machine with the Oracle instance to which you are connected, the LogMiner session might fail.
Oracle Datatypes Supported for CDC
Infoworks uses Oracle LogMiner to retrieve changes from the Oracle redo logs. Since Oracle does not log data or does not completely log data with some datatypes in the redo logs, Infoworks Oracle CDC with LogMiner cannot retrieve change data for all Oracle datatypes.
Following table indicates the Oracle datatypes supported by Infoworks Oracle CDC with LogMiner:
| Oracle Datatypes | Supported | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| BFILE | N | Data for columns that have this datatype are not completely logged in the Oracle redo logs and cannot be captured. |
| BINARY_DOUBLE | Y | - |
| BINARY_FLOAT | Y | - |
| CHAR | Y | - |
| DATE | Y | - |
| FLOAT | Y | - |
| LOBs | N | - |
| LONG | N | Columns of this datatype cannot be included in capture registrations. |
| LONG RAW | N | Columns of this datatype cannot be included in capture registrations. |
| NCHAR | Y | - |
| NUMBER | Y | PowerExchange handles NUMBER columns as follows: Numbers with a scale of 0 and a precision value less than 10 are treated as INTEGER. Numbers with a defined precision and scale are treated as NUMCHAR. Numbers with an undefined precision and scale are treated as DOUBLE. |
| NVARCHAR2 | Y | - |
| RAW | Y | - |
| ROWID | Y | - |
| TIMESTAMP | Y | - |
| TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE | N | - |
| TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE | N | - |
| UROWID | N | - |
| VARCHAR2 | Y | - |
| XML types | N | - |
Configuring Oracle for CDC
For details on configuring Oracle for LogMiner based CDC, see How to Configure Oracle for CDC.
Configuring Table for Oracle Log-Based Ingestion
The configuration for table is exactly same as query-based except a few configurations. For descriptions of fields, refer to the Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions section.
SQL Server Log-Based Incremental Ingestion
Through MSSQL Server Log Based method, data is ingested into Hive and continuously synchronized with the database using captured CDC tables provided by MSSQL Server. But this method works only with the enterprise editions of MSSQL Server. In this method, change data capture must be enabled for the incremental tables. Before enabling for a table, it must be enabled for the schema in which the table is present.
Infoworks uses SQL Server transactional replication to capture change data from SQL server distribution databases. For CDC to work, you must enable SQL Server Replication on the system from which change data is to be captured. If your database has a high volume of change activity, you should use a distributed server as the host of the distribution database.
To configure CDC in Infoworks, you must define a capture registration for each source table. In the capture registration, you can select a subset of columns for which the data is to be captured.
Infoworks supports ActiveDirectoryPassword with ms-sql.jar. Following is a sample connection string with AD login:
jdbc:sqlserver://testingclsfss.database.windows.net:1433;database=testingcluster;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=false;hostNameInCertificate=.database.windows.net;loginTimeout=30;authentication=ActiveDirectoryPassword*
Planning SQL Server CDC
Before you configure SQL server CDC, ensure that the following prerequisites and user authority requirements are available. Also, review the restrictions to configure CDC correctly.
Prerequisites
Infoworks CDC has the following SQL Server prerequisites:
- Infoworks CDC requires an edition of Microsoft SQL Server 2008 or later that supports transactional replication. You must configure and enable transactional replication on the source system to perform CDC.
- Infoworks uses SQL Server 2008 Server Management Objects (SMO) to manage SQL Server publications. SMO is a .NET Framework object model used by applications to manage and administer SQL Server objects and services. You must install SQL Server 2008 SMO and related packages before you create or edit capture registrations. For your convenience, Infoworks provides the installation packages for these SQL server objects.
- The Microsoft SQL Server Agent and Log Reader Agent must be running on the Windows machine from which change data is extracted. Usually, the SQL Server Agent remains running after it is initially started.
- Each source table in the distribution database must have a primary key.
- If the Infoworks product is installed on a Windows machine that is different from the one where the Microsoft SQL Server source runs, you must install the SQL server client components on the Infoworks machine.
- Ensure that the Infoworks product runs on the Windows system that contains the Microsoft SQL Server source or on another Windows system.
User Authority for SQL Server CDC
Ensure that proper authority is available to complete registration and SQL server configuration tasks.
Following are the authorities required:
- System Administrator authority or SA, to enable transactional replication on the publication database.
- DB_OWNER authority to create registration groups and capture registrations from Infoworks.
- Read access to the database to run change data extractions against the SQL Server distribution database.
SQL Server Datatypes Supported for CDC
Infoworks supports most SQL server datatypes for CDC, with some exceptions.
The following table indicates the SQL Server datatypes supported for CDC by Infoworks:
| SQL Datatypes | Supported | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| bigint | Y | - |
| binary | Y | - |
| bit | Y | - |
| char | Y | - |
| date | Y | - |
| datetime | Y | - |
| datetime2 | Y | - |
| datetimeoffset | Y | Infoworks treats this datatype as varchar. |
| decimal | Y | - |
| float | Y | - |
| geography | N | - |
| geometry | N | - |
| hierarchyid | N | - |
| image* | N | Use varbinary(MAX) instead. |
| int | Y | - |
| money | Y | - |
| nchar | Y | - |
| numeric | Y | Use nvarchar(MAX) instead. |
| nvarchar | Y | - |
| real | Y | - |
| smalldatetime | Y | - |
| smallint | Y | - |
| smallmoney | Y | - |
| sql_variant | N | Infoworks does not capture change data for sql_variant columns but does capture change data for other columns in the same table. |
| text* | Y | Use varchar(MAX) instead. |
| time | Y | - |
| timestamp | Y | - |
| tinyint | Y | - |
| uniqueidentifier | Y | Infoworks imports the uniqueidentifier datatype as a varchar datatype of 38 characters. |
| user-defined datatypes (UDTs) | Y | Infoworks treats a UDT in the same way as the datatype on which the UDT is based. |
| varbinary | Y | - |
| varchar | Y | - |
| xml | Y | Infoworks treats this datatype as varchar(MAX). |
**Infoworks might not capture change data for columns that includes image, ntext, or text datatype, due to SQL server transactional replication restrictions on these column types. Instead, use the alternative datatypes that Microsoft recommends, as indicated in the *Comments column.
SQL Server CDC Operational Considerations
Following are the operational considerations for SQL server CDC:
- Infoworks can capture change data from SQL Server distribution databases for which Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) is enabled. No special configuration tasks are required.
- Infoworks does not capture change data for SQL Server system tables.
- The maximum length of a row for which Infoworks can capture and process change data is 128,000 bytes.
- Infoworks does not capture the user ID that is associated with the original transaction that updated the database.
- The timestamp that Infoworks records for each captured change indicates when the change was captured, not when the original transaction occurred.
- Infoworks does not capture change data for derived columns that are not persisted. SQL Server computes values for these columns at run-time based on an expression but does not store the values in a table.
- SQL server publishes deferred updates to SQL Server tables as DELETEs followed by INSERTs rather than as UPDATEs. Consequently, Infoworks propagates deferred updates as DELETEs followed by INSERTs, even if you select AI for the Image Type attribute in the CDC connection. Infoworks does not include Before Image (BI) and Change Indicator (CI) information in DELETE and INSERT records. To capture a deferred update as an UPDATE for business reasons, set the SQL Server 8207 trace flag. This flag causes the SQL Server Replication Log Reader to combine the DELETE and INSERT pair into a single UPDATE. For more details on SQL Server processing of deferred updates and the SQL Server 8207 trace flag, see the SQL Server documentation.
- Infoworks does not support the use of local aliases when connecting to SQL server and creating publications at registration creation.
- If you need to switch the status of multiple SQL Server capture registrations from active to inactive or from inactive to active, use the DTLUCBRG utility with the MSSOPTS UPDATESTATUS parameter. This optional parameter enables you to switch the status of many registrations in one operation and regenerate the associated SQL server publications.
- You can run Infoworks on a Windows system other than the Windows system where the SQL Server source distribution database runs. On the Infoworks system, you must install the Microsoft SQL Server Native Client and define an MSQL CAPI CONNECTION statement that provides connection information for the SQL Server source distribution database in the dbmover configuration file. Also, in the dbmover configuration files on the Infoworks Service machine, define a NODE statement that points to the Infoworks system.
Configuring SQL Server for CDC
You must perform a few configuration tasks to prepare SQL server for Infoworks CDC.
If the SQL Server tables have a high level of update activity, use a distributed server as the host of the distribution database from which to capture change data. This practice prevents competition between Infoworks CDC and your production database for CPU use and disk storage.
Infoworks uses SQL Server Management Objects (SMO) to manage SQL Server publications. SMO is a .NET Framework object model that applications can use to manage and administer SQL Server objects and services. You must install SMO and some related packages before you create or edit capture registrations.
Infoworks provides the 64-bit installation packages for the required SMO objects and packages for your convenience.
- On the system where you run the Infoworks utilities, install the following SQL Server 2008 SMO objects and packages by using the installer .msi files.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Management Objects
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Replication Management Objects
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Native Client
- Microsoft SQL Server System CLR Types
NOTE: You must install the Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Replication Management Objects even if you use SQL Server 2012 or SQL Server 2014.
- Start the SQL Server Agent and Log Reader Agent if they are not running. For more details, see your Microsoft SQL Server documentation.
- Configure and enable SQL Server transactional replication on the publication database. For more details, see your Microsoft SQL Server documentation.
- Verify that each source table in the distribution database has a primary key.
Enabling Logs in MSSQL Server
Logs in MSSQL server is enabled using the CDC program of the SQL Server. This program is bundled with Enterprise, Developer, and Evaluation editions of MSSQL Server installations. Once logs are enabled for a table, the corresponding table changes will be stored in a capture table instance in a default database called CDC. The capture table name can be the same as source table name (step 2 will be executed in enabling logging) or user can configure this while enabling logging for the table (step 3 will be executed while enabling logging).
Following is a two-step process {[1,2] or [1,3]} to enable logging. In these scripts, to execute the commands, we assume that there is a database called automation_db and a table timestamps_inserts_updates in that database.
- Enable CDC for a database automation_db. This is basically executing CDC program on the database:
use automation_db;EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_db;- Enable CDC for table timestamp_inserts_updates with default capture instance name.
NOTE: If you do not specify the name of the capture instance, the capture instance name will be same as source table name in the CDC schema.
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table @source_schema = N'automation_db', @source_name = N'timestamp_inserts_updates', @role_name = N'NULL' GO- Enable CDC for table with user-given captured instance name.
NOTE: If you specify the name of the capture instance while enabling logging for the table, the source table name is timestamp_inserts_updates logging the CDC table name as name_of_capture_instance.
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table @source_schema = N'automation_db', @source_name = N'timestamp_inserts_updates', @role_name = N'NULL', @capture_instance = N'name_of_capture_instance' GOOnce the logging is enabled for a table, the metadata of the corresponding captured table will be stored in the cdc.change_tables table. You can use the following query to verify list of captured tables:
select * from cdc.change_tables;Following figure shows the sample output of the CDC-enabled tables:

Creating Source
In the Admin section (Admin > Source > New Source), create a source and select the source type as SQL Server. Enter the Hive schema name and HDFS location.
Configuring Source
Specify the JDBC URL for the database along with username, password, and schema.
Fetching Metadata
Navigate to Source Configuration and click crawl metadata. Once the metadata is stored in the Infoworks metastore, you can configure the tables to be crawled.
Configuring Table
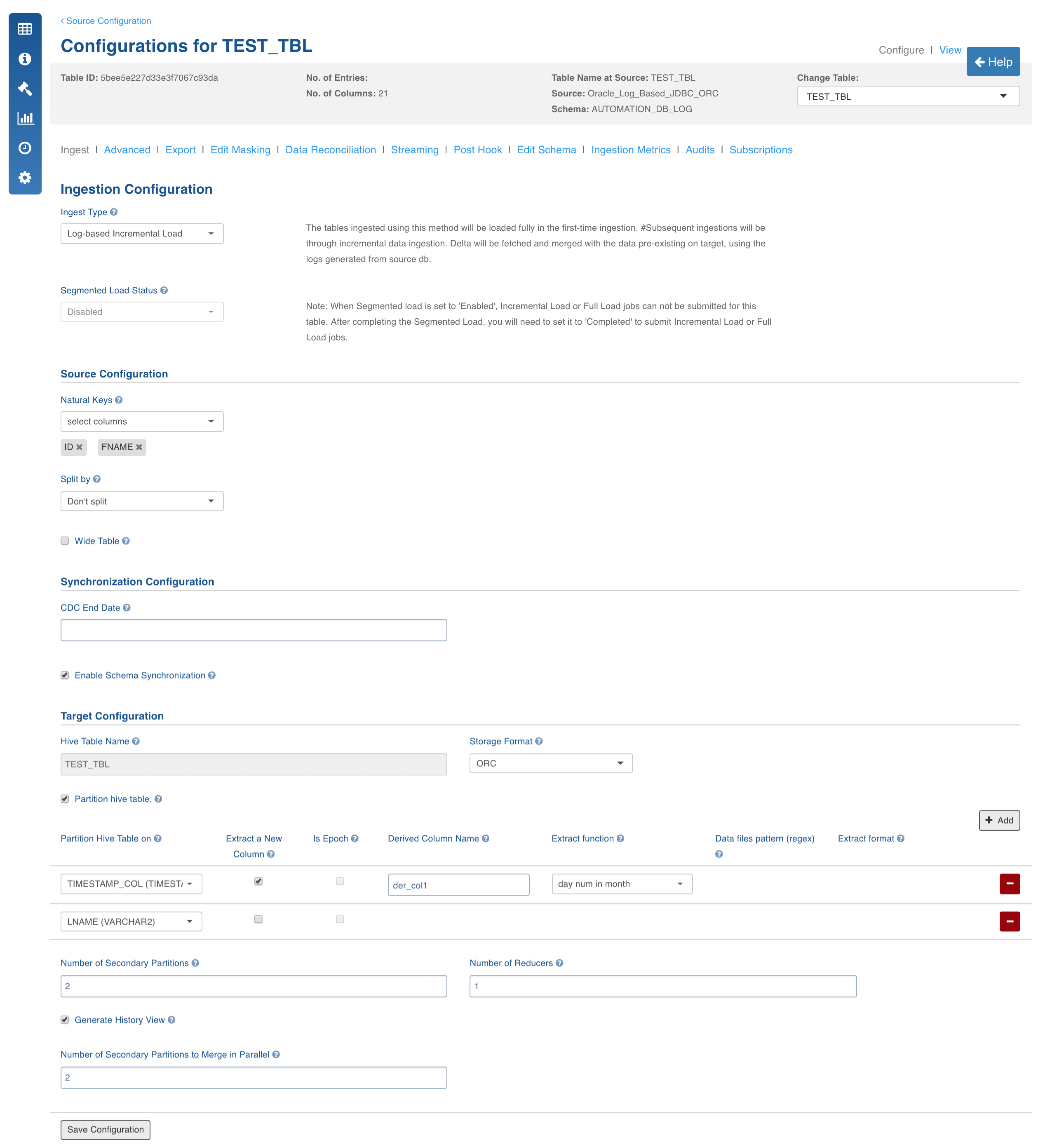
The configuration for table is same as query-based, except a table-level configuration, Captured Table Name, specific to log-based under the Synchronization Configuration section. The default value is schemaname_tablename. If the database user or database admin enables the change data capture for the table using an explicit name, that capture-table-name should be specified. As shown in the following figure, the schema name is automation_db and the table name is sampletable.
Running Job
Once the tables are configured, add the tables you want to crawl to a tablegroup, enter the value for maximum connections to source and maximum parallel tables that you want to crawl at a time and click initialize and ingest for full-load.
To view the running jobs, click the Ingestion Logs icons.
For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
DB2 Log-Based Incremental Ingestion
In DB2 log-based incremental ingestion, we continuously synchronise data into Hive using CDC log tables for the corresponding DB2 tables. Logging in DB2 database server is enabled using the SQL Replication Capture program (asnclp, asncap and apply). The SQL Replication program creates CDC and target tables (replication tables) for the corresponding source table.
For details on how to enable logging in DB2, see the Appendix chapter.
Planning DB2 CDC
Before you configure DB2 CDC, ensure that the following prerequisites and user authority requirements are met. Also, review the restrictions to configure CDC properly.
Prerequisites
Following are the Infoworks CDC DB2 server prerequisites:
- Archive logging must be active for the database that contains the source tables from which change data is to be captured.
- DB2 source tables must be defined with the DATA CAPTURE CHANGES clause for capture processing to occur.
- A valid DB2 environment must exist for the Infoworks user.
Required User Authority for DB2 CDC
For Infoworks to read change data from DB2 logs, the user ID that you specify for database access must have SYSADM or DBADM authority. Usually, this user ID is specified in the UDB CAPI_CONNECTION statement in the dbmover.cfg file.
DB2 Datatypes Supported for CDC
Infoworks supports most DB2 datatypes for CDC. The following table identifies the DB2 source datatypes supported by Infoworks for CDC:
| DB2 Datatypes | Supported | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| bigint | Y | - |
| BLOB | N | If you register a table with large object (LOB) columns, Infoworks does not capture changes for the LOB columns but can capture changes for other columns in the table. |
| CHAR | Y | - |
| CLOB | N | If you register a table with LOB columns, Infoworks does not capture changes for the LOB columns but can capture changes for other columns in the table. |
| DATE | N | If you register a table with LOB columns, Infoworks does not capture changes for the LOB columns but can capture changes for other columns in the table. |
| DECFLOAT | N | If you register a table with DECFLOAT columns, Infoworks does not capture changes for the DECFLOAT columns but can capture changes for other columns in the table. |
| DECIMAL | Y | - |
| DOUBLE | Y | - |
| GRAPHIC | Y | - |
| INTEGER | Y | - |
| LONG VARCHAR | Y | - |
| LONG VARGRAPHIC | Y | - |
| REAL | Y | - |
| REF | N | DB2 does not allow change data capture for tables with REF columns. |
| SMALLINT | Y | - |
| TIME | Y | - |
| TIMESTAMP | Y | - |
| UDTs (User-defined datatypes, such as DISTINCT and STRUCT.) | N | - |
| VARCHAR | Y | - |
| VARGRAPHIC | Y | - |
| XML | N | - |
DB2 CDC Considerations
Consider the following CDC capabilities and restrictions when planning DB2 CDC processing:
- To extract change data on a DB2 client machine that is remote from the DB2 server where the change data is captured, both machines must have the same architecture. Else, change data capture processing might fail.
- If the source tables are compressed, ensure that you have a compression dictionary that is compatible with the compressed DB2 log records from which Infoworks reads change data for the tables. Else, DB2 will not be able to decompress the log records for Infoworks read requests. Usually, the compatible compression dictionary is available because DB2 maintains the current compression dictionary and a backup of the previous compression dictionary on disk.
- If you run the DB2 REORG TABLE utility or the DB2 LOAD utility with the REPLACE or RESUME NO option against compressed source tables, Infoworks recommends that you specify the KEEPDICTIONARY option for the utility. The KEEPDICTIONARY option forces DB2 to retain the current compression dictionary, if it exists. If you use the RESETDICTIONARY option, DB2 rebuilds compression dictionary. In this case, the previous compression dictionary that matches the DB2 log records might not be available any longer.
- Infoworks cannot capture change data for the following DB2 datatypes:
- DECFLOAT, LOB, and XML datatypes: You can create a capture registration for a table that includes columns with DECFLOAT, LOB, and XML datatypes. However, the registration does not include these columns, and Infoworks does not capture change data for them. Infoworks does capture change data for the other columns in the registered table that have supported datatypes.
- User-defined datatypes: Tables that include columns with user-defined datatypes cannot be registered for change data capture. Infoworks cannot capture change data for these tables.
- To add or drop partitions in a partitioned database and then redistribute table data across the updated partition group, or to reconfigure a database partition group, you must use a special procedure. Else, Infoworks might not be able to resume change data capture properly.
- If you alter a column datatype to or from FOR BIT DATA, Infoworks does not detect the datatype change. Infoworks continues to use the datatype that is specified in the existing capture registration.
- If you alter a source table to change the default value of a DB2 column of CDC interest, Infoworks does not detect this DDL change during capture processing. As a result, the correct default value is not available when Infoworks performs the following operations:
- Delivers the pre-existing short rows for a table to which columns were added.
- Delivers rows for source tables that use the VALUE COMPRESSION option and that include a column with the COMPRESS SYSTEM DEFAULT option and a default value.
- In a partitioned database, if an UPDATE to a table row changes the partition key and that change causes the row to move to another partition, Infoworks processes the UPDATE as two operations, DELETE and INSERT. However, based on the DB2 log information, Infoworks cannot predictably determine the order in which to perform the DELETE and INSERT operations. If the INSERT is processed first, both the original row and the updated row appear on the target until the DELETE is processed.
- Infoworks uses multithreaded processing for change data capture. By default, Infoworks uses up to nine threads. To configure the number of threads, specify the THREADING parameter in the UDB CAPI CONNECTION statement. If you have a DB2 partitioned database, you can use a maximum of one thread for each database partition node plus two additional threads for the CAPI and merge processing.
Configuring DB2 for CDC
Following are the tasks to configure DB2 for Infoworks CDC:
- In the DB2 Control Center Configure Database Logging Wizard, enable archive logging for the DB2 database. For more details, see the IBM DB2 documentation.
- Set the following user environment variables in any process that runs Infoworks CDC or the DTLUCUDB program:
- Set DB2NOEXITLIST to ON.
- Set DB2CODEPAGE to 1208.
- Verify that the DB2 source tables are defined with the DATA CAPTURE CHANGES clause.
- To enable Infoworks to report the authorization ID and application that is associated with a DB2 transaction, set the DB2_LOGGING_DETAIL registry variable to APPLINFO in DB2.
- To set this variable for the current DB2 instance, enter the following command:
db2set DB2_LOGGING_DETAIL=APPLINFO - To set this variable for all DB2 instances on the system, enter the following command:
db2set -g DB2_LOGGING_DETAIL=APPLINFO - If a table that is selected for change data capture includes columns with LONG datatype, use the INCLUDE LONGVAR COLUMNS clause to alter the table so that Infoworks can capture data for the LONG columns.
Enabling Logs in DB2 Server
Logging in DB2 database server is enabled using the SQL Replication Capture program (asnclp, asncap and apply). The SQL Replication program creates CDC and target tables (replication tables) for the corresponding source table.
To set up the replication, perform the following steps from command line:
- Run the following command to create CDC, target tables from the DB2 command line:
$DB2HOME/bin/asnclp -f sqlrep.asnclp
Following are sample contents of the ansclp script. In the script below, capture program is run for a test_rep database with userid as DB2INST2 and password as infoworks. CDC is specifically enabled for test_tbl table. The change data capture for the table will be stored in the test_tbl_cdc table and the corresponding replication table will be stored in the test_tbl_target in the same schema. You can specify the target schema for creating CDC and target tables.

- After running the asnclp program, start the SQL Replication Capture (asncap) program for the database test_rep from a DB2 command window (run in the background):
asncap capture_server=test_rep & - Run Apply program in the background:
asnapply control_server=sample apply_qual=MYQUAL20. - Drop the target database created if the replication of the table is not required.
- Query the test_tbl_cdc table to see CDC.
NOTE: This may take up to a minute. By default, the Apply program sleeps one minute when it finds no data to replicate.
- For more details on SQL Replication, see Introduction to SQL Replication and Setting Up SQL Replication.
Creating a Source
In the Admin section (Admin > Source > New Source), create a source and select the source type as DB2. Enter the Hive schema name and HDFS location.
Configuring a Source
Specify the JDBC URL for the database along with the username, password, and schema.
Fetching Metadata
Navigate to the Source Configuration page and click crawl metadata. Once the metadata is stored in the Infoworks metastore, you can configure the tables to be crawled.
Configuring a Table
The configuration for table is same as query-based, except the Change Schema Name, Change Table Name configurations. The default value for Change Table Name is cd_tablename. If the database user or database admin enables the change data capture for the table using an explicit name for the table and for the schema, then the change table name and change schema name must be specified.
As shown in the following figure, the schema name is cd_schemaName and the table name is cd_BATCH_INSERTS_UPDATES. For descriptions of other fields, refer to Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions section.
Running a Job
Once the tables are configured, add the tables you want to crawl to a tablegroup, enter the value for maximum connections to source, maximum parallel tables that you want to crawl at a time and click initialize and ingest for full-load.
To view the running jobs, click the Ingestion Logs icon.
For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group. The job status will be displayed.
Sybase Log-Based Incremental Ingestion
Overview
Through Sybase log-based approach, the data is ingested into Hive and is kept continuously synchronized with the database using the DBTRAN utility provided by Sybase. This utility has to be set up on the edge node where Infoworks services are running.
Log files from the sybase server will be stored in a temporary location on edge node, which you can configure. The corresponding folder should be created on the edge node.
Configurations
To support log-based data synchronization in Sybase, you must set up the following three global level parameters in the admin configuration page:
- SYBASE_EDGENODE_TEMP_FOLDER: The directory where you should place the database log file.
- SYBASE_INSTALLATION_PATH: The folder where the DBTRAN utility is found on the edge node.
- SYBASE_CLIENT_SOURCING_PATH: This is the path for sourcing Sybase client.
Optional Configurations
Following are the optional source-level parameters:
- LOG_FILE_NAME: The log file name that will be stored in the temporary folder created on the edge node. The default value is log. If the log file name is different, you must specify the corresponding name (without .log).
- FIRST_CDC_OFFSET: During first incremental ingestion, Infoworks reads and parses the complete log data present in the log file. If you want to bring just the incremental data, you must specify the offset from where you want to bring.
Enabling Logs in Sybase Server
Sybase IQ includes IQINIT admin utility used to create database. Whenever the database is created with this utility, the transactional logs for the database will be automatically stored in the log file. You must have the access to the file system to create the .db file. You can disable the transactional logs by explicitly mentioning the -f option when running start_iq command line utility.
Following is the command to create database and to enable logging in Sybase:
NOTE: In this command, database called automation_db is created using the database credentials.
$SYBASE_HOME/IQ-{version}/bin64/iqinit automation_db.db -dba <user_name>,<password>Creating Source
In the Admin section (Admin > Source > New Source), create a source and select the source type as SybaseIq. Enter the Hive schema name and HDFS location.
Configuring Source
Specify the JDBC URL for the database along with username, password, and schema.
Fetching Metadata
Navigate to the Source Configuration pageand click crawl metadata. Once the metadata is stored in Infoworks metastore, you can configure the tables you want to crawl.
Configuring Table
The following screen illustrates the table configuration values for a Sybase log-based incremental ingestion:
For descriptions of other fields, refer to Source Table Configuration Field Descriptions section.
Running Job
Once the tables are configured, add the tables you want to crawl to a tablegroup, enter the value for maximum connections to source, maximum parallel tables that you want to crawl at a time and click Initialize and Ingest for full-load.
To view the running jobs, click the Ingestion Logs icon.
For CDC, click Ingest Now in the table group.
Known Issues
- Derived Splitby and Derived Partition are not supported.
- Schema Synchronization is not supported.
- Split-by key will be used only during full-load but not during CDC
Hybrid Source Synchronization for Oracle Databases
Infoworks supports the following mechanisms to synchronize data from Oracle using change data capture:
- Log-based synchronization using Oracle db logs
- Query-based synchronization using timestamps or BatchIDs
- Hybrid Source synchronization using third party replication tools such as Golden Gate.
Hybrid Source synchronization operates by directly loading the source table(s) via Infoworks initial bulk loading. Once the full table is ingested using Infoworks, you can configure Hybrid synchronization to read the CDC records from an Oracle table maintained by tools such as Oracle Golden Gate.
Creating Source
In the Admin section (Admin > Source > New Source), create a source and select the source type as Oracle. Enter the Hive schema name and HDFS location for the data to be stored.
Configuring Source
Enter the JDBC URL, username, password and schema for the source database from where the initial bulk load must be loaded.
Fetching Metadata
Navigate to the Source Configuration page and click Crawl Metadata. Once the metadata is stored in Infoworks metastore, you can configure the tables you want to crawl.
Configuring a Table for OGG
Open the table configuration page for which the table must be configured for OGG and perform the following:
- Select Ingest Type as Ogg-based Incremental Load.
- Select the Natural Key for the table.
- Select split-by key if any.
- In the Synchronization Configuration section, enter the archival server details like JDBC URL, username, password and schema name. Captured_table_name is the name of the table in the target server to which the source table is mapped.
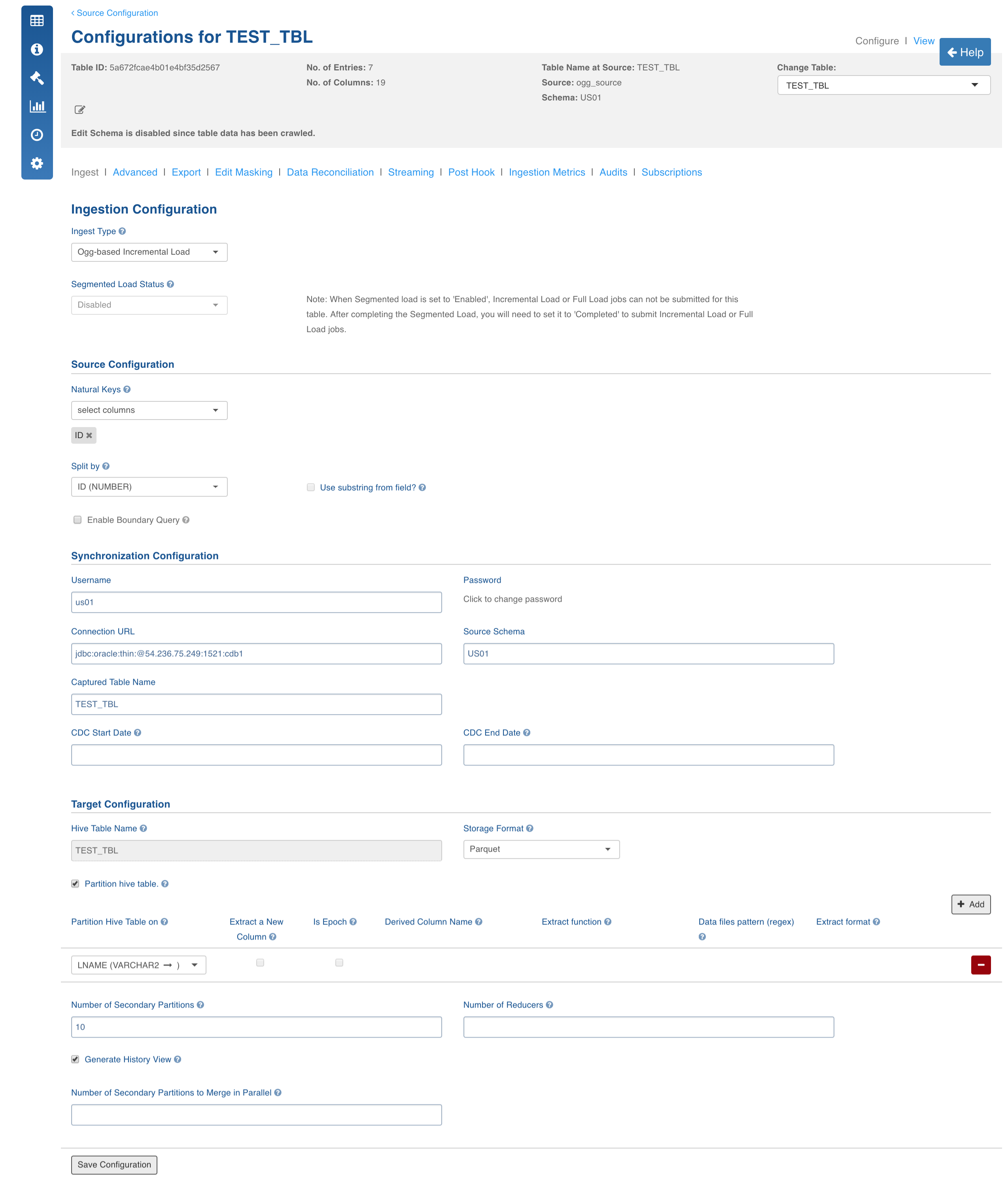
The other configurations include storage format, partition table on, no.of secondary partitions, no.of reducers and number of merge jobs to run in parallel which are same as any normal ingestion job.
Advanced Configurations at table Level
The Table Configurations page allows you to configure any configurations related to the table. If the configuration is not found at the table level, Infoworks obtains it from the source Advanced Configuration or at global level.
Table level > Source level > Global level
Fetching Metadata
Key Name: OGG_REFRESH_COL, Value: The name of the column in the target table through which the incremental records will be fetched.
Key Name: DML_COL, Value: The name of the column in the target table to identify if an incremental record is an INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE.
DML_COL values supported by Infoworks are INSERT, SQLCOMP UPDATE, DELETE.
Running Bulk Initial Load
Once all the configurations are done for the ogg-table, add the table in a Table Group and run Initialize and Ingest Now for loading the history data from the source table.
Running Incremental Load Job
Run Ingest now to fetch the change data from the golden gate target table in the archival server. Infoworks reduces multiple records for the same natural key to single record and place all the history transactions for the records in the history table, if history view is enabled.
RDBMS Schema Synchronization
This feature includes the addition of new columns in RDBMS tables and changes applied on the target table in Hive (for both current view and historic view) during incremental ingestion. Ingested records will be backfilled with the default value of the newly added columns. The schema synchronization (only addition of new columns) is enabled using a table-level configuration.
Currently, schema synchronization is supported for following databases for different types of incremental delta fetches:
- Query-Based Incremental Ingestion: The schema changes are directly read from the table metadata crawl. Currently, we support schema synchronization for Teradata (JDBC), Teradata (TPT), Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, Netezza, SAP HANA, MySQL, Sybase, MariaDB, Vertica, Redshift and Apache Ignite.
- Log-Based Incremental Ingestion: In this approach, the schema changes are read from the table metadata and not from the DDL statements in the database log. Currently, we support schema synchronization for Oracle.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential