Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Full Ingestion
The tables or sources that are fully ingested will always be truncated and reloaded on target.
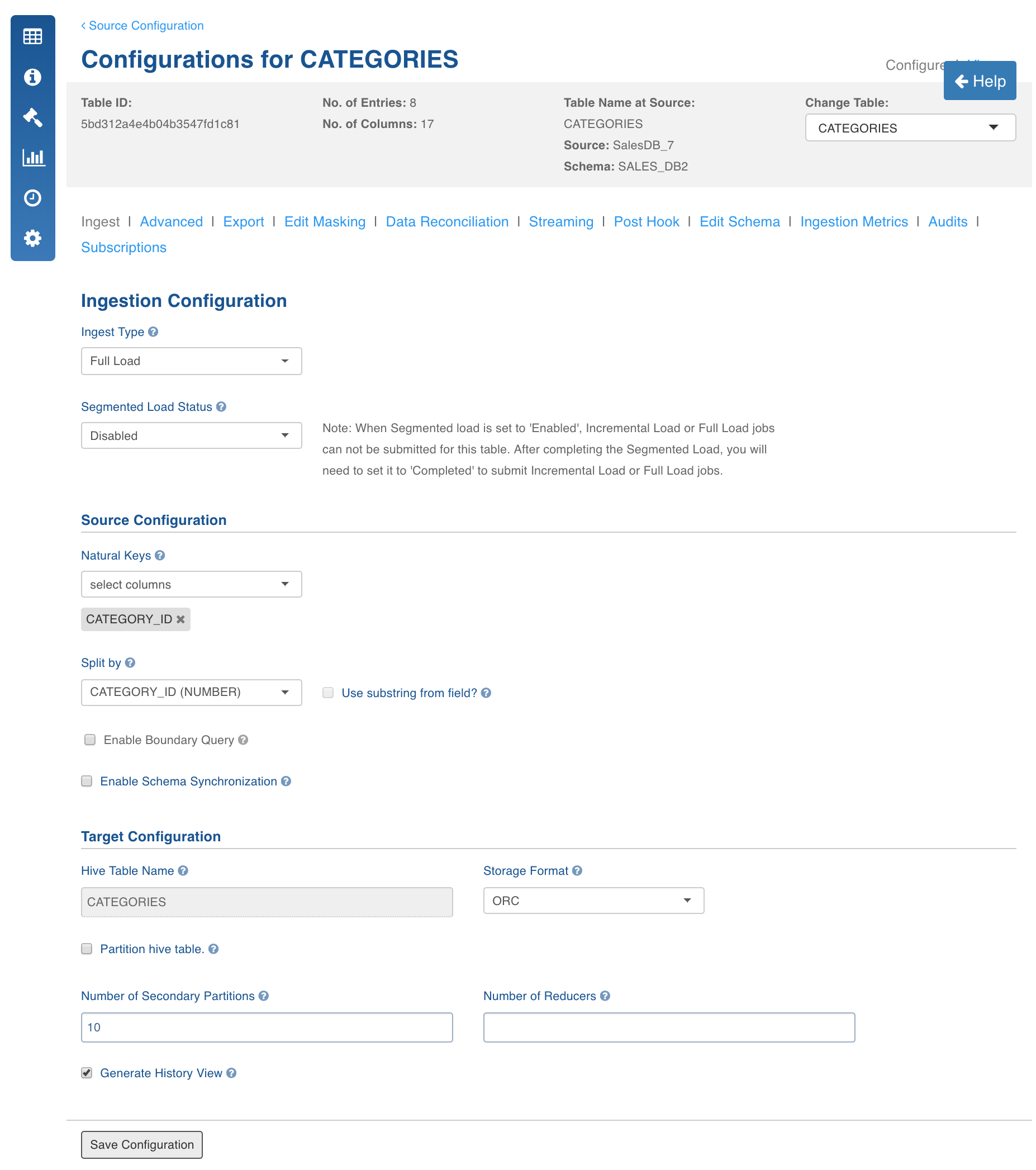
Following are the steps to perform full ingestion for a table:
- Click the Sources menu and click the required source.
- Click the Configure button for the required table.
- In the Configuration page, set the Ingest Type to Full Load, and enter the required values.
Using TD Wallet for Teradata TPT Source
NOTE: Ensure that TD Wallet has been set up for the Infoworks user.
If the Source Type is Teradata and the Fetch Data Using is TPT, you can specify the Teradata Wallet Key, where the database password is stored.
For example, if the TD Wallet is set up and a key, TD_PASSWORD, is added with the database password as the value then, when configuring the source for TPT, you can select the Is Teradata wallet setup for Infoworks user? option and provide the key (TD_PASSWORD in this example) in the Key to retrieve Teradata Password from Wallet field to retrieve the password from the Teradata wallet.
Table Configuration Field Descriptions
The following table includes the fields related to all ingestion types. Refer to this table for source table configuration of all ingestion types.
| Configuration Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Ingestion Configuration | |
| Ingest Type | Describes ingestion type of the table. {types} |
| Segmented Load Status | Used to crawl large tables by breaking into smaller chunks. For detailed configuration parameters, see Segmented Ingestion. |
| Source Configuration | |
| Natural Keys | Used to identify the row uniquely. This field is mandatory in incremental ingestion tables. This is used to identify and merge incremental data with the already existing data on target. Distribution of data into secondary partitions for a table on target will be computed based on the hashcode value of the natural key. NOTE: You cannot update the value of natural key column while updating a row on source; all the components of the natural key are immutable. |
| Split by | Used to crawl the table in parallel with multiple connections to database. Split-by column can be an existing column in the data or derived from an existing column. NOTE: Keys which increase or decrease gradually can be used as split-by. Click the Use substring from field option to derive a split-by column from an existing column. |
| Use substring from field? | Check this option and enter the other field values to derive from the parent column. NOTE: In case of date, datetime, timestamp column types you can derive a split-by. The possible split-by options are year, month, year-month, month-day and day-num-in-month. |
| Enable Schema Synchronization | Used to synchronize the Hive table schema if the source table is modified after ingestion. Check this option to enable schema synchronization. NOTE: For the timestamp, query-based, and Batch ID-based ingestion types, this option is displayed in the Synchronization Configuration section of the page. |
| Enable Boundary Query | The query to use for creating splits. For details, see the Boundary Query section. |
| Synchronization Configuration | |
| Timestamp Column for Insert | Source column to be used as insert watermark. |
| Timestamp Column for Update | Source column to be used as update watermark. NOTE: It can also be the source column to be used as insert watermark. |
| Slowly Changing Dimension Type | Type of the query based ingestion. Slowly Changing Dimension 1 (SCD1) always overwrites the existing record in case of updates. |
| Configure Insert Query | Query to be configured to obtain the incremental inserts. The query must be able to select all the columns in the table along with the timestamp in the audit table. |
| CDC Start Date | CDC start date and time. |
| CDC End Date | CDC end date and time. |
| External Audit Schema Name | Audit table schema where the audit information of recaddts for the table is maintained. |
| External Audit Table Name | Audit table name where the recaddts for the record is stored. |
| External Audit Join Column | Join column between audit table and source table. |
| External Audit Timestamp Column | Timestamp column in the audit table, which maintains record audit. |
| Batch-ID Column | Column used to fetch delta. |
| Start Batch ID | Numeric value of Batch ID column (configured by the user during table configurations) starting which the delta is fetched. |
| End Batch ID | Numeric value of Batch ID column (configured by the user during table configurations) till which the delta is fetched. |
| Target Configuration | |
| Hive Table Name | Name of the table in Hive which will be used to access the ingested data. |
| Storage Format | Storage format (ORC or Parquet) |
| Partition Hive Table on | Used to partition the data in target. The partition column also can be derived for date, datetime and timestamp column. This will further partition the data. A hierarchy of partitions are supported with both normal partitions and derived partitions. NOTES: Ensure that the partition columns data is immutable. You can provide a combination of normal and derived partitions in the hierarchy. |
| Extract a New Column | Check this option for supported datatypes to derive a partition from an existing column. NOTE: Fill the corresponding field values based on the derived type. |
| Is Epoch | When extracting a new column, checking this field indicates whether the selected column is epoch. This allows you to select the partitions from epoch value based on the date’s function. For example, year month, year, month, date. Epoch is supported for all numeric datatypes except int and float. |
| Derived Column Name | This is a mandatory field to be filled when deriving a partition column. NOTE: Ensure no other columns in this table have the same name. |
| Extract Function | The extract function. If the parent column is a timestamp or date column, you can select extract function as one of the following: day num in month, month, year, year month, month day. If the parent column is other than timestamp or date, use the regular expression as the extract function. NOTE: This is a mandatory field to be selected when deriving a new column. |
| Data file pattern (regex) | If you select regular expression as the extract function, you must enter corresponding regular expression. NOTE: This field is a mandatory field if regex is used as an extract function. |
| Extract format | When using regex derived partition, this field specifies the values to extract from a data pattern to partition the data. NOTE: This field is mandatory if regex is used as an extract function. |
| Number of Secondary Partitions | The target data can be distributed among various partitions and each partitions in turn can have various secondary partitions. A table with no primary partition can also have secondary partitions. Secondary partition helps in parallelising the ingestion process. |
| Number of Reducers | The number of reducers for the ingestion map reduce job. Increasing the number of reducers helps reduce the ingestion duration. This will help in processing the MR jobs faster. This will be effective with the combination of partition key and number of secondary partitions. In any data processing using MR job, this will help in bringing the parallelism based on the data distribution across number of primary partitions and secondary partitions on Hadoop. |
| Generate History-View | If this configuration is enabled, history view table will be created (along with the current view table) in Hive, which contains the versions of incremental updates and deletes. |
| Number of Secondary Partitions to Merge in Parallel | It is a number that represents number of secondary partitions can be merged in parallel for a table. |
| Number of Secondary Partitions to load in-memory for Merge | It is a number that represents number of parallel merge jobs that will be loaded in memory while the merge for previous set of secondary partitions are in progress during map side merge. |
Data Viewer - Superset
Superset is a visualization platform that allows you to query and create visual models from Hadoop data. Superset enables you to visualize the data stored in Hive after being ingested from source.
Following are the steps to query a superset:
NOTE: The configuration, ENABLE_DATAVIEWER, must be set to true to enable the data viewer.
- In the Source Configuration page, click View for the required table record. The Data page is displayed with the data viewer.
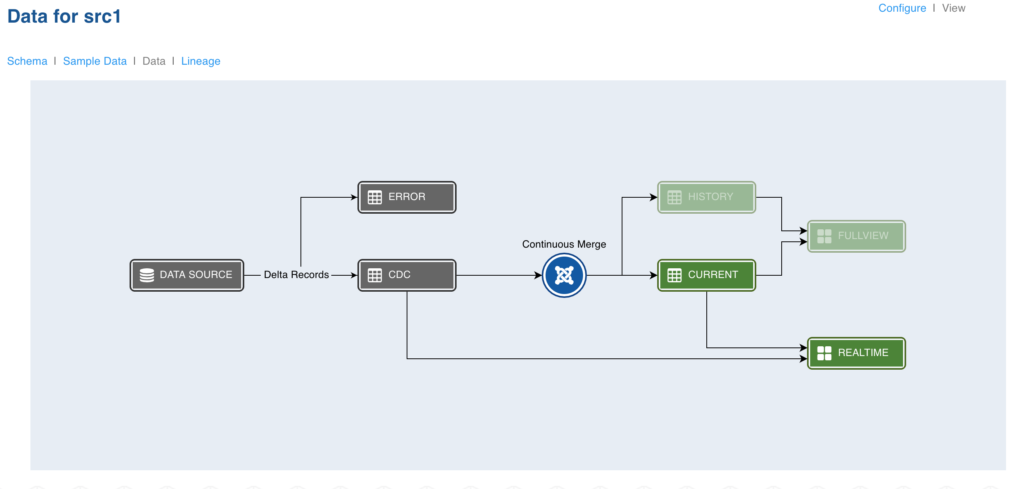
- Click the required table to view the Apache superset. A new window with the Apache superset will be displayed as follows:
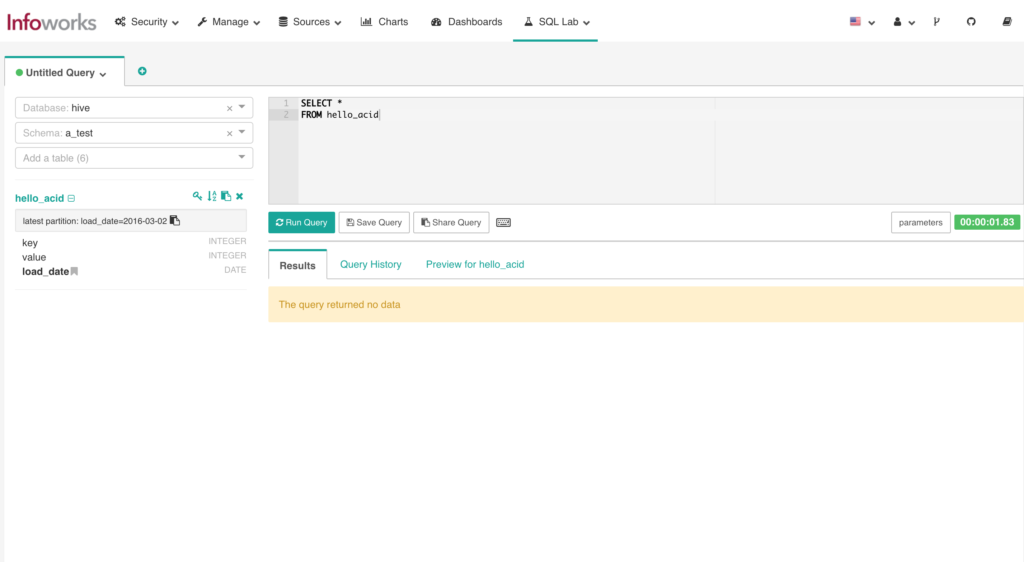
- Run the queries to obtain the required data from the Hive tables.
Table Operations
Following are the steps to truncate, delete, recrawl and reorganize the table data:
- In the Source Configuration page, click the Actions button for the required table.
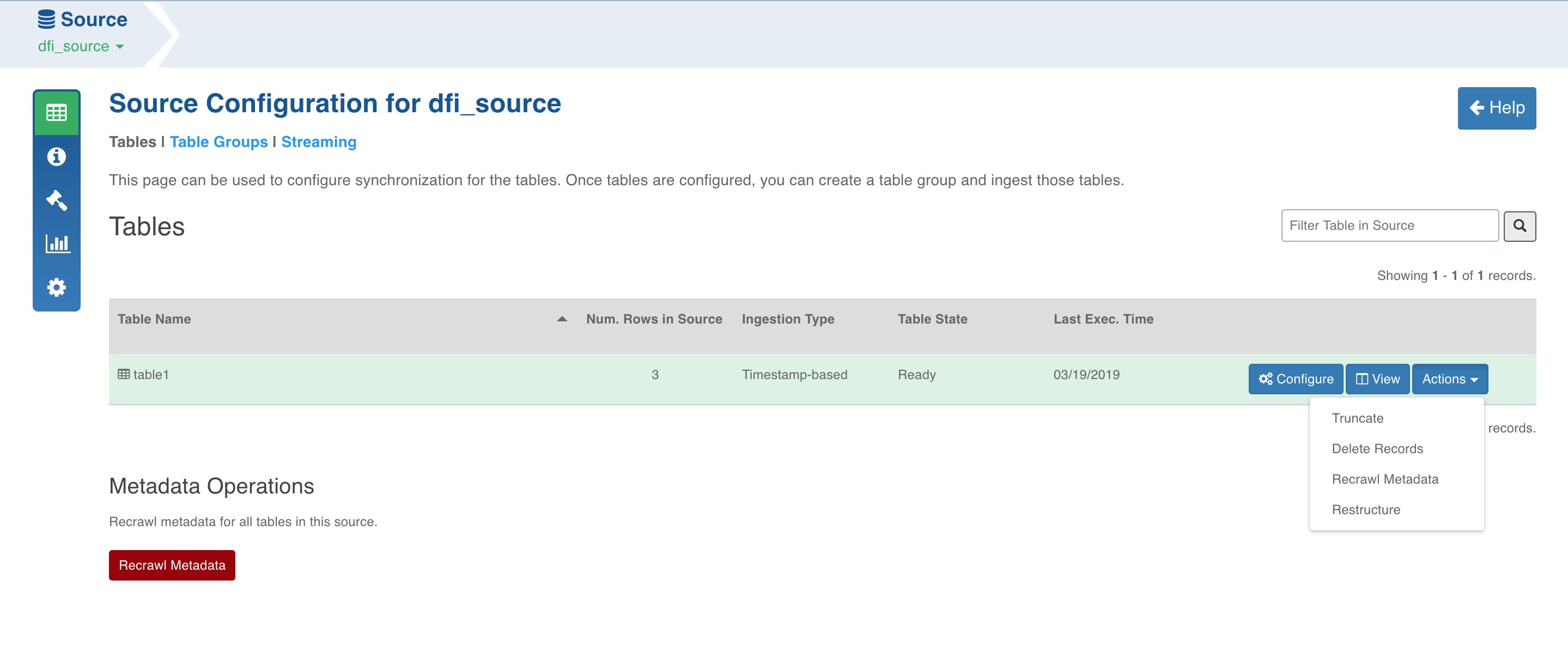
Perform either of the following:
- Click Truncate to delete data from the target and reset the table metadata (row count and last ingested timestamp).
- Click Delete Records and specify a select query. This query will run on the current Hive table corresponding to the DFI table and will delete all the result rows from the current Hive table. This option is disabled if natural key is not selected.
- Click Recrawl Metadata to refresh the column list based on the schema from the source system.
NOTE: This option does not update the row count and last ingested time stamp on the table.
- Click Restructure to reorganize the table data based on the configurations given for the job.
- Click the Recrawl Metadata button in the Metadata Operations section to recrawl metadata for all the tables.
NOTE: This option does not update the row count and last ingested time stamp for the tables.
- Click Fetch New Tables to crawl the new tables added to the source schema.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential