Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
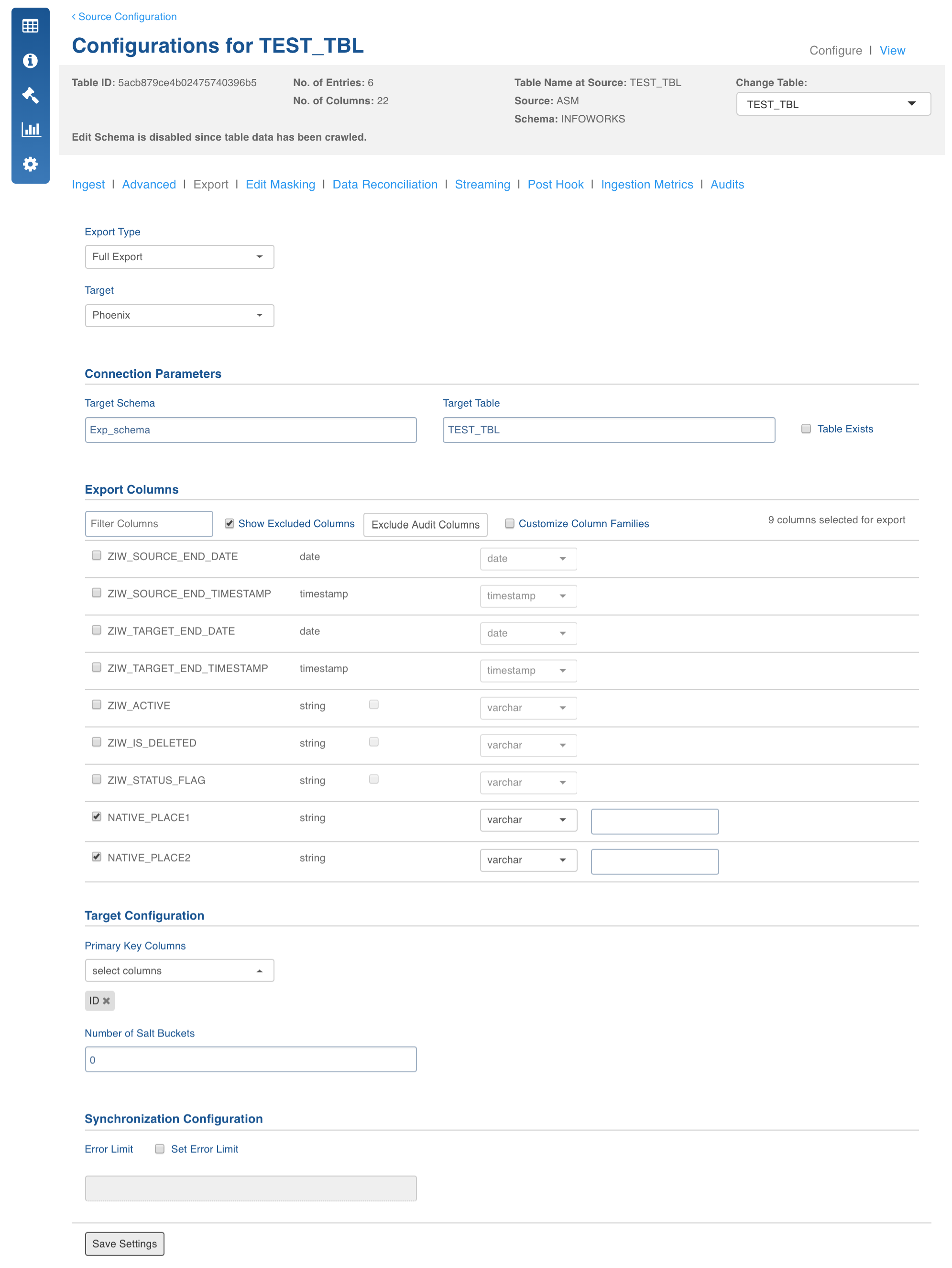
Phoenix Export
This feature exports the data from Hive to Phoenix database.
Following are the two ways to export data to the Phoenix database which can be configured by setting the advanced configuration, phoenix_export_engine, in the pipeline or source:
- SPARK: This is the default option which exports data to the Phoenix database using spark. It directly reads data from Hive and writes to the Phoenix database by opening multiple writers parallelly.
- CSV Bulk Export: This option exports data to the Phoenix database via the CSV bulk export utility. The data from Hive is written to CSV files which are then bulk exported to phoenix. It is recommended to use this option if data being exported is very huge.
Field Description
- Export Type: Select Full Export/Incremental Export.
- Target Database: Select the database type to be exported as Phoenix.
Connection Parameters
- Target Schema: Enter the schema in which the target table will be created.
- Target Table: Enter the name of the target table.
- Table Exist: By default, first time load into a target table will drop it and re-create the table with the parameters specified. If you don't want this to happen, you can select this checkbox.
NOTE: If you select this option, ensure that the existing table has all the columns and properties created. Infoworks will not create or check the existing table for any property in this case and the export job might fail if the corresponding columns are not found. Although, Infoworks does not use the table properties specified in the configurations like primary key and salt buckets, it still expects the configuration to remain same during incremental export.
- Export Columns: Select the columns that must be exported to the target table. At least one column must be selected. The Select All and Deselect All buttons can be used to make the selection faster. You can also select the Target Data Type for each column. The table will be created on the Phoenix database as per the target data type selected.
- Customize Column Families: Select this checkbox to modify column family instead of using the default column family.
- Primary Key Columns: Enter the primary key columns. These columns help to determine a row uniquely. The row key is constructed from the primary key columns in the order selected by the user.
- Number of salt buckets: Enter the number of salt buckets to be created in the phoenix table. Default value is 0.
NOTE: For any subsequent incremental export, it is mandatory to have the same configuration (columns, primary key, etc.) as previous export. Any change in configuration will throw an error during job run.
Phoenix Export Datatypes
The export feature supports the following datatypes in Hive:
- TINYINT
- SMALLINT
- INTEGER
- BIGINT
- TIMESTAMP
- DATE
- STRING
- BOOLEAN
- BINARY
- CHAR
- VARCHAR
The following datatypes are not supported:
- UNION
- ARRAY
- STRUCT
- MAP
Best Practices
- Combination of Primary Key columns must be unique for each row. It must be selected in the order in which queries are run on Phoenix, since indexing will be performed in the same order.
- If customizing column families, note that HBase currently does not perform well above two or three column families, so keep the number of column families in your schema low.
- You can use the Table Exist option to use any predefined Phoenix table with advanced options like compression and encryption, provided the table columns matches the columns selected in the export columns section.
Troubleshooting
IW Constants and Configurations
- IW_SECURITY_KERBEROS_ENABLED: Checks if kerberos is enabled in cluster. The default value is false.
- zk_connection_string: The zookeeper connection string (comma separated zookeeper quorum:port). The default value is localhost:2181.
- hbase_connection_string: The hbase connection string.The default value is /hbase-unsecure if kerberos disabled and blank if kerberos enabled.
- To provide any type mapping from Hive to phoenix, create a file with the name phoenix.properties in the folder {IW_HOME}/conf/mappings and add any type in the hive_type=phoenix_type format, for example, string=VARCHAR.
Spark Configuration
- spark_master: spark master address. By default, the value is picked from conf.properties file located at {IW_HOME}/conf/conf.properties.
- Any extra spark configuration can be added by editing the file located at {IW_HOME}/conf/spark-export.conf. CSV Configurations
The following configurations (specified in advanced configuration at source or pipeline level) can be used for CSV bulk export jobs to tune the mapreduce job:
- phoenix_export_mr_map_mem_mb: Indicates the maximum mapper memory that can be used by the CSV bulk export mapreduce job. If the value is not specified, the default value is obtained from the iw_jobs_default_mr_map_mem_mb configuration in the conf.properties file.
- phoenix_export_mr_red_mem_mb: Indicates the maximum reducer memory that can be used by the CSV bulk export mapreduce job. If the value is not specified, the default value is obtained from the iw_jobs_default_mr_red_mem_mb configuration in the conf.properties file.
- phoenix_export_mr_java_opts_ratio: Indicates the ratio of total memory to be used for java heap for CSV bulk export mapreduce job. The default value is 0.8. For example, if the configuration value is 0.8 and the mapper memory is 2gb, the heap space for mapper is around 1.6 gb.
The following configurations are also used at a global level for CSV bulk export:
- phoenix_export_mr_extra_config: allows you to provide additional configurations to the CSV bulk export mapreduce job.
- phoenix_field_separator: the field separator when creating CSV. By default it is , (comma).
- phoenix_escape_char: the escape character when creating CSV. By default it is \ (back slash).
Known Issues
- Cancelling the job in CSV bulk export will not automatically cancel the mapreduce job which exports data from CSV to Phoenix.
For more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential