DataFoundry 2.7.2
2.7.2
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Netezza Export
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Field Description
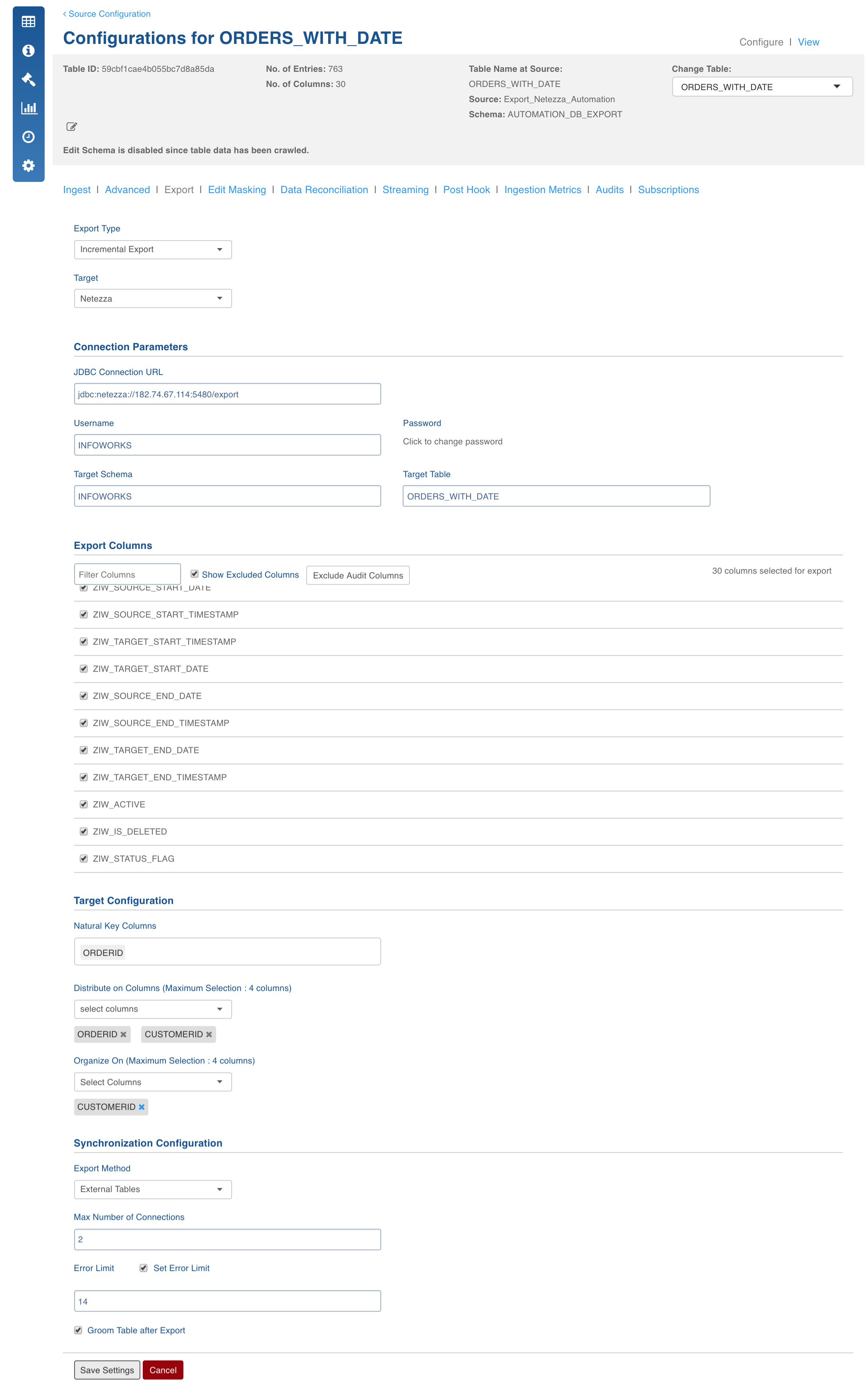
- Export Type: Select Full Export/Incremental Export into Netezza.
- Target Database: The database type you want to export to (Netezza).
- JDBC Connection URL: The connection URL needed to connect to the target database.
- Username: Username of the target database.
- Password: Password of the target database.
- Target Schema: The schema in which you want the target table to be created.
- Target Table: Name of the target table.
- Export Columns: The selections of columns that must be exported to the target database. The user must select at least one column. User can use the Select all and Deselect All buttons to make the selection faster.
- Natural Key Columns: Natural Key Columns are the columns that help determine a row uniquely. Primary Index and Partition Column must be a part of the Natural Key Columns for export to Netezza.
- Distribute On Columns: The distribution column for the table created on Netezza. The distribution key determines how to distribute (or stripe) the table data across all active data slices in the system.
- Organize On Columns: The Organize on columns for the table created on Netezza. Organizing keys are useful for the more frequently used columns in query predicates, and if the column cardinality is high.
- Export Method: This includes two options:
- External Tables: The export will be done using Netezza external tables. Each mapper will write to a FIFO file which will go to Netezza using Netezza external tables. This should be the method of choice, but should not be used when binary column is selected or end of line character is in the data.
- Batch Insert: In this method, all the mappers write to Netezza using insert statements. This method should be used when there is binary data that you want to export.
- Max Number Of Connections: The maximum number of connections that you want to allow to write to the target database.
- Set Error Limit: If this checkbox is checked, you can specify an error limit.
- Error Limit: The limit on the numbers of rows that go to error table, before the job fails.
- Groom Table After Export: If this checkbox is selected, a "Groom table records" query is executed on the table that has been exported. The Groom table query removes outdated and deleted records from the table.
Feature Scope and Known Issues
- These datatypes in Hive are supported by the export feature: TINYINT, SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT, TIMESTAMP, DATE, STRING, BOOLEAN, BINARY, CHAR, VARCHAR.
- These datatypes in Hive are not supported by the export feature: UNION, ARRAY, STRUCT, MAP.
- Currently, Incremental Export after the first export with zero rows in not supported. In such situation, please perform a full export once there is some data in the Hive table; post which, you can perform incremental exports.
Best Practices
- The export method should be "External Tables" by default. If there are binary columns in the table, use "Batch Insert".
- Natural Key should always be unique for the table.
- Set an error limit to verify that the data has been transferred correctly.
Troubleshooting
IW Constants and Configuration
- netezza_export_enclose_char: The character which would be used to enclose data in the temporary file while transferring (Only applicable for external tables mode).
- netezza_export_delimiter: The record delimiter in the temporary file while transferring (Only applicable for external tables mode).
- netezza_export_lines_termination_character: The line termination character in the temporary file while transferring (Only applicable for external tables mode).
- netezza_export_null_value: The null value in the temporary file while transferring (Only applicable for external tables mode).
- netezza_export_should_allow_control_characters_in_data: If there are control characters (1-31 ASCII value) in the data, use this configuration to enable transferring of that kind of data.
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on
Next to read:
SQL Server ExportFor more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential
Discard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message