Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Replication Process
Creating Cluster
Cluster - A cluster is a representation of a Hive Data Warehouse in Infoworks Replicator. It can act as a source or destination of the replication.
A cluster can only be created by an admin. Following are the steps to create a cluster:
- Log on to Infoworks ADE as Admin.
- Click the Admin menu.
- Click the Clusters icon and click the New Cluster button.
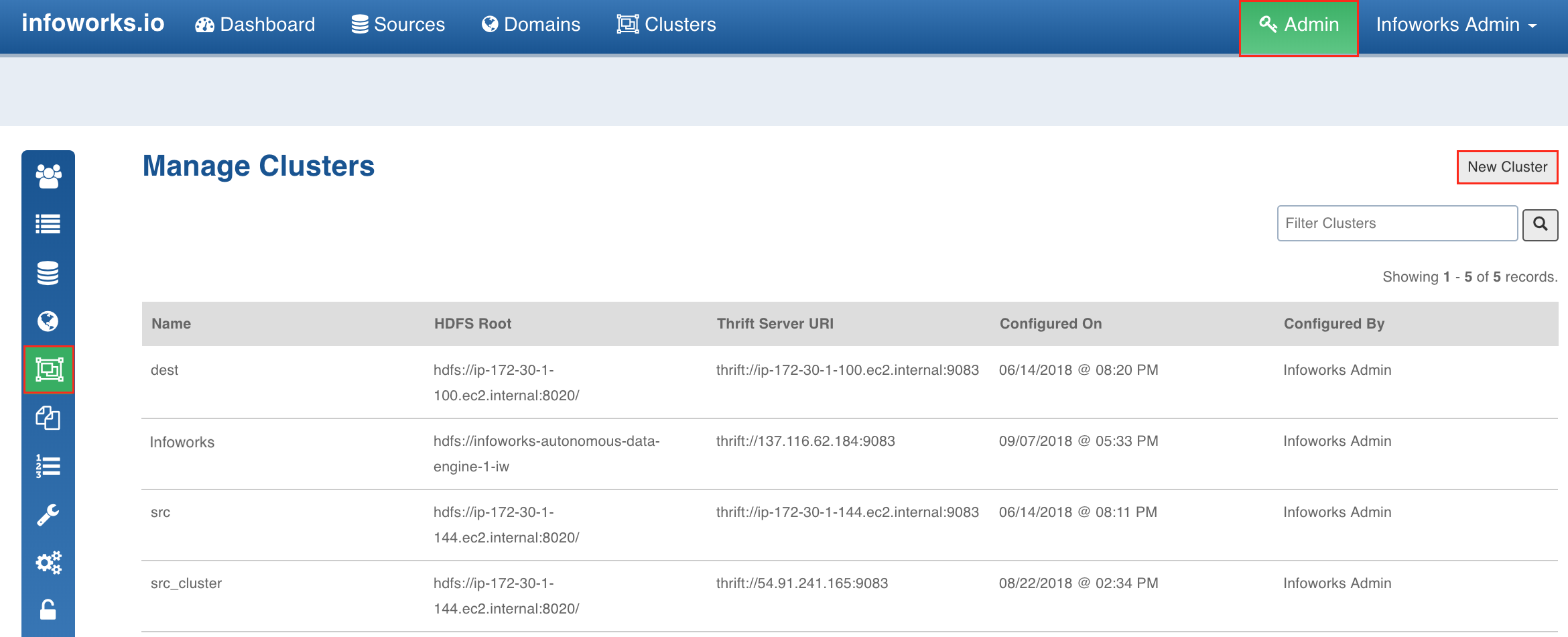
- Enter the following details:
- Cluster Name: Name of the cluster.
- HDFS Root: namenode qualified root of HDFS.
- Hive Metastore URL(Thrift): URL of the Hive thrift metastore.
- Temp Directory: Directory for temp data. This path must be HDFS root qualified.
- Output Directory: Directory for job results. This path must be HDFS root qualified.
- Advanced Configurations: This field is optional. If the Hive cluster is kerberized and ssl enabled, add the following key value pair:
- Config Name: SECURE_CLUSTER_PROPERTIES
- Value:
hive.metastore.kerberos.principal=hive/_HOST@YOUR-REALM.COM;hive.metastore.sasl.enabled=true; hadoop.rpc.protection=privacy;hive.server2.thrift.sasl.qop=auth

- Click Save. The cluster will be created and displayed in the Manage Cluster page.
Limitation
- The HDFS Root path must end with a / (slash).
Crawling Source Cluster Metadata
After creating a cluster, you can perform a metadata crawl which will fetch all the Hive schemas and tables from the Hive Data Warehouse. From this fetched list, you can select a subset of tables and schemas to be replicated.
Following are the steps to crawl the metadata:
- Click the Clusters menu.
- Click the required cluster to be used as the source cluster.
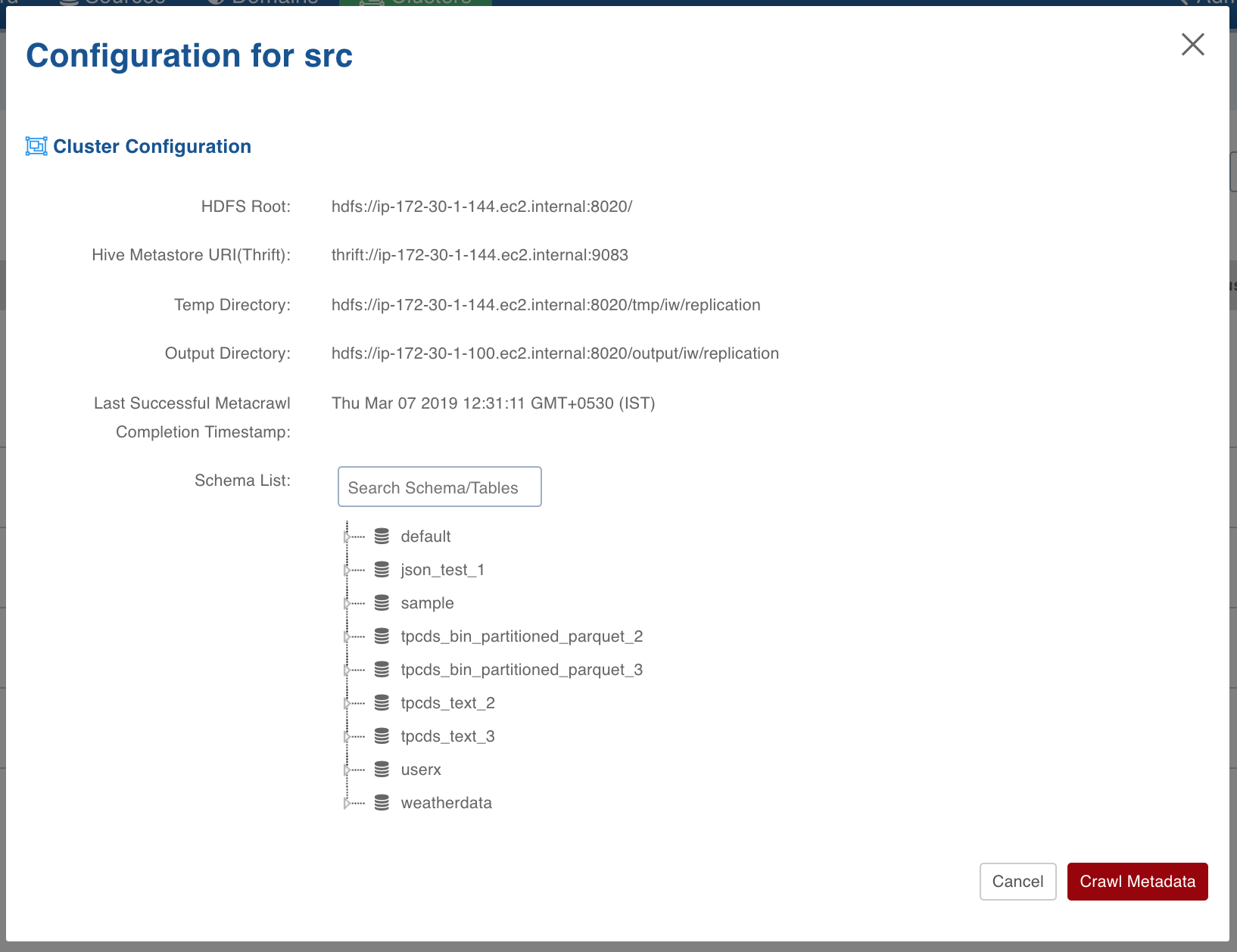
- In the pop-up window, click the Crawl Metadata button. The metadata will be crawled and the schema/table tree will be displayed in the Schema List section.
Creating Domain
Domain - A domain is a logical grouping of the workflows.
A domain can be created only by an admin. Following are the steps to create a domain:
- Click the Admin menu.
- Click the Domains icon and click the New Domain button.
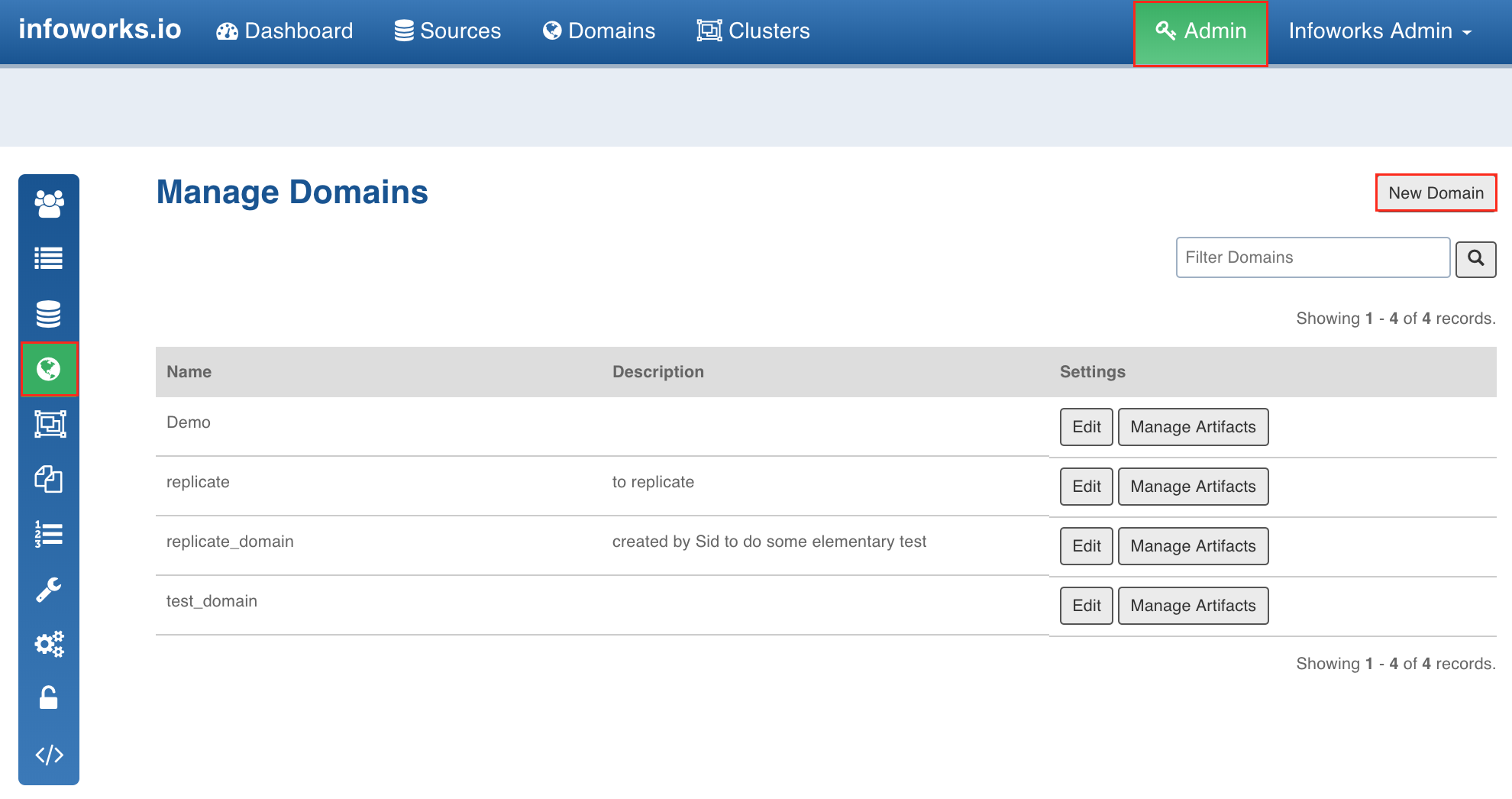
- Enter the Name and Description and click Save.
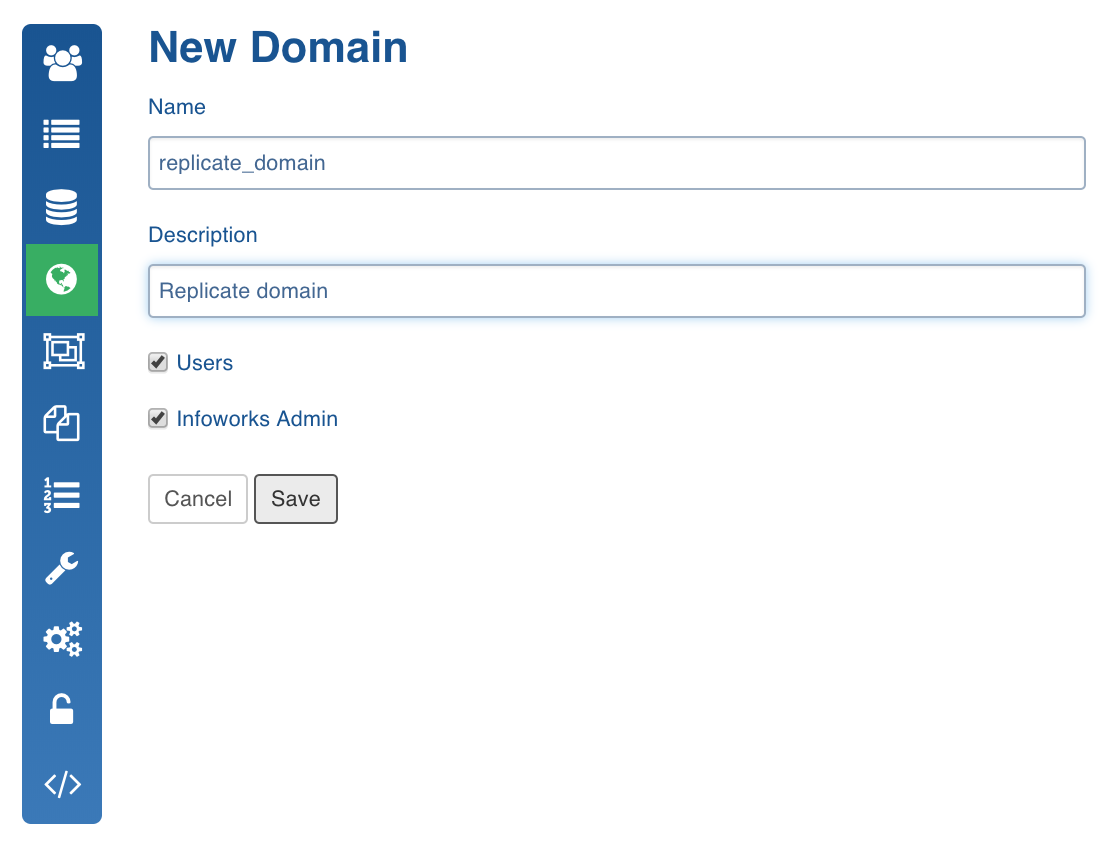
The domain will be created and displayed in the Manage Domains page.
Creating Workflow
Workflow - A workflow is a collection of tasks that can be performed in a sequence and automated. The tasks are represented as nodes, and edges define dependencies among the tasks. These tasks can be DB queries, bash scripts, replicator tasks, etc.
Following are the steps to create a workflow:
- Click the Domains menu and select the domain you created.
- Click the Workflows icon and click the New Workflow button to create the workflow.
- Enter the Name and Description and click Save.
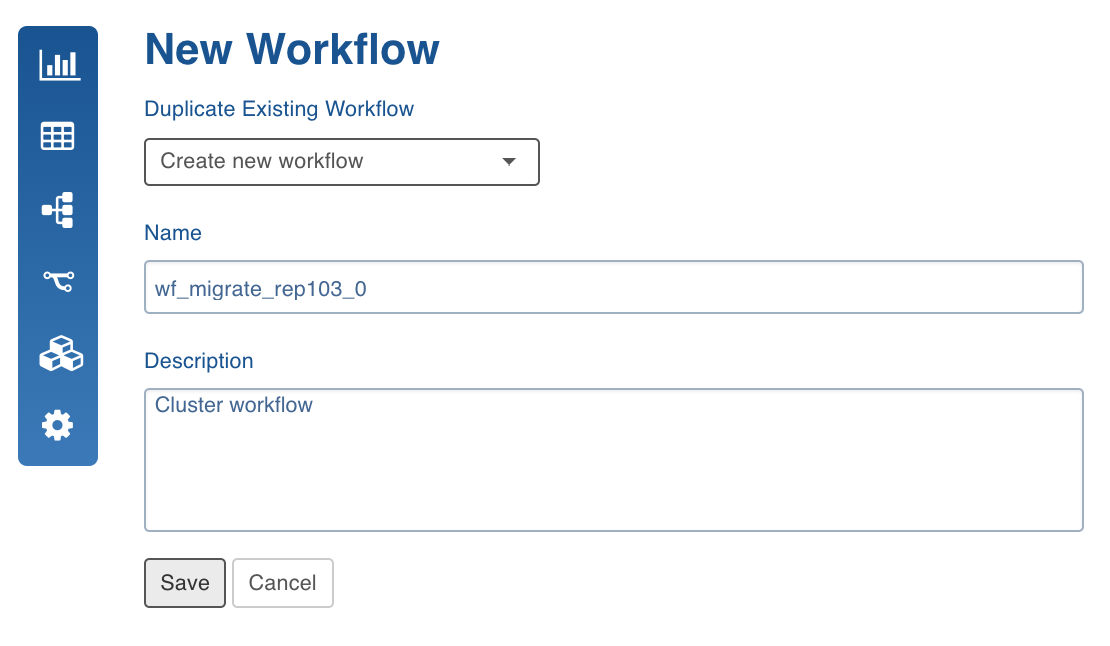
The workflow will be created and displayed in the Workflows page.
Designing Workflow
- Click the workflow you created.
- Click the Open Workflow Editor button. You can add nodes and tasks in the editor to create a workflow.
- Drag and drop each node on the editor and double-click the nodes to configure them.
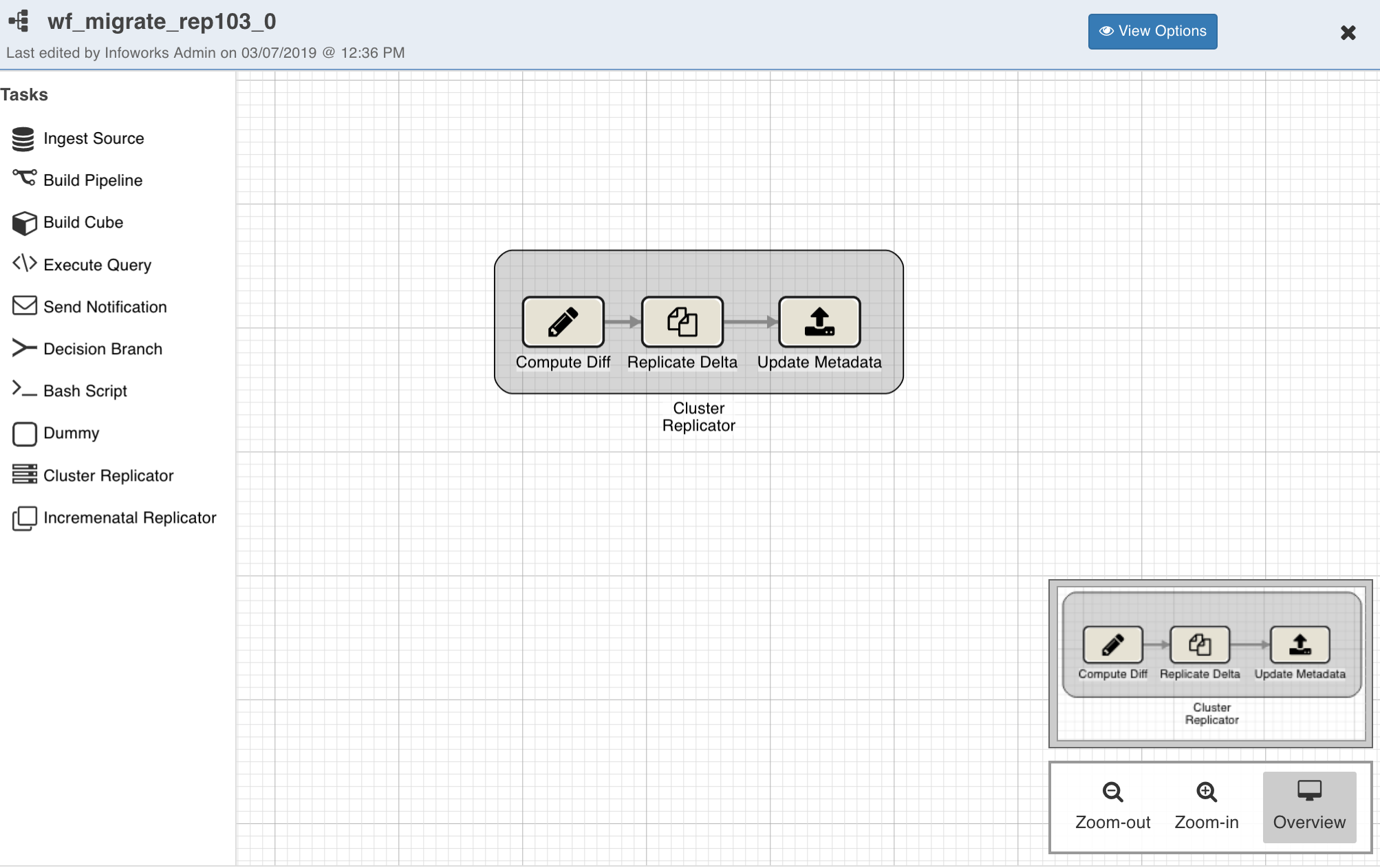
For replicators, the following nodes can be used:
- Bash Script Node: To call a bash script or run command(s). Multiple commands must be separated by semicolon or must be added in separate lines.
- Cluster Replicator Node: To migrate the Hive entities from source cluster to destination cluster.
- Incremental Replicator Node: To replicate live changes from one cluster to another.
- Send Notification Node: To trigger notifications after particular task(s) in the dag.
Configuring Bash Script Node
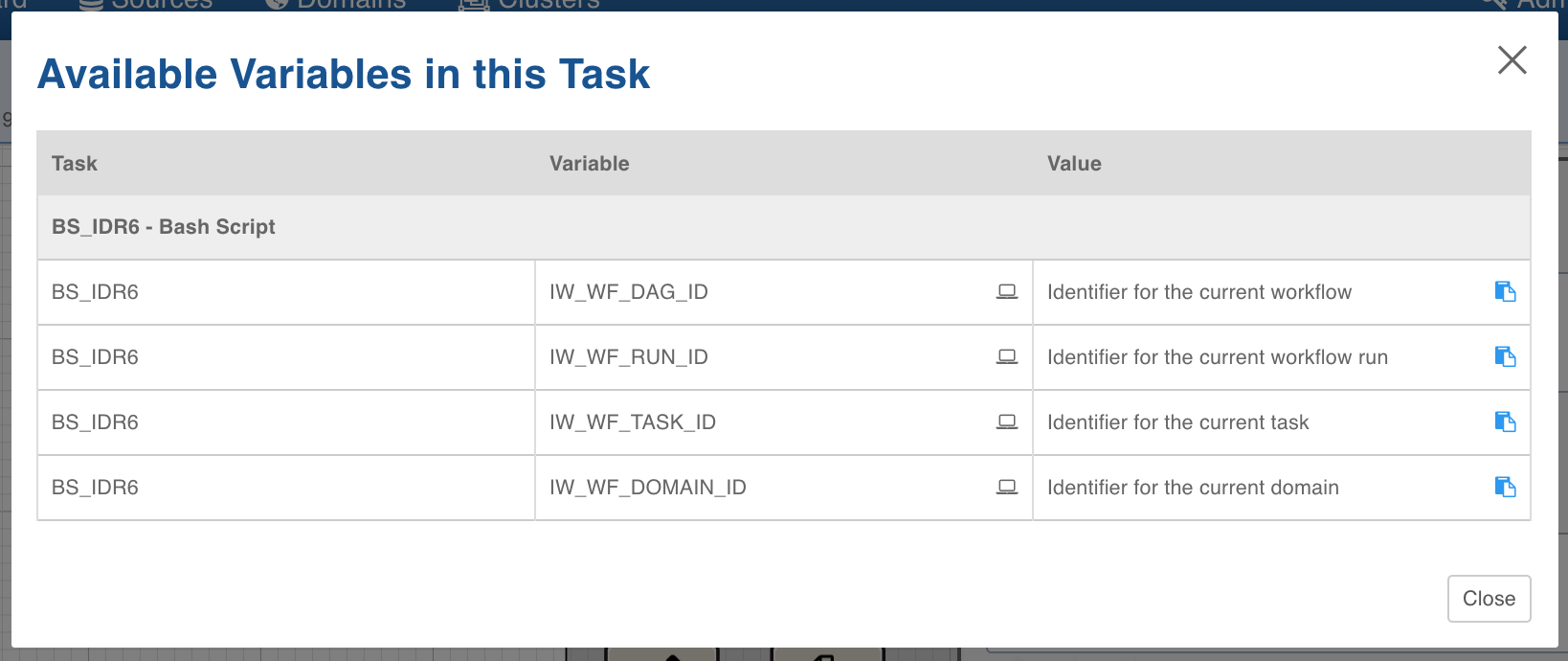
For bash nodes, you can use some pre-defined environment variables in your command or script. You can double-click the Bash Script node and click View available variables to view the predefined environment variables.
Currently the following variables are available:
- IW_WF_DAG_ID: Identifier of the current workflow.
- IW_WF_RUN_ID: Identifier of the current workflow run.
- IW_WF_TASK_ID: Identifier of the task/node of the workflow.
- IW_WF_DOMAIN_ID: Identifier of the current domain.
Configuring Cluster Replicator Node
NOTE: Ensure that the source and destination clusters are created and metadata is crawled for the source cluster.
You can double-click the Cluster Replicator node and configure the following fields:
- Source Cluster: The cluster to be migrated from.
- Destination Cluster: The cluster to be migrated to.
- Metastore Parallelism Factor: The number of parallel processes for the metastore replication task.
- Copy Parallelism Factor: The number of parallel process for the data copy task.
- Overwrite: The flag to overwrite the destination table corresponding to the source table (if the destination table is already available on the destination).
- Select Source Cluster Schema: The schemas and tables to be migrated.
- Add Advanced Properties: The configurations to indicate specific behaviour.
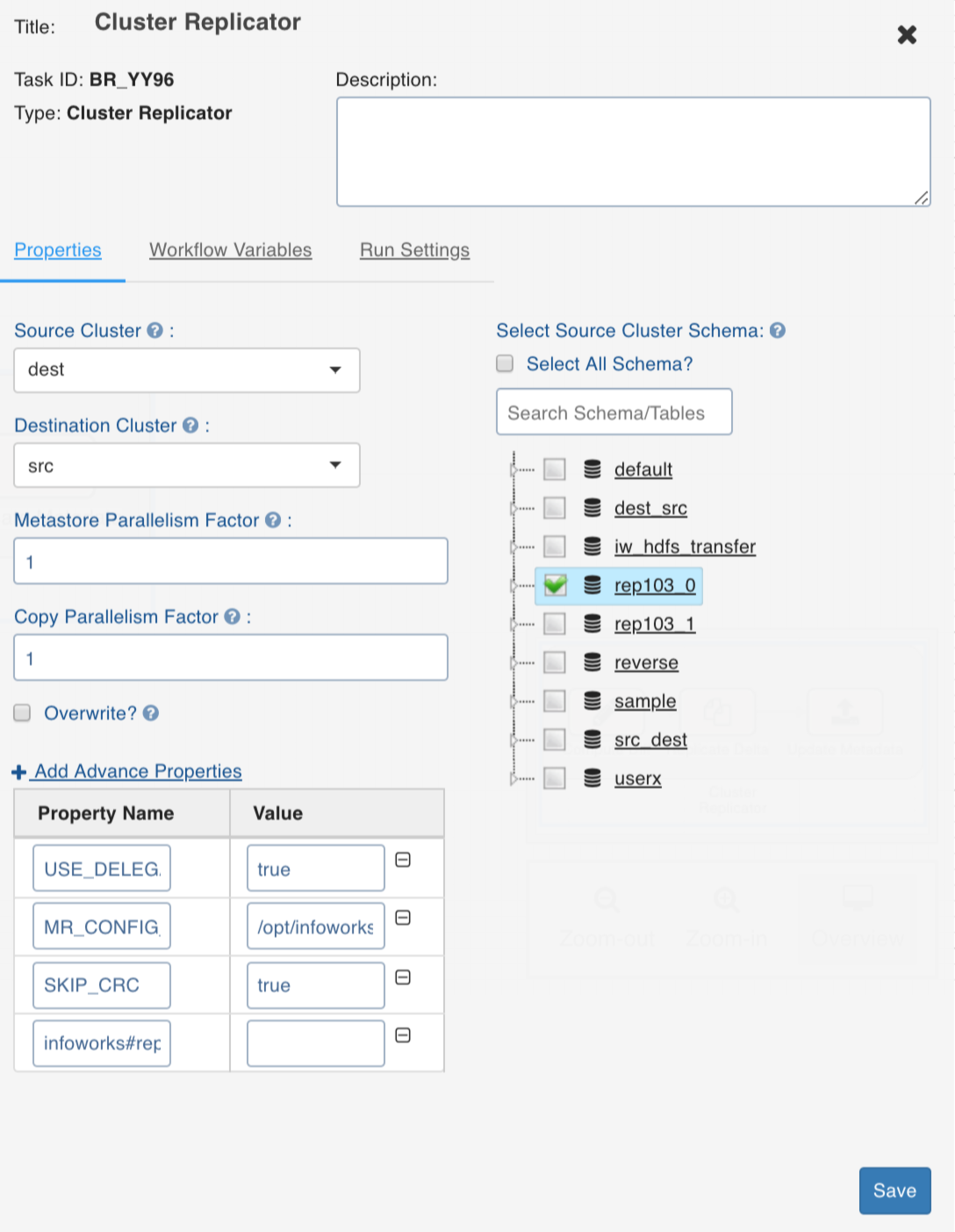
Following are the advanced configurations supported:
- USE_DELEGATION_TOKENS_FOR_HIVE: This configuration must be set the value to true in kerberized clusters. The default value is false.
- SKIP_CRC: To skip verification of checksum and must be configured for data transfer between encryption zones.
- BANDWIDTH: To throttle the amount of data used by each parallel unit copying the data.
- DIR_MAPPING_FILE: Used when the location directory structure of destination for a table data must be different from the source location directory structure. This must be a path of the file which includes source to destination location mappings on each line. For example, /a/b/c=a/b2/c.
- MR_CONFIG_FILE: To add properties to MR jobs of the three sub-tasks in the batch replication node.
- PRESERVE_STATUS: This configuration must be set as a string of concatenated characters where each character corresponds to preserving a file attribute while copying files from source to destination.
- r: preserve replication factor
- b: preserve block size
- u: preserve user name
- g: preserve group name
- p: preserve permissions
- c: preserve checksum type
- a: preserve acl
- x: xattribs
Feedback Tables
Every stage in the batch replication creates a corresponding table in Hive.
The tables are created in a schema which is named as <src>_<dst> where, <src> and <dst> are names of the source cluster and the destination cluster as provided in Infoworks ADE.
In the figure above, <src> is src_cluster and <dst> is dst_cluster.
The tables names and schemas are as follows:
- replication_step1_output
- replication_step2_output
Each row in this table indicates file copy task and its success/failure status.
- replication_step3_output
Each row in this table indicates metadata copy task and its success/failure status.
Configuring Incremental Replication Node
NOTE: Ensure that the source and destination clusters are created and metadata is crawled for the source cluster.
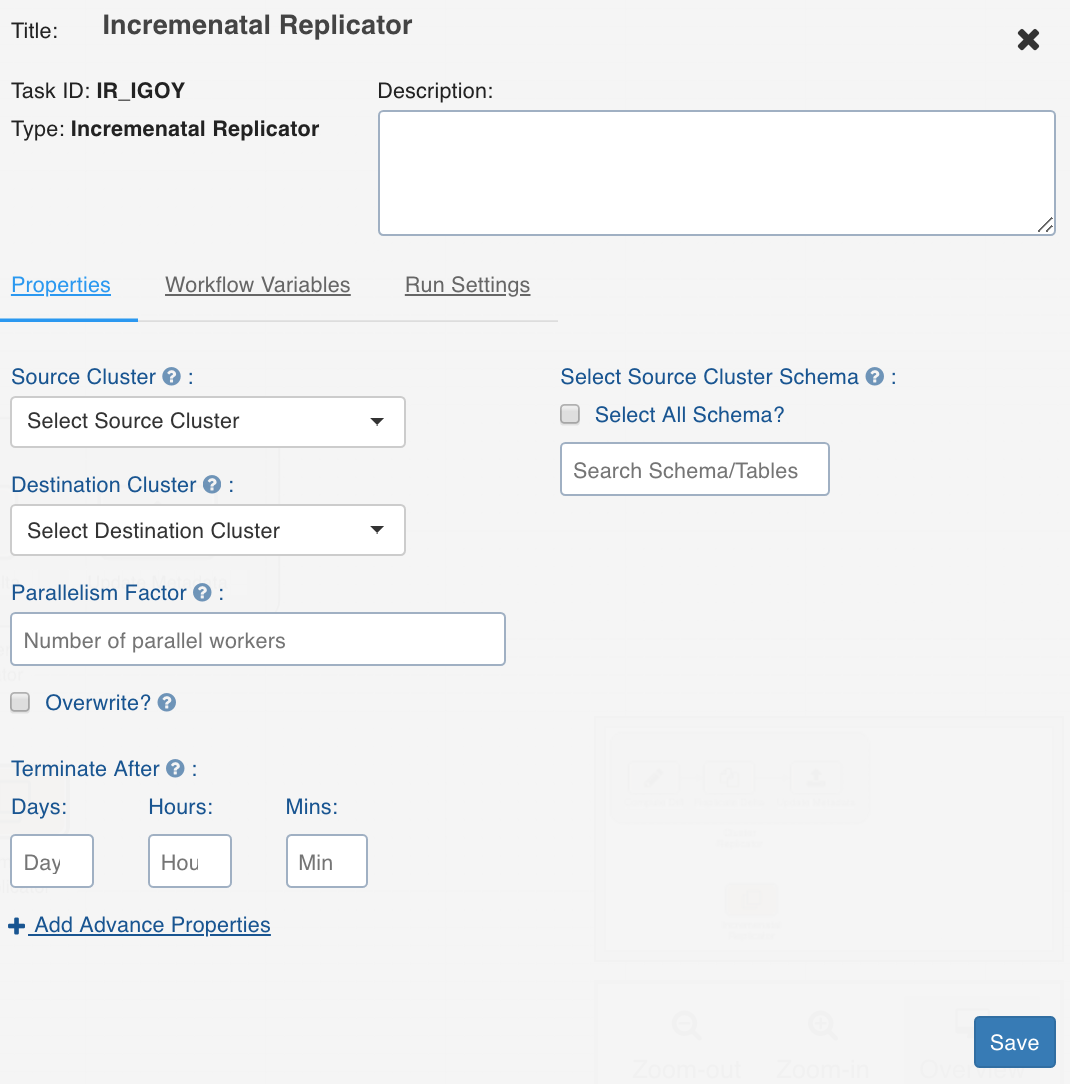
You can double-click the Incremental Replicator node and configure the following fields:
- Source Cluster: The cluster to be migrated from.
- Destination Cluster: The cluster to be migrated to.
- Parallelism Factor: The number of parallel processes for the replication task.
- Overwrite: The flag to overwrite the destination table corresponding to the source table (if the destination table is already available on the destination).
- Terminate After: The duration for which the incremental replication will be run.
- Select Source Cluster Schema: The schemas and tables to be migrated.
- Add Advanced Properties: The configurations to indicate specific behaviours.
Following are the advanced configurations supported:
- SKIP_CRC: To turn off the checksum check. This must be configured during transfer between encryption zones.
- BANDWIDTH: To throttle the amount of data used by each parallel unit copying the data.
- DIR_MAPPING_FILE: Used when the location directory structure of destination for a table data must be different from the source location directory structure. This must be a path of the file which includes source to destination location mappings on each line. For example, /a/b/c=a/b2/c.
- MR_CONFIG_FILE: To add properties to MR jobs of the three sub-tasks in the batch replication node.
- PRESERVE_STATUS: To set the following:
- AUDIT_LOG_JDBC_URL: JDBC URL for Infoworks postgres. The default value is jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/infoworks-replicator
- AUDIT_LOG_DB_USER: Username for Infoworks postgres. The default value is infoworks-user.
- AUDIT_LOG_DB_PASSWORD: Encrypted database password. The following command can be used to encrypt password:
/opt/infoworks/apricot-meteor/infoworks_python/infoworks/bin/infoworks_security.sh -encrypt -p <password>- AUDIT_LOG_DB_TABLE: audit_log
- AUDIT_LOG_MAPRED_STATS_DB_TABLE: mapred_stats
- STATE_JDBC_URL: JDBC URL for Infoworks postgres. The default value is jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/infoworks-replicator
- STATE_DB_USER: Username for Infoworks postgres. The default value is infoworks-user.
- STATE_DB_PASSWORD: Encrypted database password.
- STATE_DB_TABLE: replication_jobs
- STATE_KV_DB_TABLE: key_value
- AUDIT_LOG_OBJECTS_DB_TABLE: audit_objects
- SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_FILE: Java properties file to set system properties.
- Set following properties if Infoworks postgres is configured for ssl connections:
- javax.net.ssl.trustStore
- javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword
Feedback Tables
The following tables are created in the Infoworks postgres server running on the edge node and available in the infoworks_replicator database:
- Audit_log: This table includes one entry for each metastore ddl operation performed in the source Hive since the Infoworks Hive metastore listener has been registered on source. For more information, see the Registering Hive Metastore Listener section.
- Replication_jobs: This table includes entries for each audit log as PENDING, RUNNING, SUCCESSFUL, FAILED or NOT_COMPLETABLE based on the state of the job.
Building Workflow
Once you design the workflow with all the required nodes, you can close the editor and execute the workflow.
Following are the steps to execute the workflow:
- Click the Build icon.

- Click the Run Workflow button. The execution will be initiated.
Scheduling Workflow
- Click the Schedule icon.
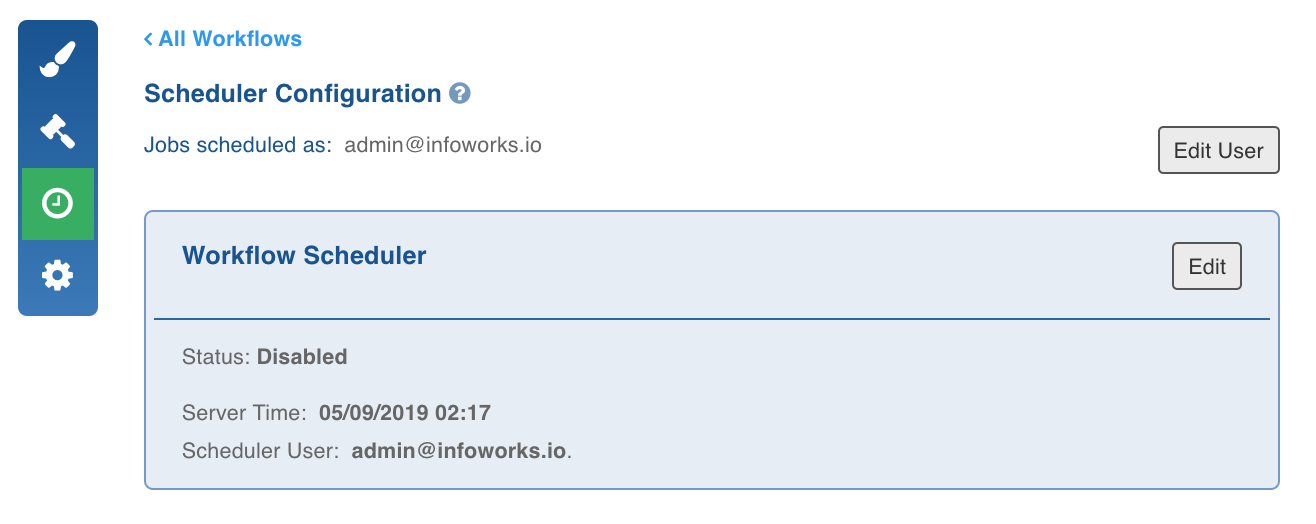
- Click Edit User and set the user credentials.
- Set the Status as Enabled.
- Select the start date and time, and configure the repeats.
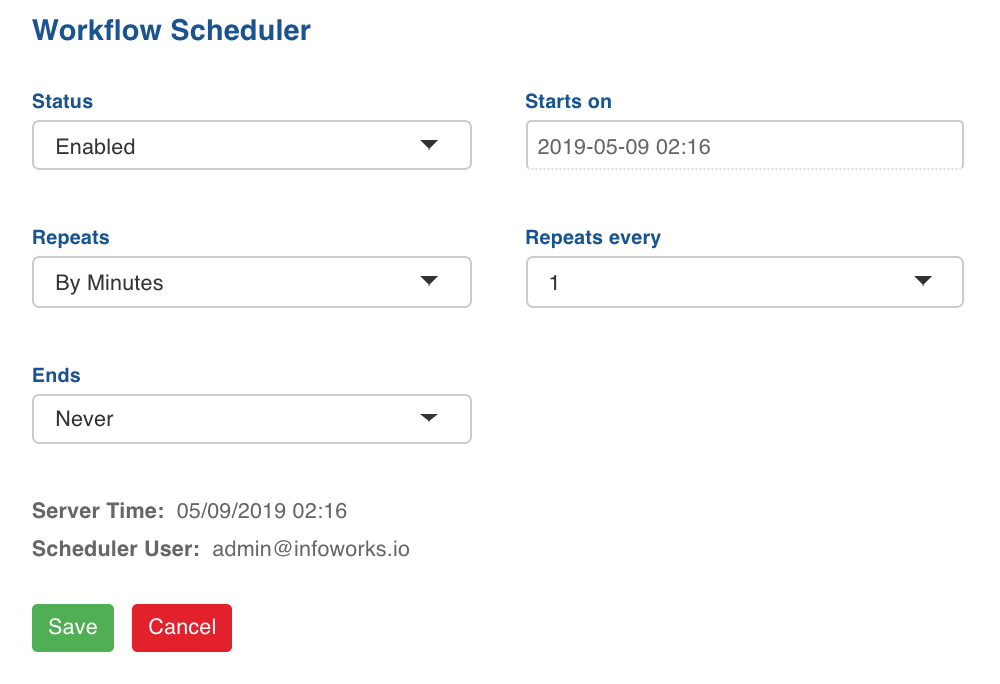
- Click Save. The workflow will be executed as per the schedule configured.
Registering Hive Metastore Listener
Hive Metastore listener - An implementation of a listener provided by Hive, used to record the live changes of source cluster to the Infoworks metastore. The incremental replication reads these changes from the iw metastore to replicate the changes on the destination cluster.
Following are the steps to register Hive hook for the source cluster:
- Go to the Cloudera Manager > Hive Configurations section.
- Set the following configurations:
<property> <name>hive.metastore.event.listeners</name> <value>infoworks.replicator.auditor.MetastoreAuditLogListener</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.audit_log.db.username</name> <value><infoworks postgres user></value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.audit_log.db.password</name> <value><infoworks-encrypted postgres password></value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.audit_log.jdbc_url</name> <value><jdbcUrl>r?ssl=true</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.audit_log.core.table_name</name> <value>audit_log</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.audit_log.objects.table_name</name> <value>audit_objects</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.truststore.path</name> <value><path to truststore</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.truststore.password</name> <value>truststore password</value></property>- Use the following command to encrypt password:
/opt/infoworks/apricot-meteor/infoworks_python/infoworks/bin/infoworks_security.sh -encrypt -p <password> - Copy the /opt/infoworks/infoworks-auditor.jar file from the edge node and paste to the Hive metastore server auxlib and restart the server. The auxlib path can be found in the Hive Auxiliary JARs Directory key in Cloudera Manager > Hive Configurations.
- Restart Hive from Cloudera Manager.
Starting HDFS Monitor
NOTE: HDFS Monitor For incremental replication, Hive external tables can be modified directly by modifying the files without impacting the Hive metadata. In such cases, the Hive listener cannot detect changes and these changes might be missed.
If external tables are available in the Hive tables on the source to be monitored, and if the tables can be modified, the HDFS Monitor Service must be run. This service listens to the changes on the source cluster HDFS, and writes the changes in the Infoworks metastore.
The incremental replicator will then replicate the changes after reading it from the metastore.
Infoworks monitor can be executed from a script which can be a part of the workflow you create for replication.
The HDFS monitor can be executed from the edge node as follows:
yarn jar /home/ec2-user/infoworks-replicator-auditor.jar infoworks.replicator.auditor.HDFSWatcher –config-file /opt/infoworks/conf/replicator/hdfs-monitor.conf –sys-file /opt/infoworks/conf/replicator/sys.confIt requires the config-file and sys-file arguments.
- Config File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?> <configuration> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.audit_log.jdbc_url</name> <value><jdbcUrl>r?ssl=truessl=true</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.audit_log.db.username</name> <value><infoworks postgres user></value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.metastore.audit_log.db.password</name> <value><infoworks-encrypted postgres password></value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.audit_log.core.table_name</name> <value>audit_log</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.audit_log.objects.table_name</name> <value>audit_objects</value> </property> <property> <name>infoworks.replicator.cluster.hdfs.root</name> <value><The hdfs path you want to monitor. It should be qualified with the hdfs root of source cluster</value> </property> </configuration>- Sys-file
javax.net.ssl.trustStore=<path to java truststorejavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=trustore passwordFor more details, refer to our Knowledge Base and Best Practices!
For help, contact our support team!
(C) 2015-2022 Infoworks.io, Inc. and Confidential